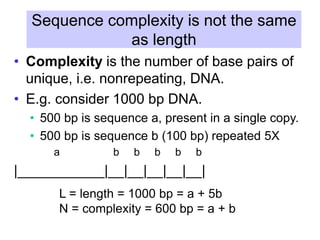
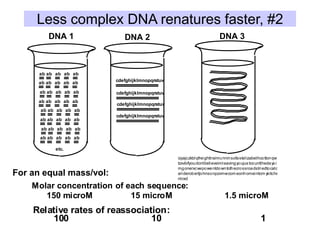
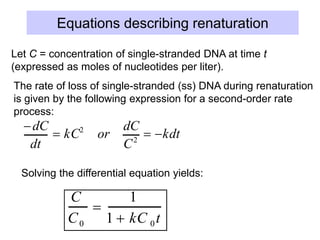
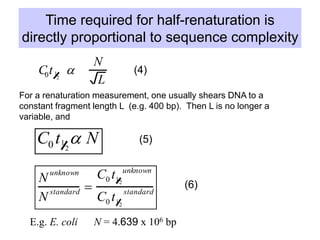
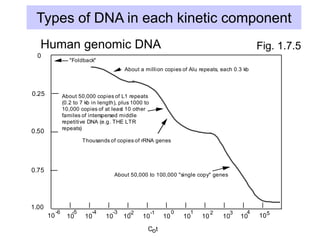
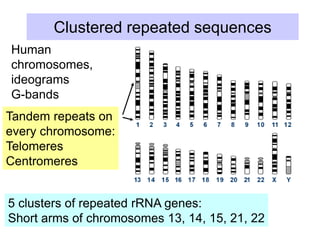
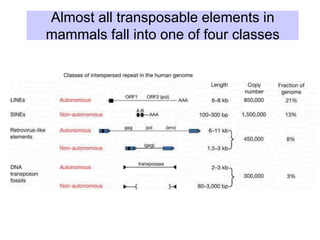
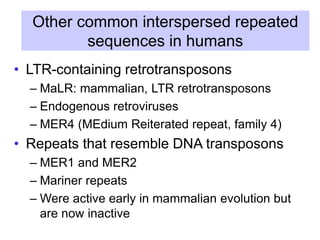
The document discusses various components that make up genomes, including genes, repetitive sequences, and different types of DNA. It describes the human genome in particular, noting it contains around 3 billion base pairs, with 3% coding for proteins. Around 40-50% is repetitive sequences from transposition. Genomics is defined as the study of genomes, including gene mapping and sequencing. Key components of genomes discussed include transposable elements like SINEs, LINEs, LTR retrotransposons, and other interspersed repeats. Comparative analysis of genome sequences can provide insights into gene number and function.