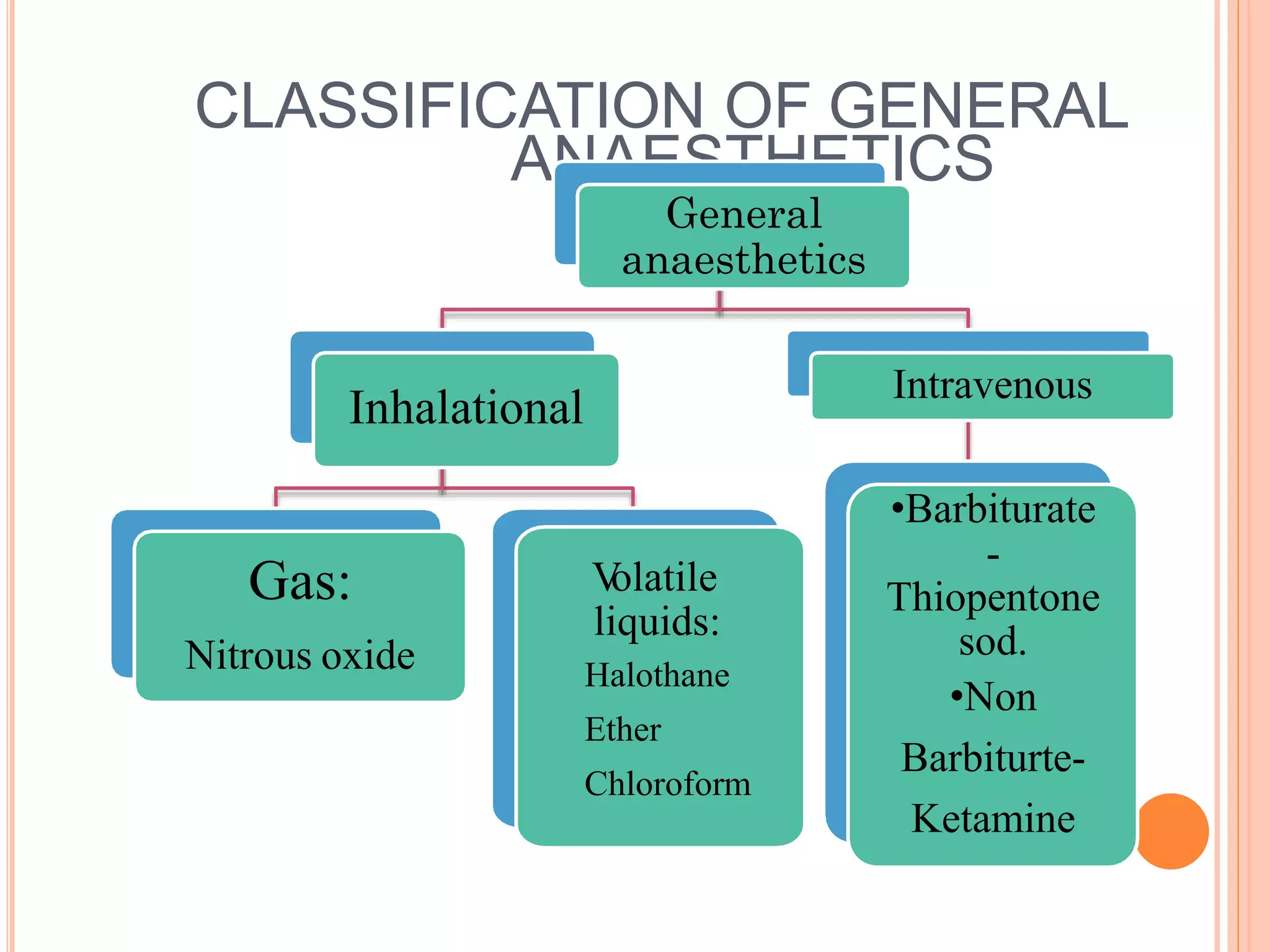
General anesthesia involves inducing a state of unconsciousness through medications that provide amnesia, analgesia, muscle relaxation, and sedation. There are two main classes of general anesthetics - inhalational gases and vapors like nitrous oxide and halothane, and intravenous agents like thiopental and propofol. These drugs work by modulating receptors like GABA, NMDA, and nicotinic receptors in the brain to produce reversible loss of consciousness. They are chosen based on properties like rapid onset of action, short duration, and minimal side effects on vital organs like the heart and lungs.