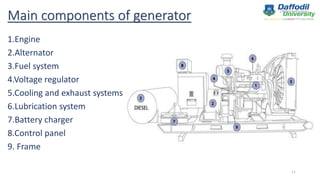
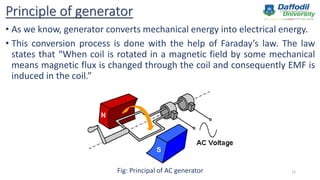
The document is a presentation outline on generators, detailing their introduction, history, classification, main components, principles of operation, uses, and advantages/disadvantages. It discusses the evolution from early electrostatic generators to modern AC and DC generators, emphasizing key figures like Faraday and Tesla. Generators are primarily used for backup and standby power across various applications, exhibiting both benefits and limitations.