This document provides definitions and explanations of key genetics concepts including:
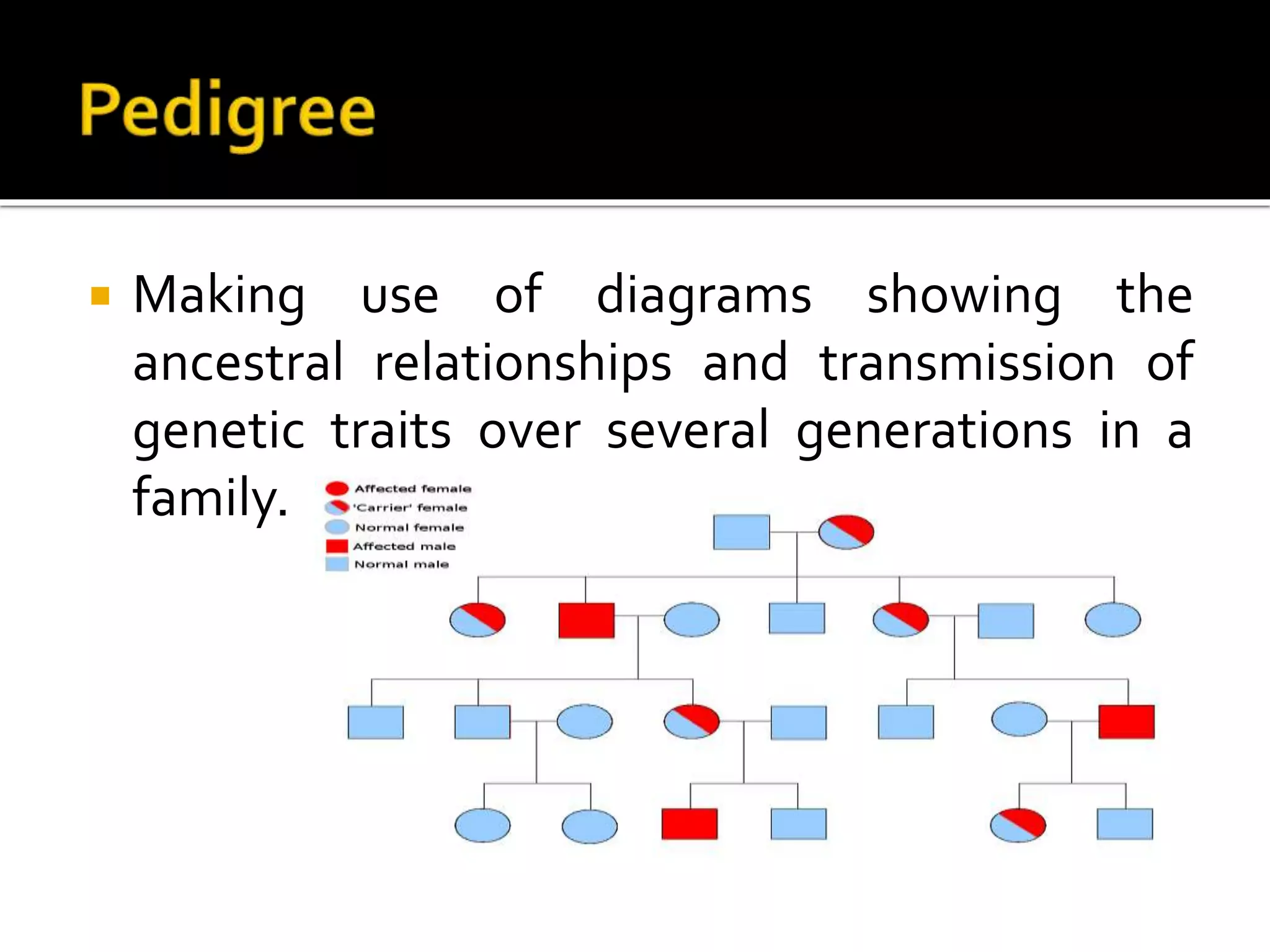
1. Pedigrees are used to show ancestral relationships and transmission of genetic traits over generations.
2. A proband is the individual in a pedigree that prompted its construction.
3. Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment describe how alleles separate and assort independently during gamete formation and fertilization.