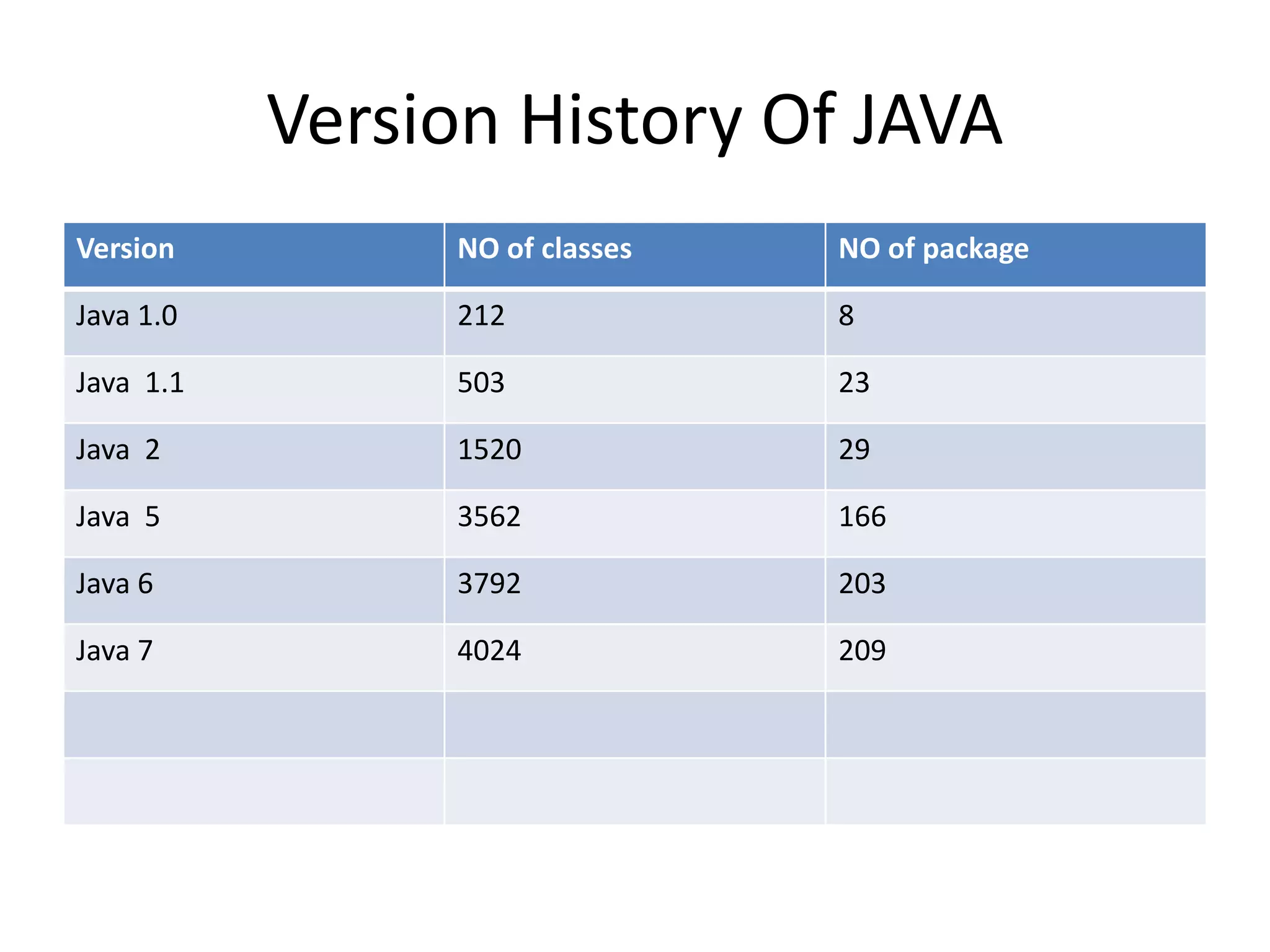
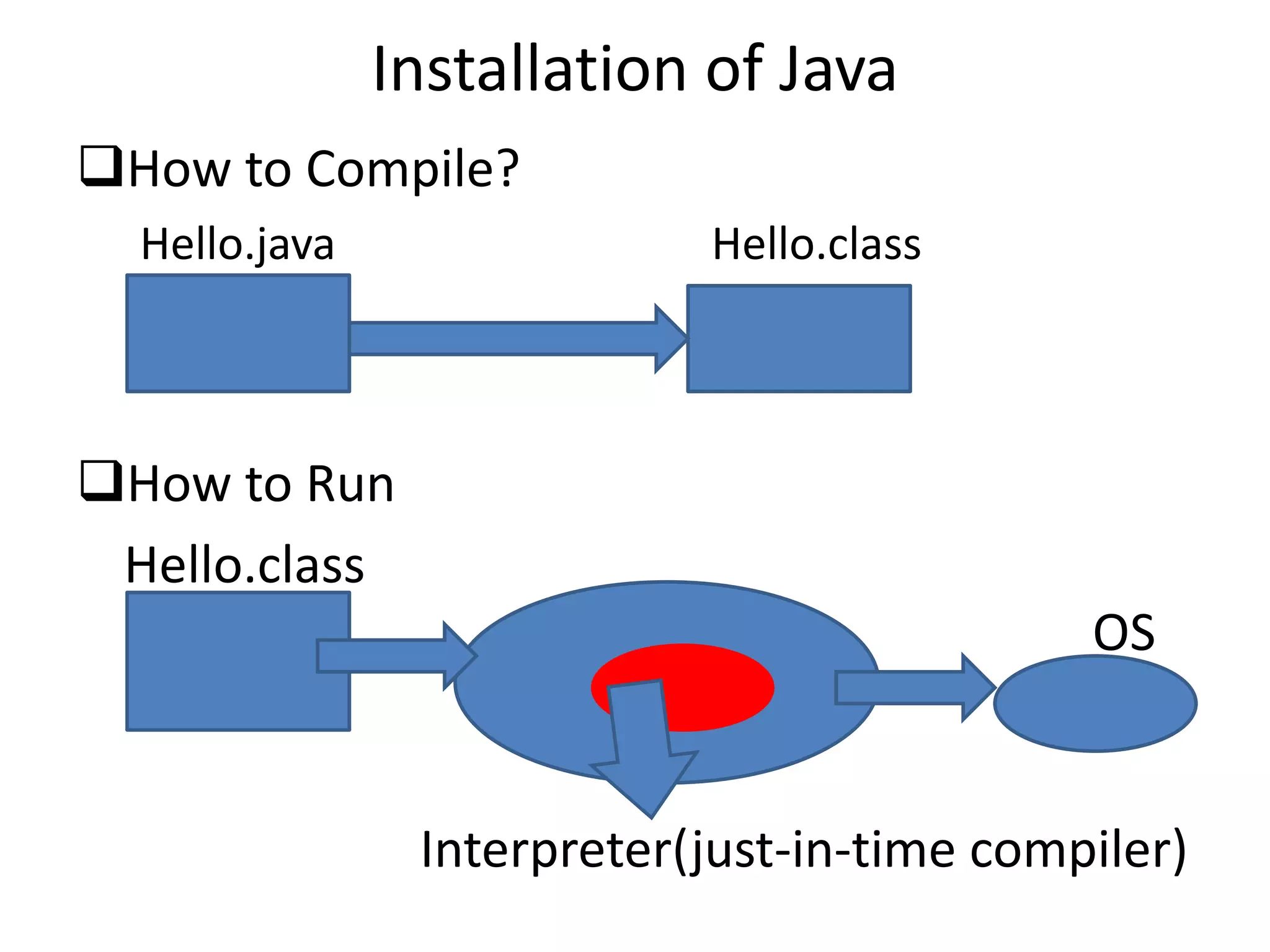
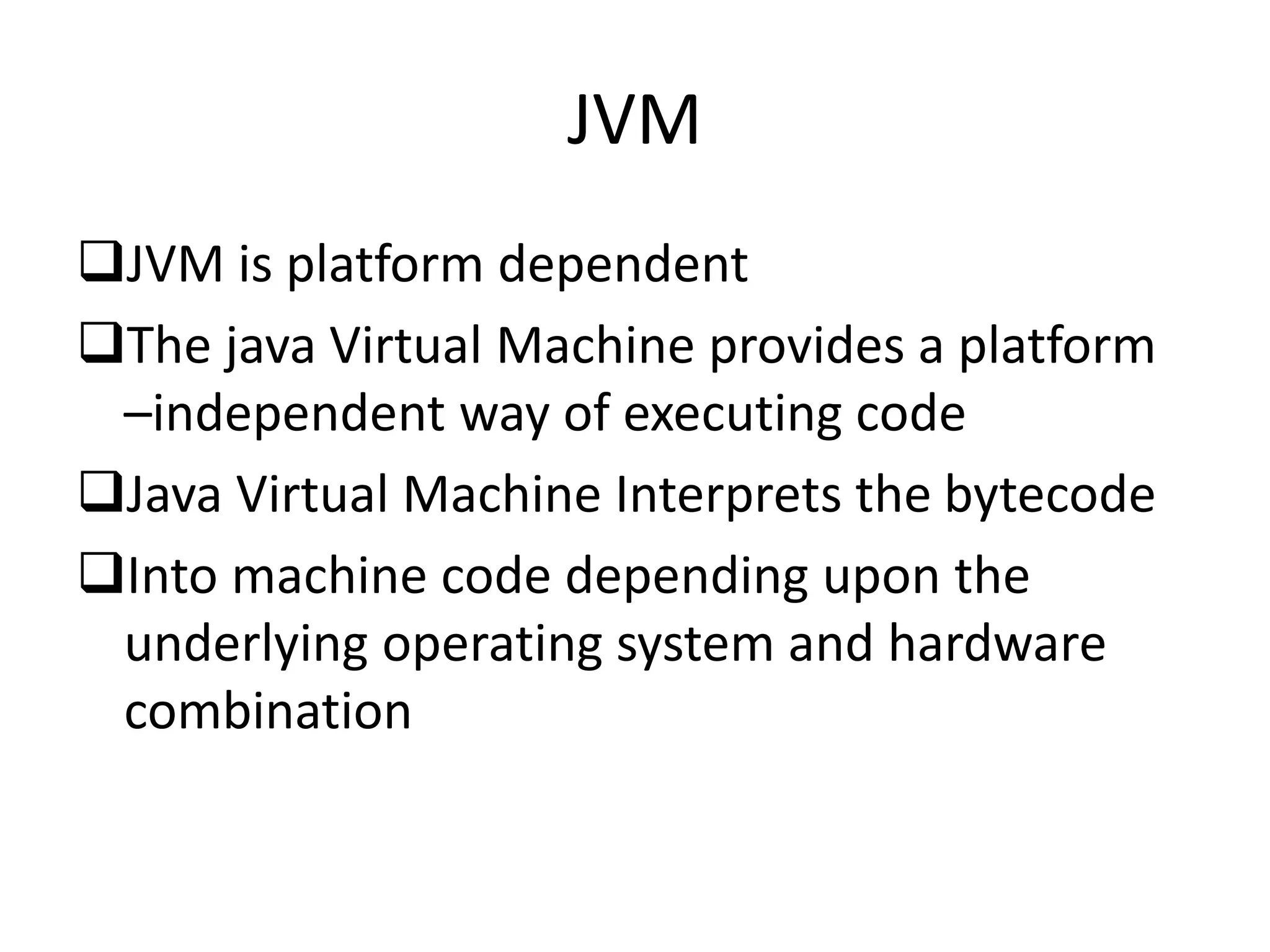
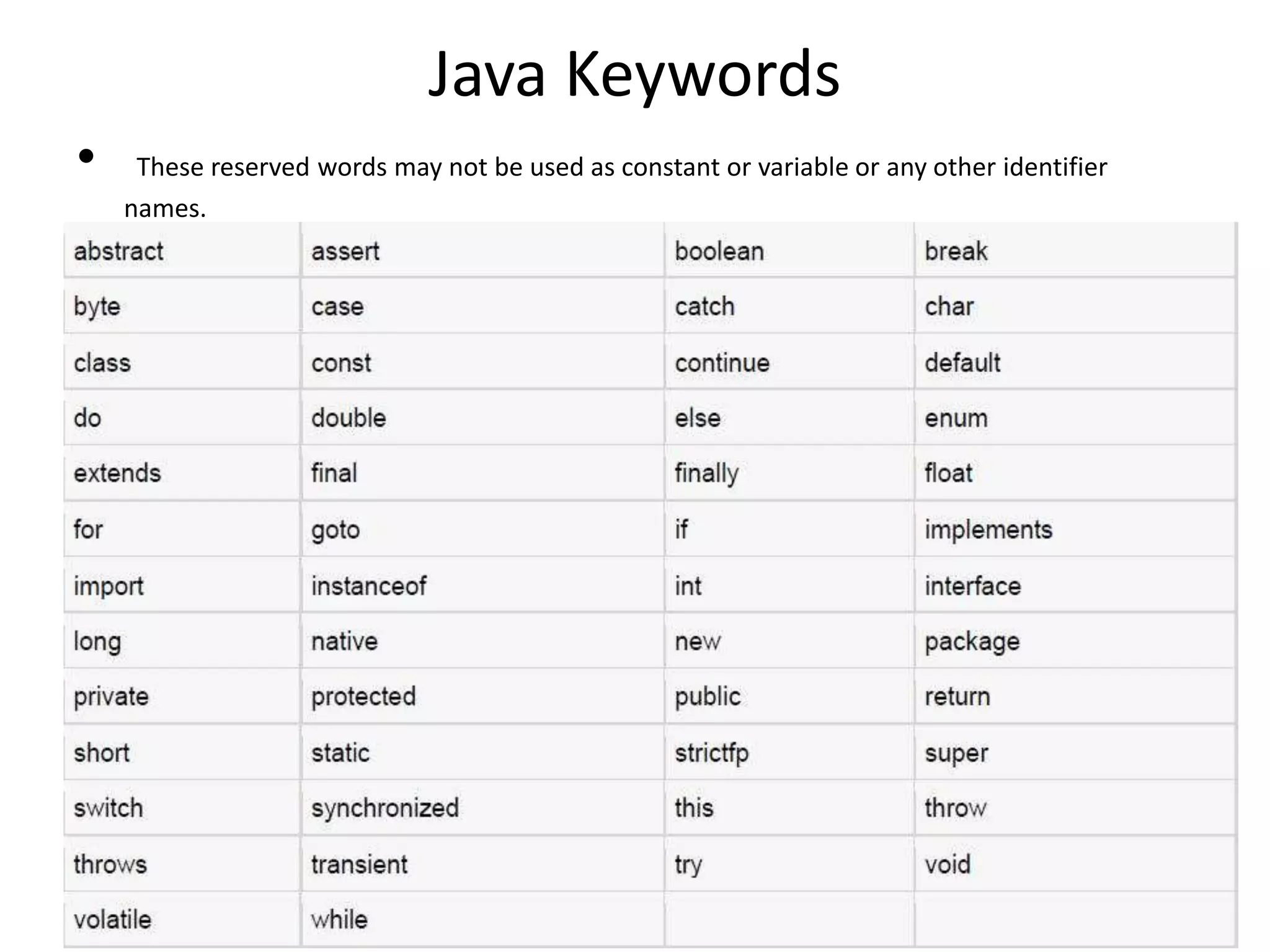
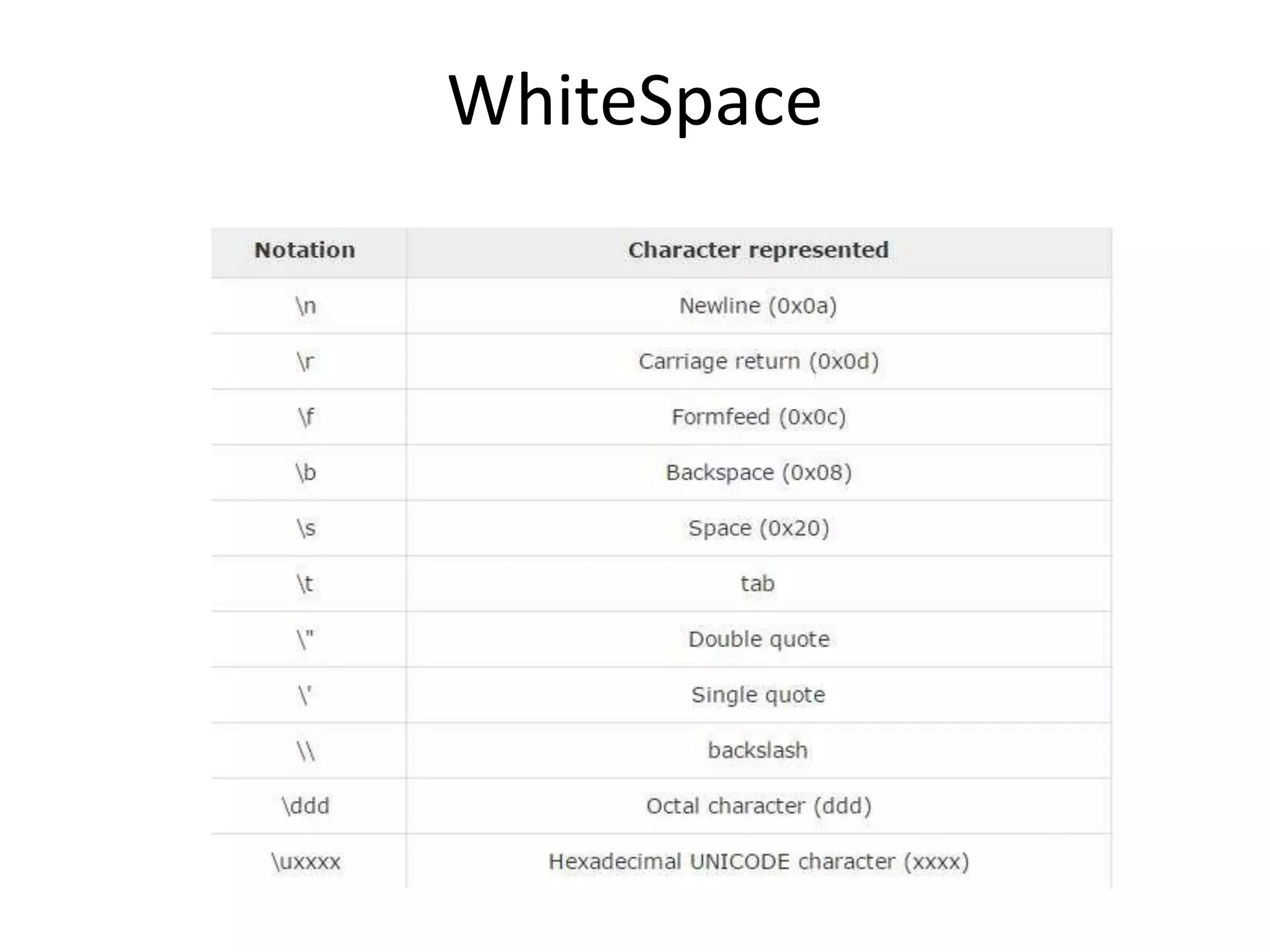
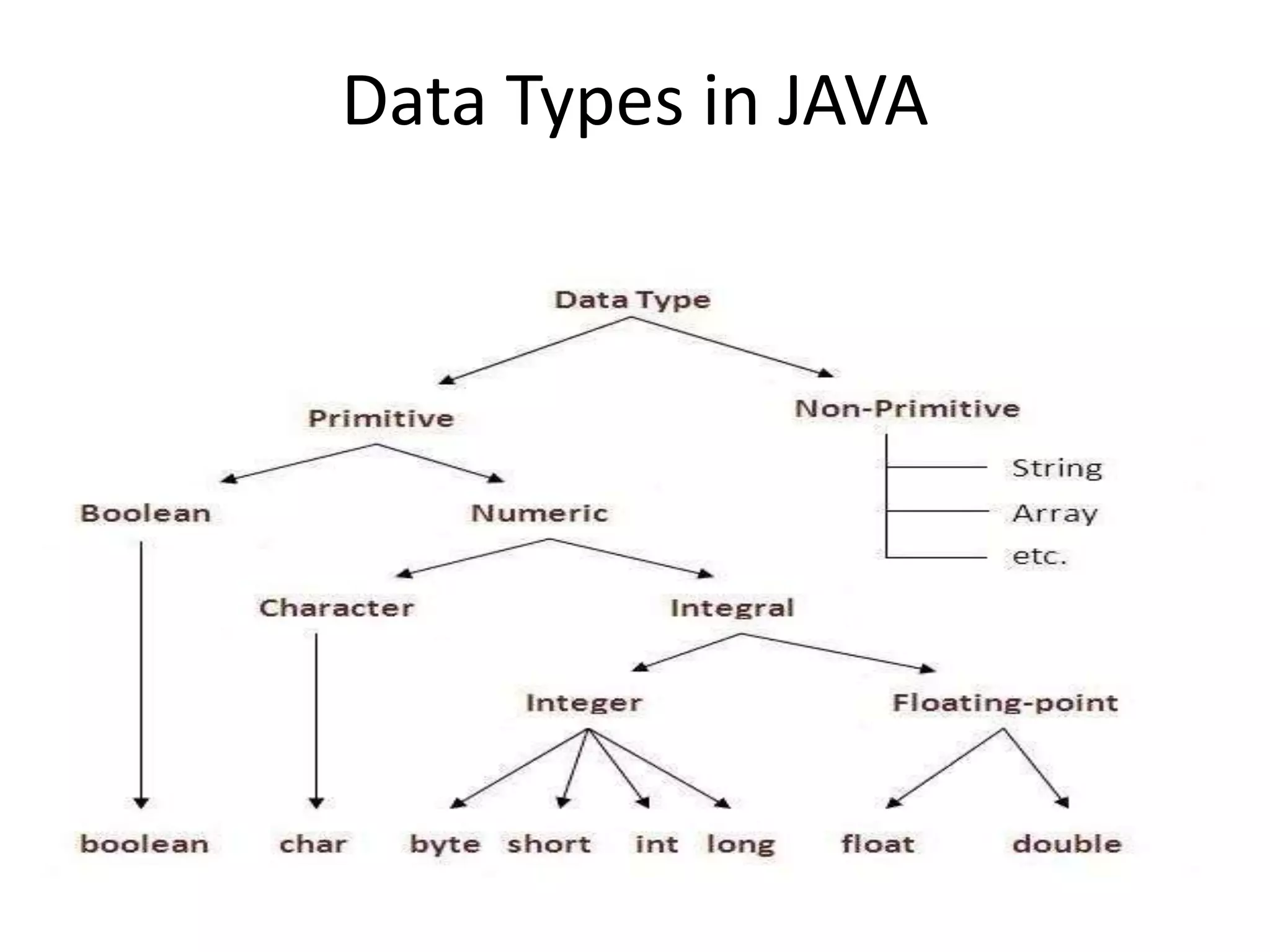
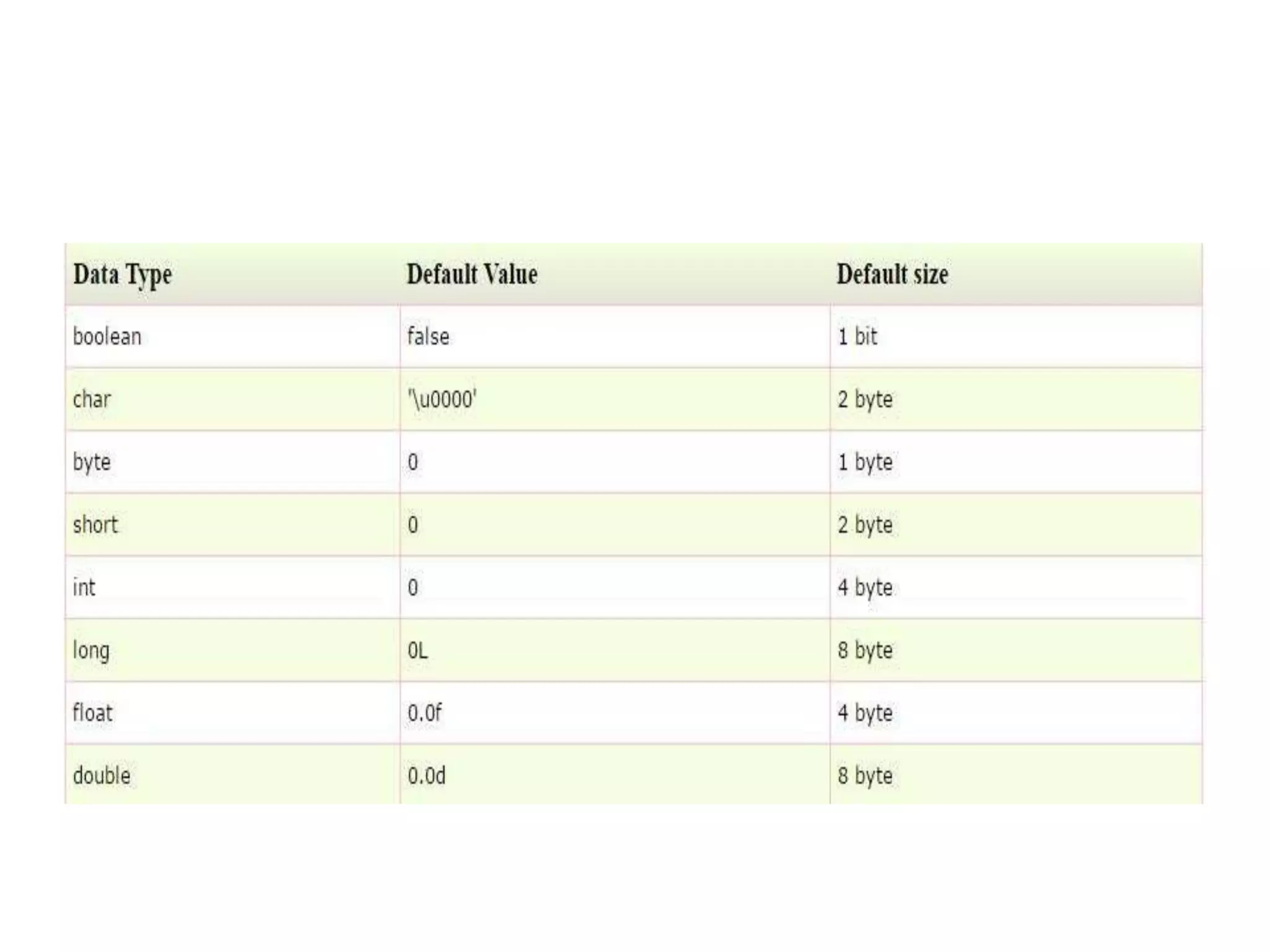
This document provides an introduction to Java. It discusses the history of Java, noting it was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in 1991. It states that Java resides on many platforms like mobile devices, desktops, servers, embedded devices, and the cloud. The key principle of Java is "write once, run anywhere." It also discusses Java libraries, versions of Java, features of Java like being object-oriented and portable, and how to install and set up Java. It provides an example of a simple "Hello World" Java program. It also covers Java data types, variables, typecasting, arrays, comments, and the Scanner class.







![First Program
Public class HelloWorld
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(“HelloWOrld”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontojava-201127155756/75/Introduction-to-java-12-2048.jpg)




![Variable
• In Java, all variables must be declared before they
can be used. The basic form of a variable
declaration is shown here:
type identifier [= value][, identifier [= value]...];
int a, b, c;// declares three ints, a, b, and c.
int d =3, e, f =5;// declares three more ints,
initializing // d and f.
byte z =22;// initializes z.
double pi =3.14159;// declares an approximation of
pi.
char x ='x';// the variable x has the value 'x'.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontojava-201127155756/75/Introduction-to-java-21-2048.jpg)


![ARRAY
• Declaring Array Variables:
To use an array in a program, you must declare a variable to
reference the array, and you must specify the type of array the variable
can reference. Here is the syntax for declaring an array variable:
dataType[] arrayRefVar; // preferred way.
or
dataType arrayRefVar[]; // works but not preferred way.
Example:
• The following code snippets are examples of this syntax:
double[] myList; // preferred way.
or
• double myList[]; // works but not preferred way.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontojava-201127155756/75/Introduction-to-java-24-2048.jpg)
![Creating ARRAY
• You can create an array by using the new operator with the following
syntax:
• arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];
• The above statement does two things:
• It creates an array using new dataType[arraySize];
• It assigns the reference of the newly created array to the variable
arrayRefVar.
• Declaring an array variable, creating an array, and assigning the reference
of the array to the variable can be combined in one statement, as shown
below:
• dataType[] arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];
• Alternatively you can create arrays as follows:
• dataType[] arrayRefVar = {value0, value1, ..., valuek};
• The array elements are accessed through the index. Array indices are 0-
based; that is, they start from 0 to arrayRefVar.length-1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontojava-201127155756/75/Introduction-to-java-25-2048.jpg)
![• Following statement declares an array variable, myList,
creates an array of 10 elements of double type and assigns its
reference to myList:
• double[] myList = new double[10];
• Following picture represents array myList. Here, myList holds
ten double values and the indices are from 0 to 9.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontojava-201127155756/75/Introduction-to-java-26-2048.jpg)

