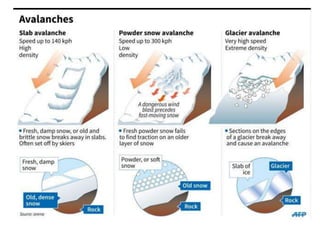
The document provides information on different types of geological disasters including avalanches, landslides, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions. It describes the causes and characteristics of each type of disaster, damage they can cause, safety tips, and areas where they typically occur. The document contains sections on predicting avalanches, landslides, and earthquakes. It also outlines responses to different disasters and future research directions to better understand these geological phenomena.