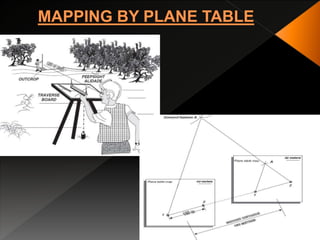
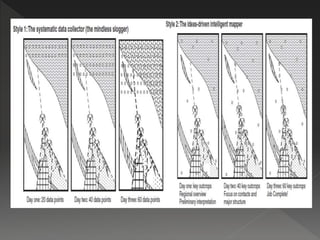
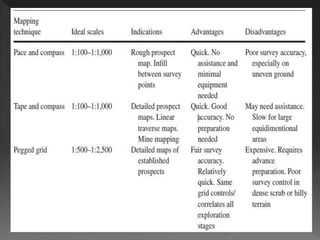
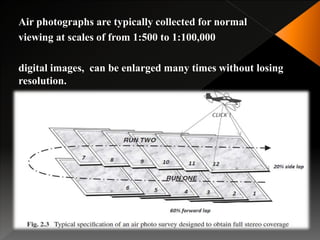
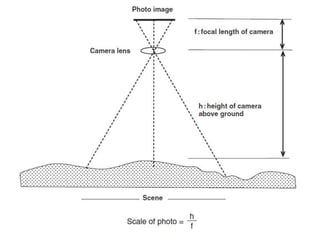
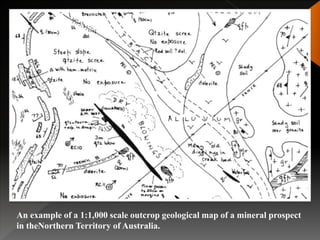
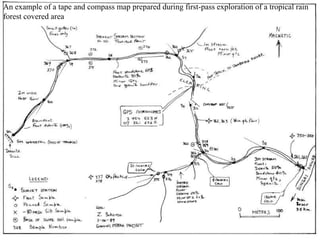
Geological mapping involves creating maps and sections that visually represent spatial geological relationships and interpretations based on field observations. Maps are created at various scales appropriate for the level of detail needed, from regional-scale maps showing broad patterns to more detailed outcrop maps of mineral prospects. Field equipment used in mapping includes compasses, clinometers, altimeters, and plane tables. Geophysical methods and aerial/satellite imagery can provide additional subsurface and regional data to supplement field mapping. Drilling and geostatistical analysis of subsurface data are also used to construct contour maps depicting formations, structures, and thickness changes.