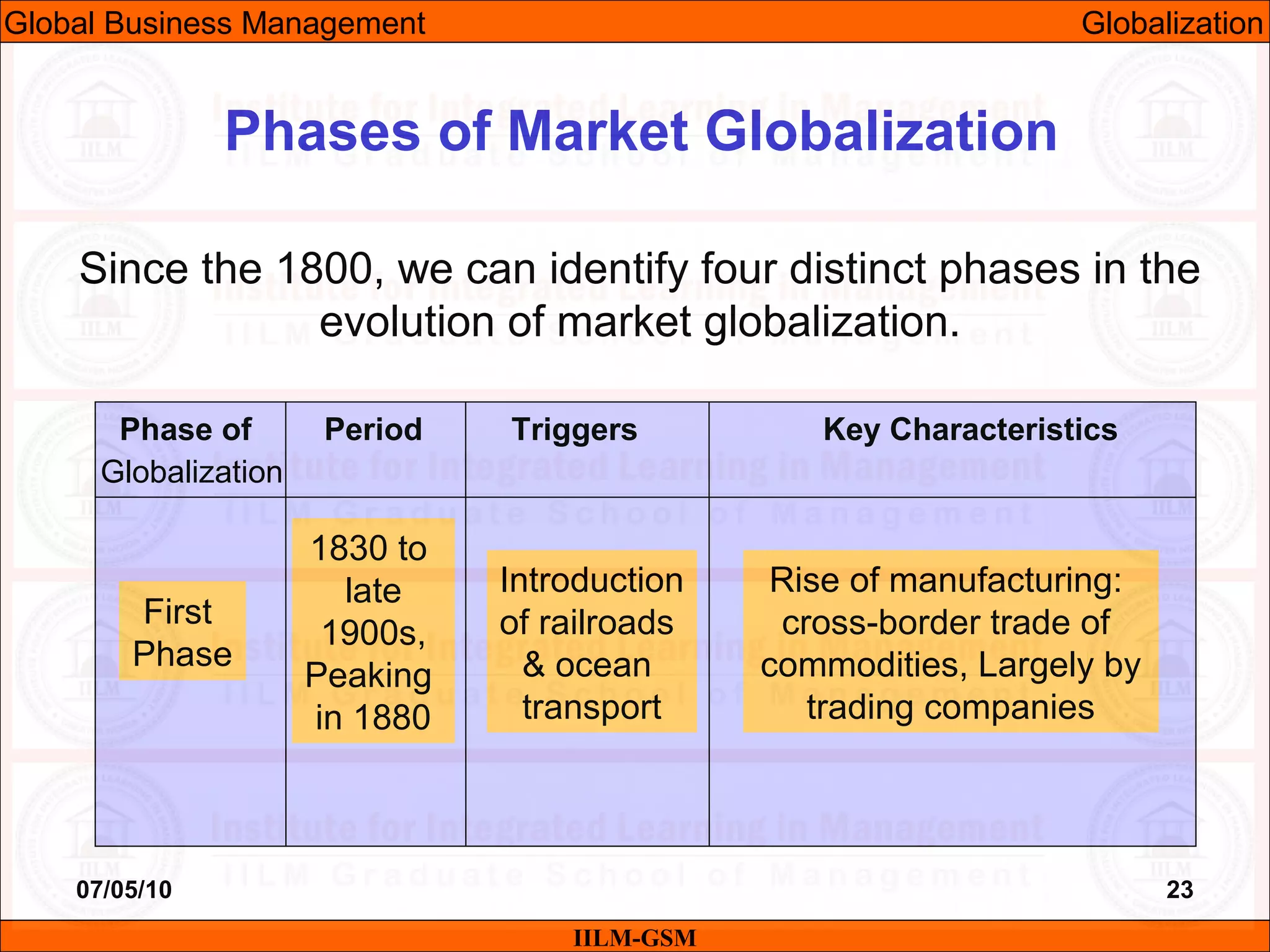
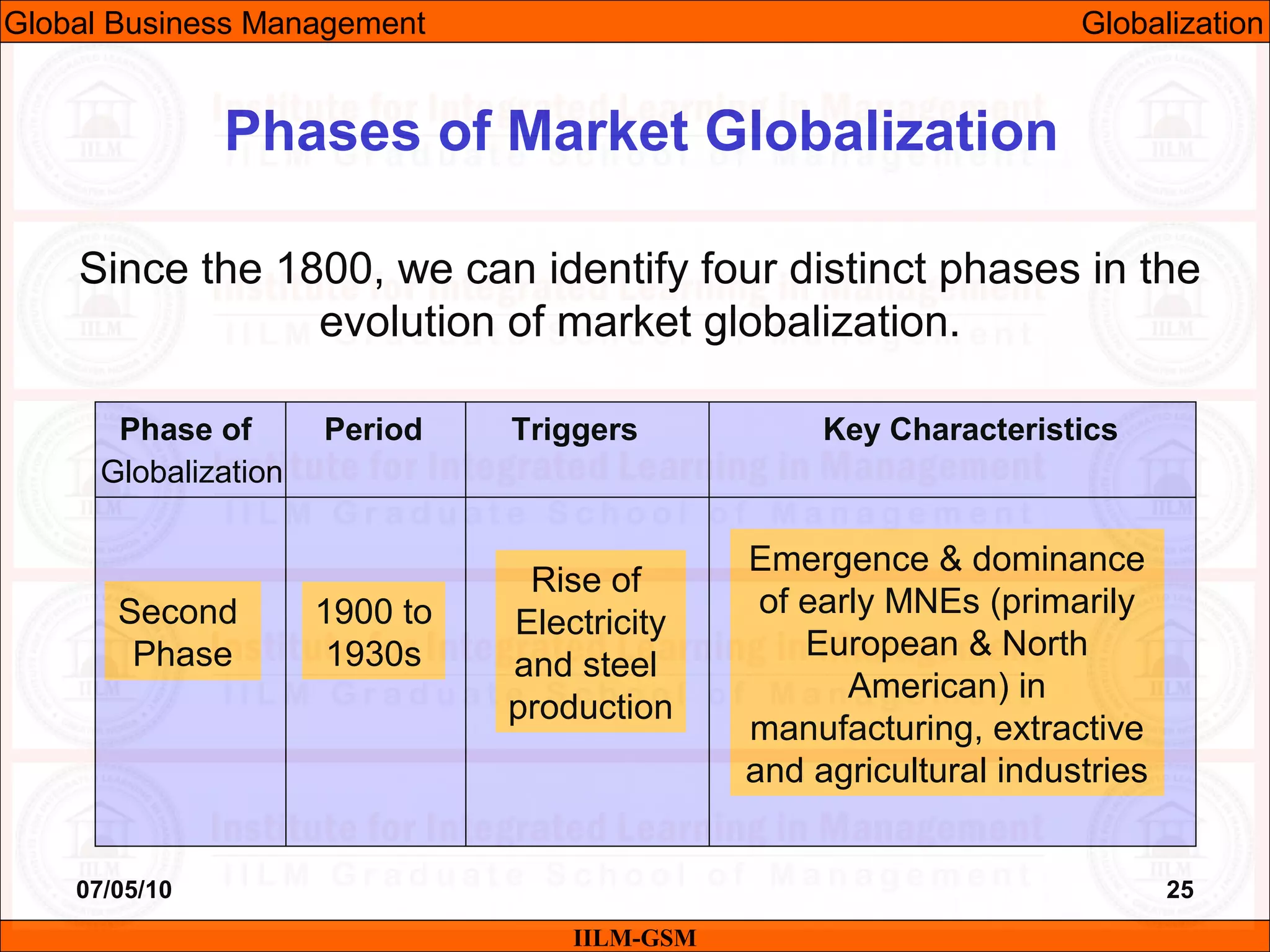
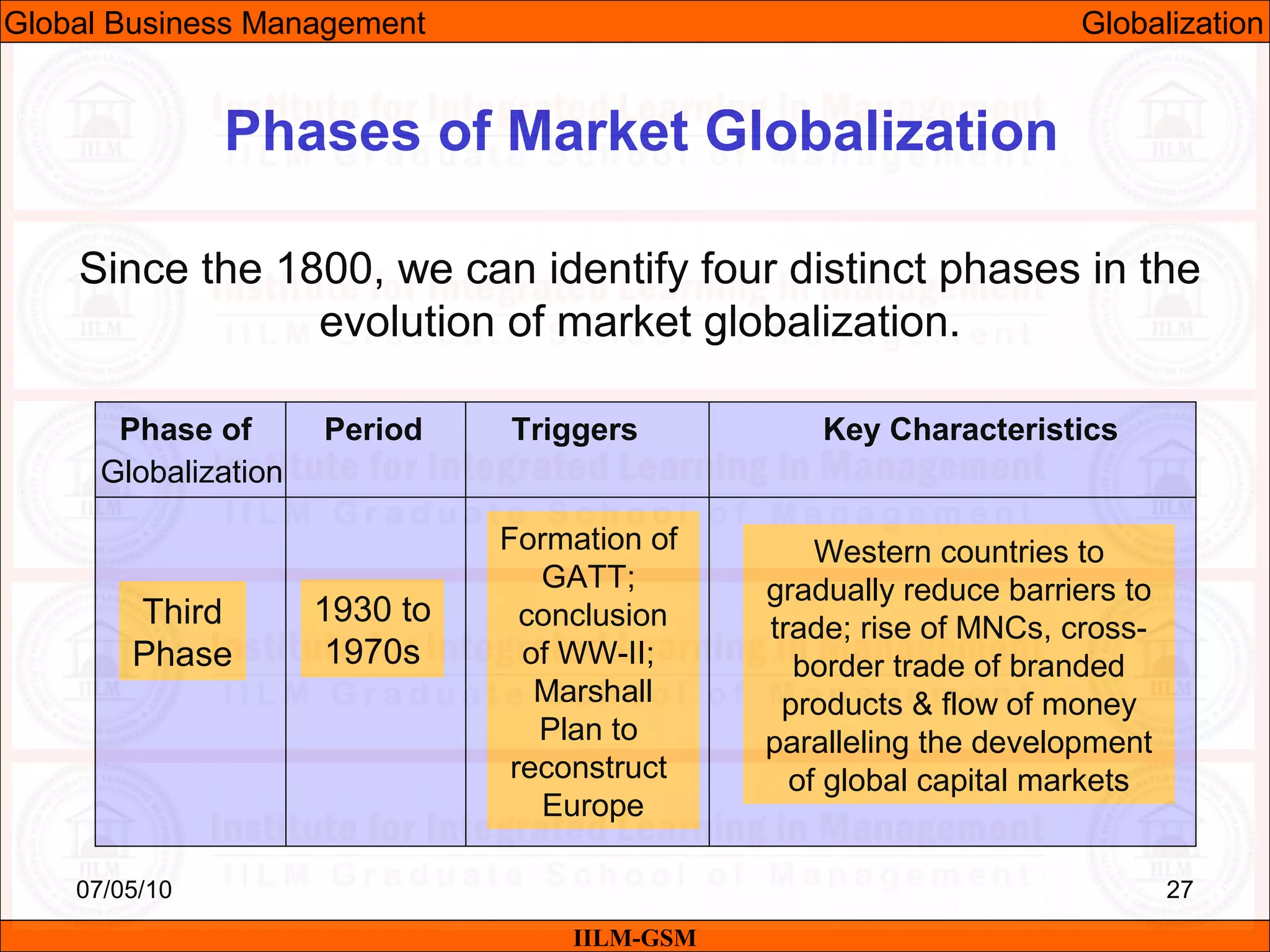
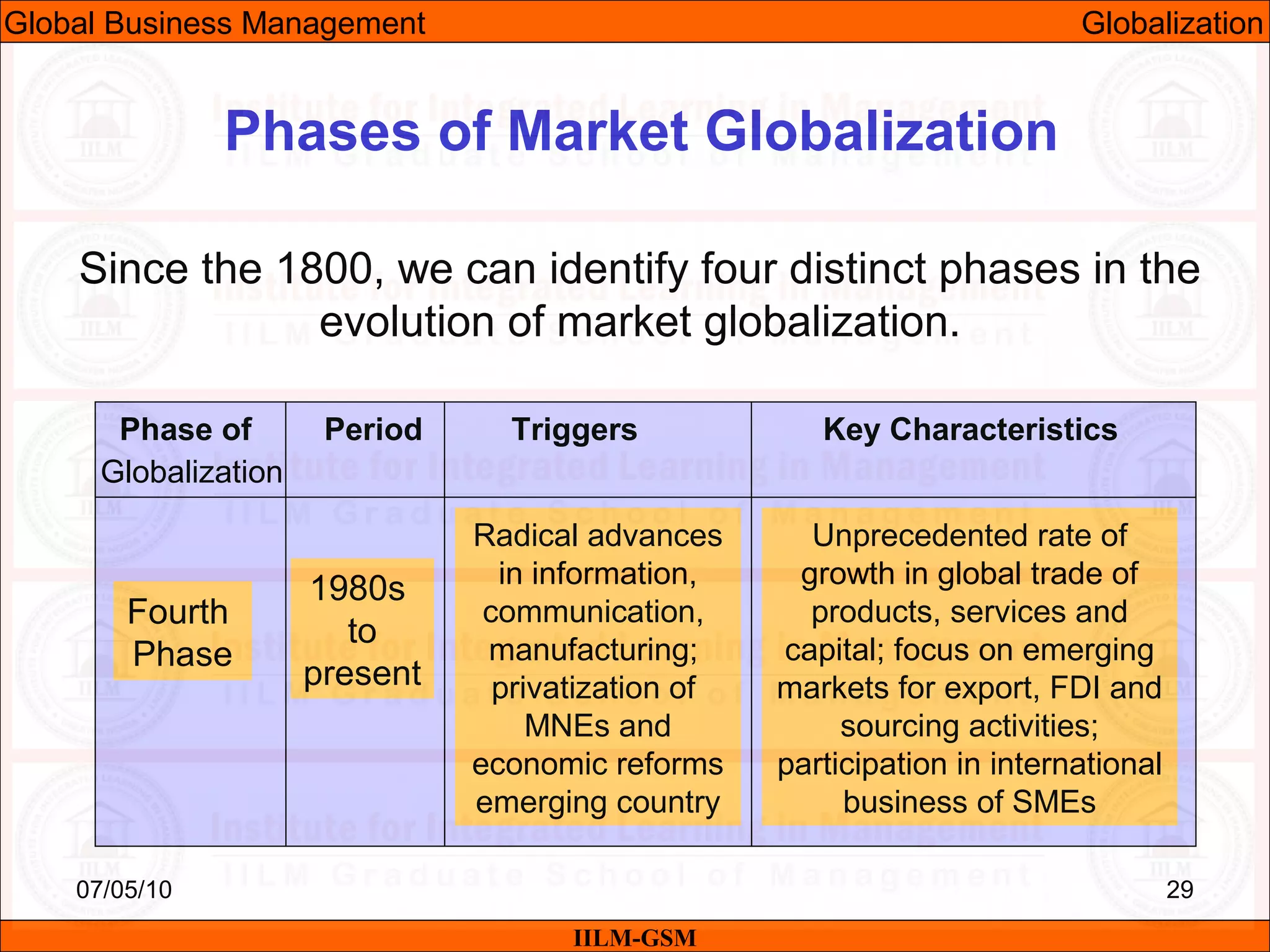
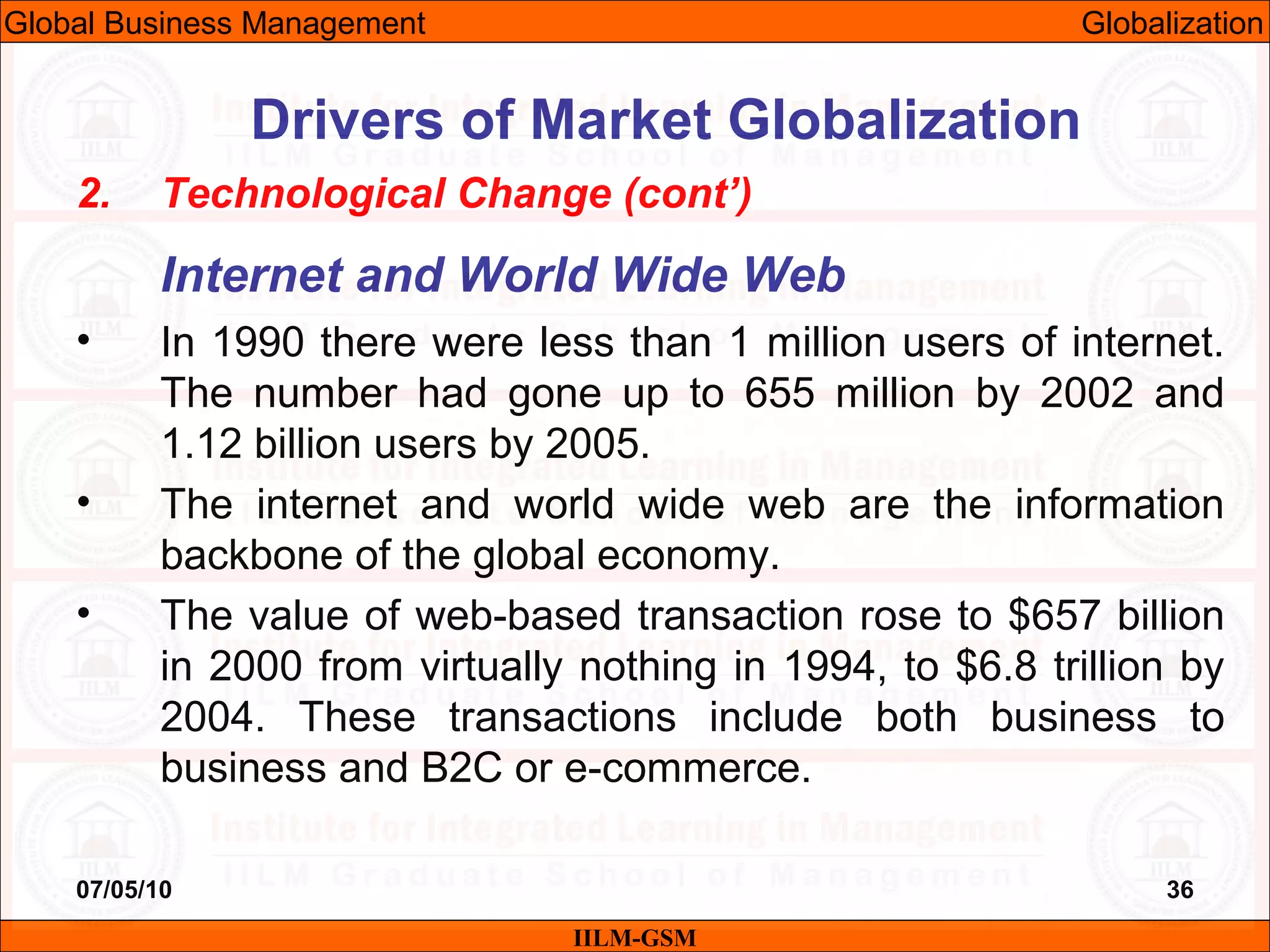
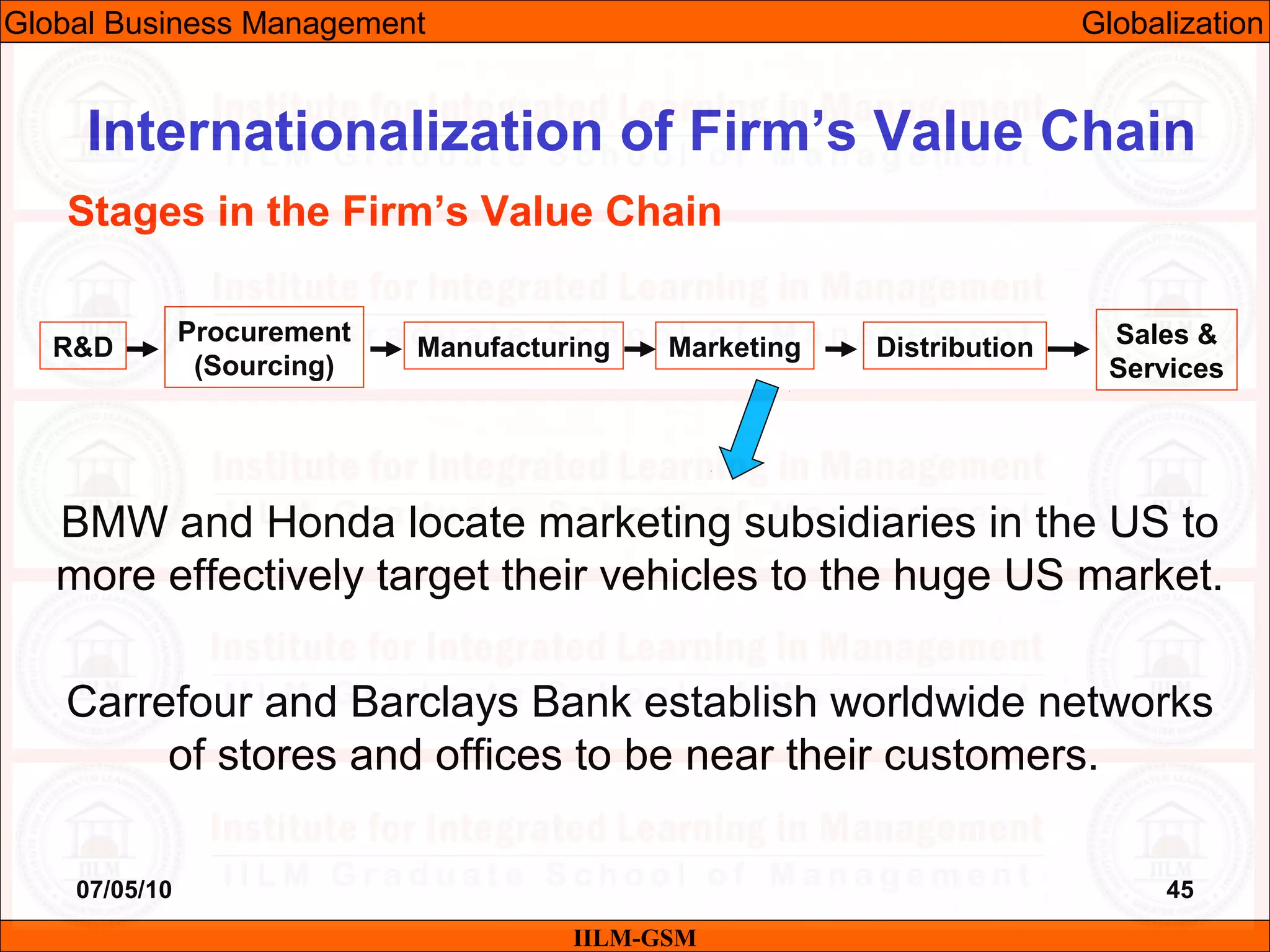
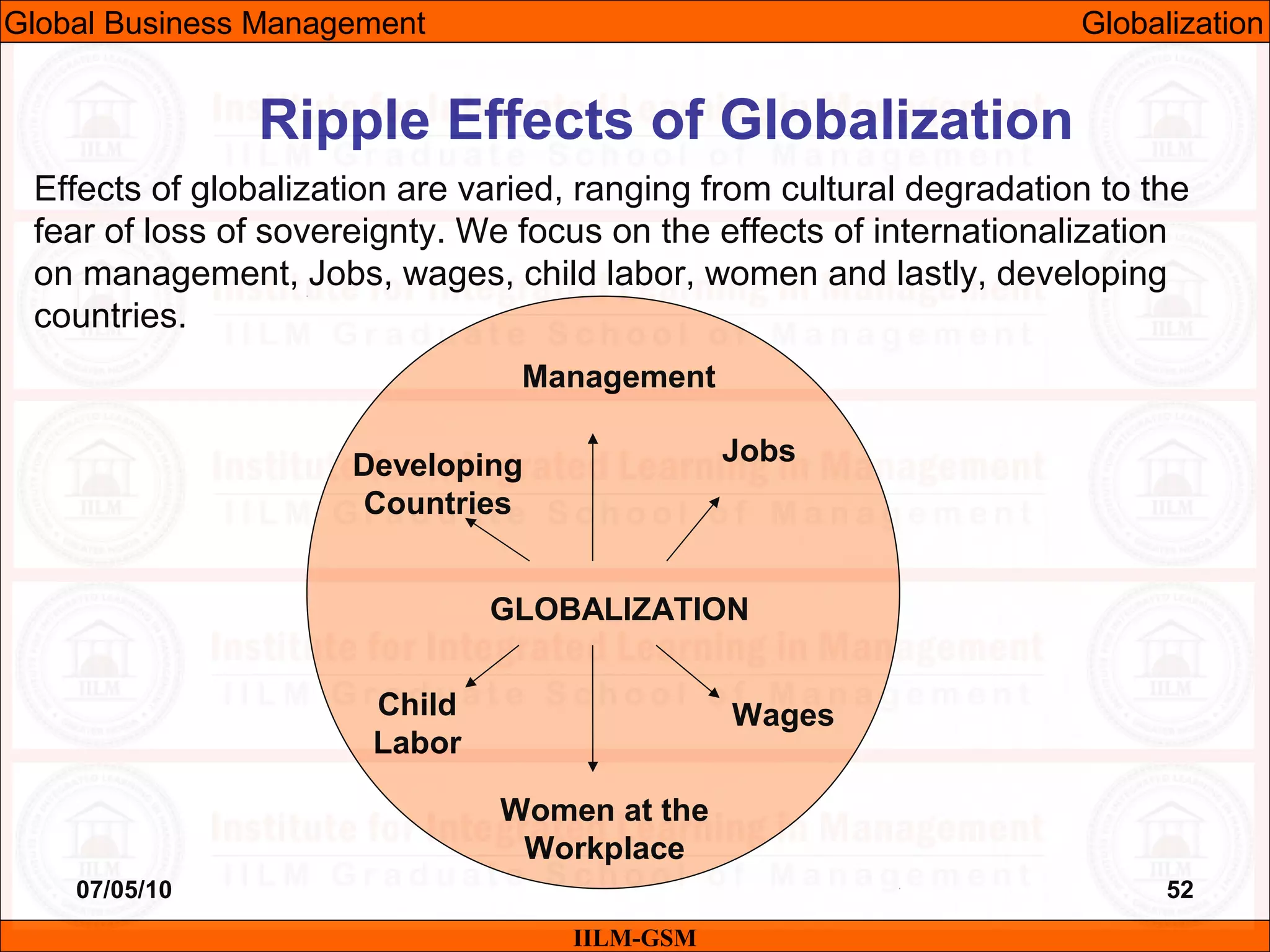
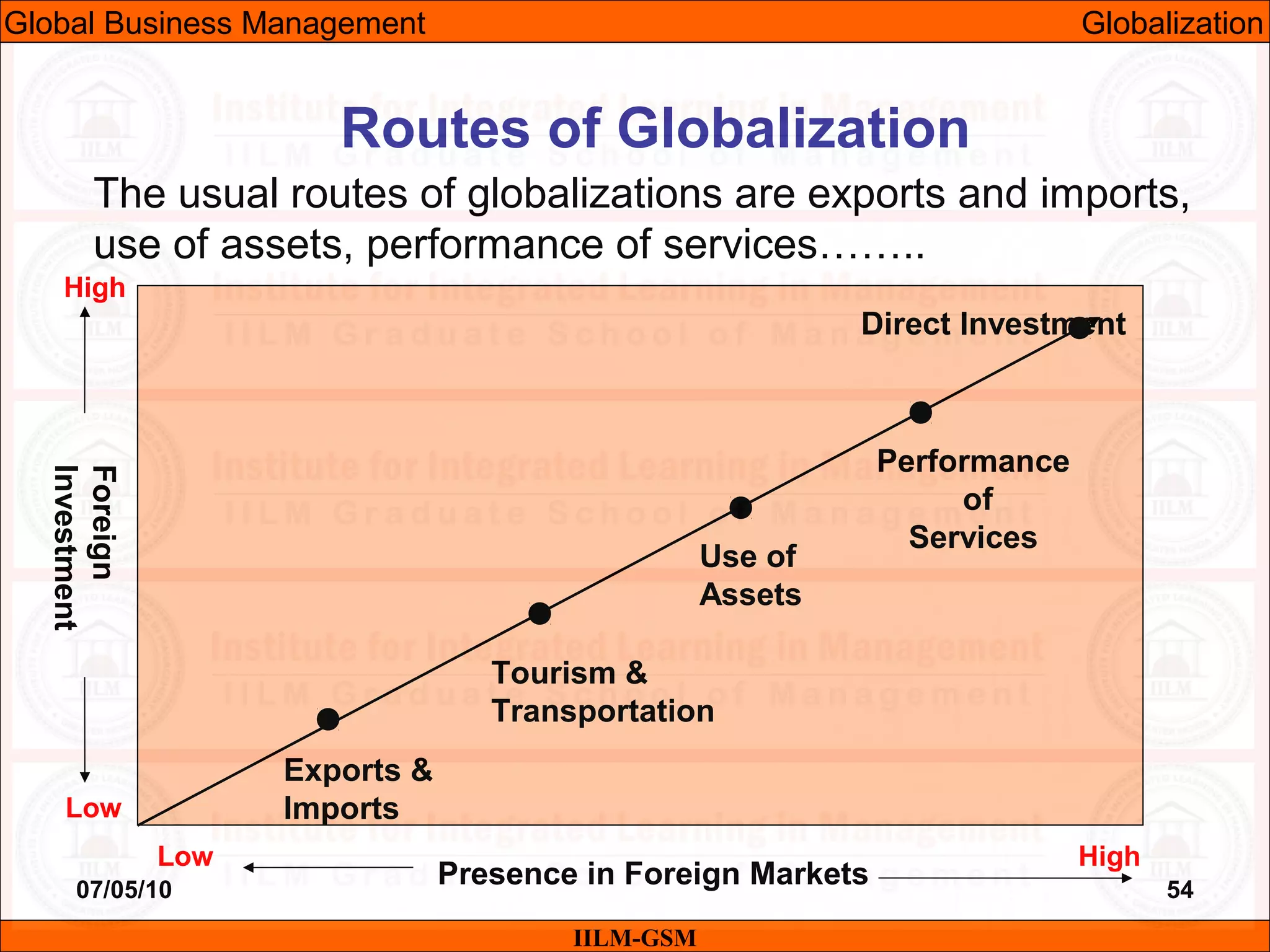
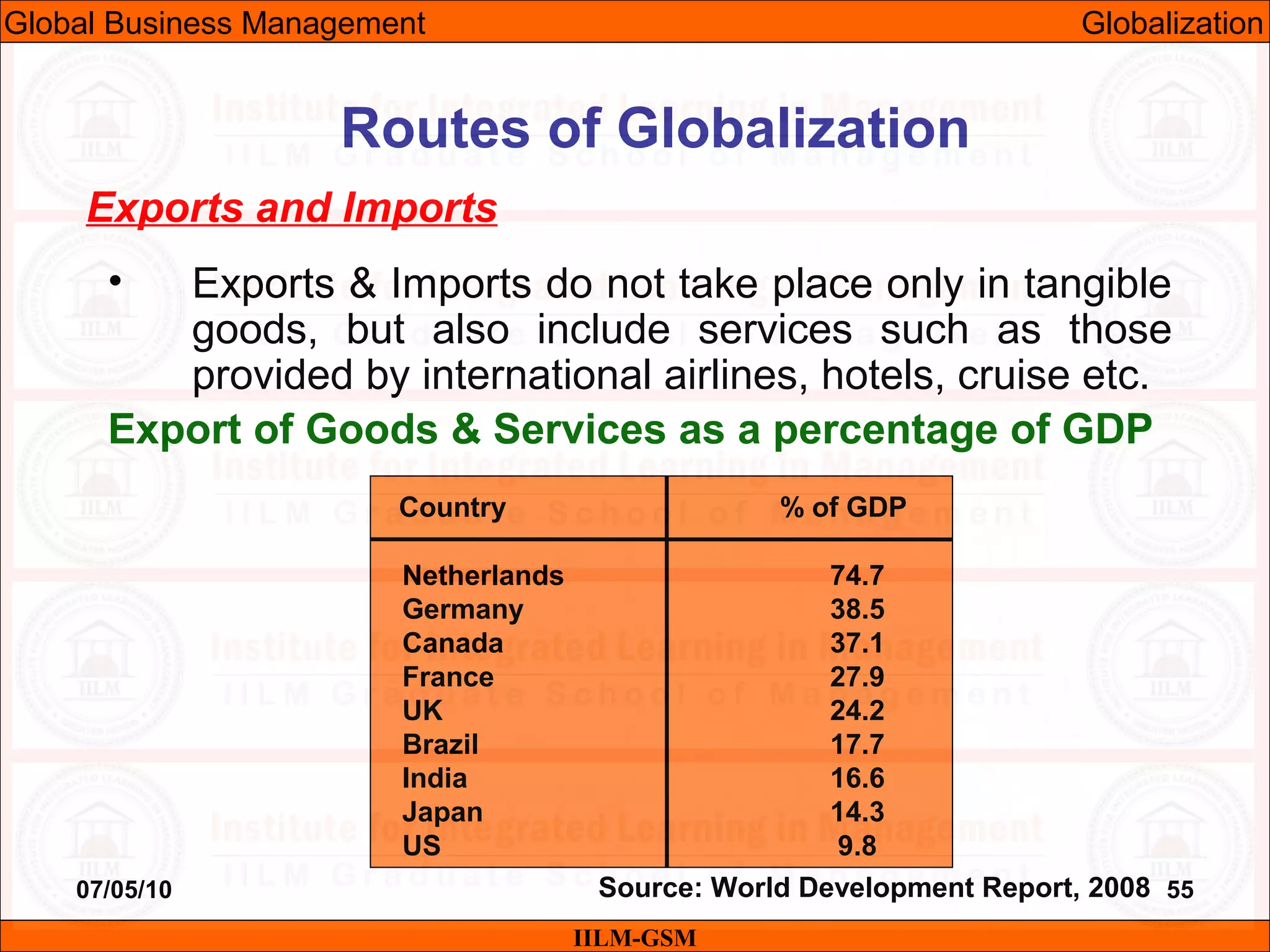
The document discusses the importance of international business knowledge for management students. It notes that graduates may find themselves working in foreign countries, so understanding international business will help prepare them mentally. The rest of the document outlines the topics and contents of a course on international business management, including globalization, global trade, economic and political environments, and foreign direct investment.