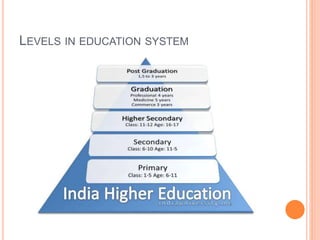
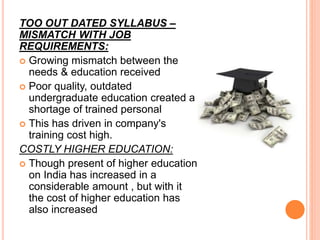
The document explores the evolution and current state of the education system in India, highlighting the historical significance, the impact of British rule, and the changes post-independence. It discusses current challenges like exam-oriented approaches, corruption, and a mismatch between education and job requirements, as well as possible solutions such as enhancing practical skills and addressing socio-economic disparities. The presentation emphasizes the need for a shift towards a more learner-centric and skill-oriented education system.