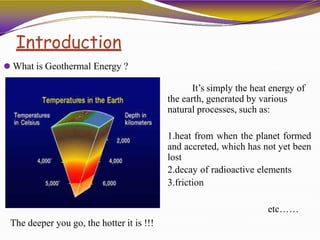
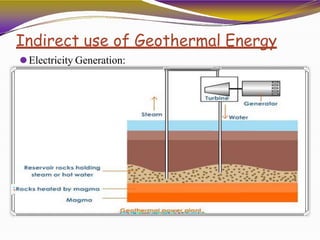
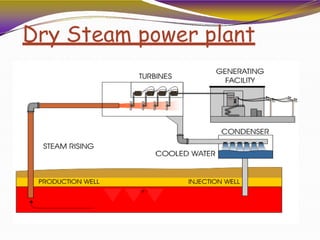
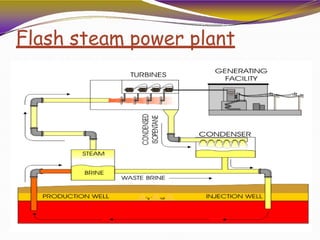
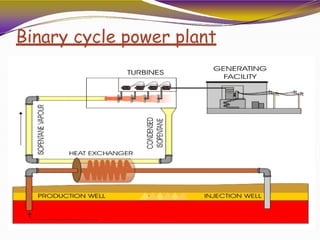
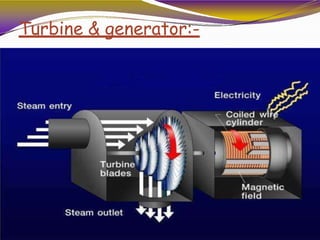
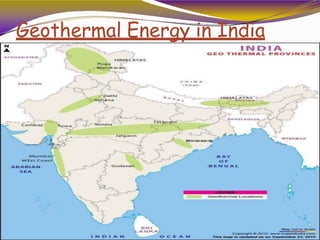
Geothermal energy is heat energy generated and stored in the Earth. It can be extracted for electricity generation or direct uses like heating buildings. There are three main types of geothermal power plants - dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle. While the initial investment is high, geothermal electricity generation becomes cost competitive over time. India has geothermal potential in several provinces but development has been limited so far. Geothermal energy provides renewable baseload power without emissions but is restricted by the location of suitable reservoirs.