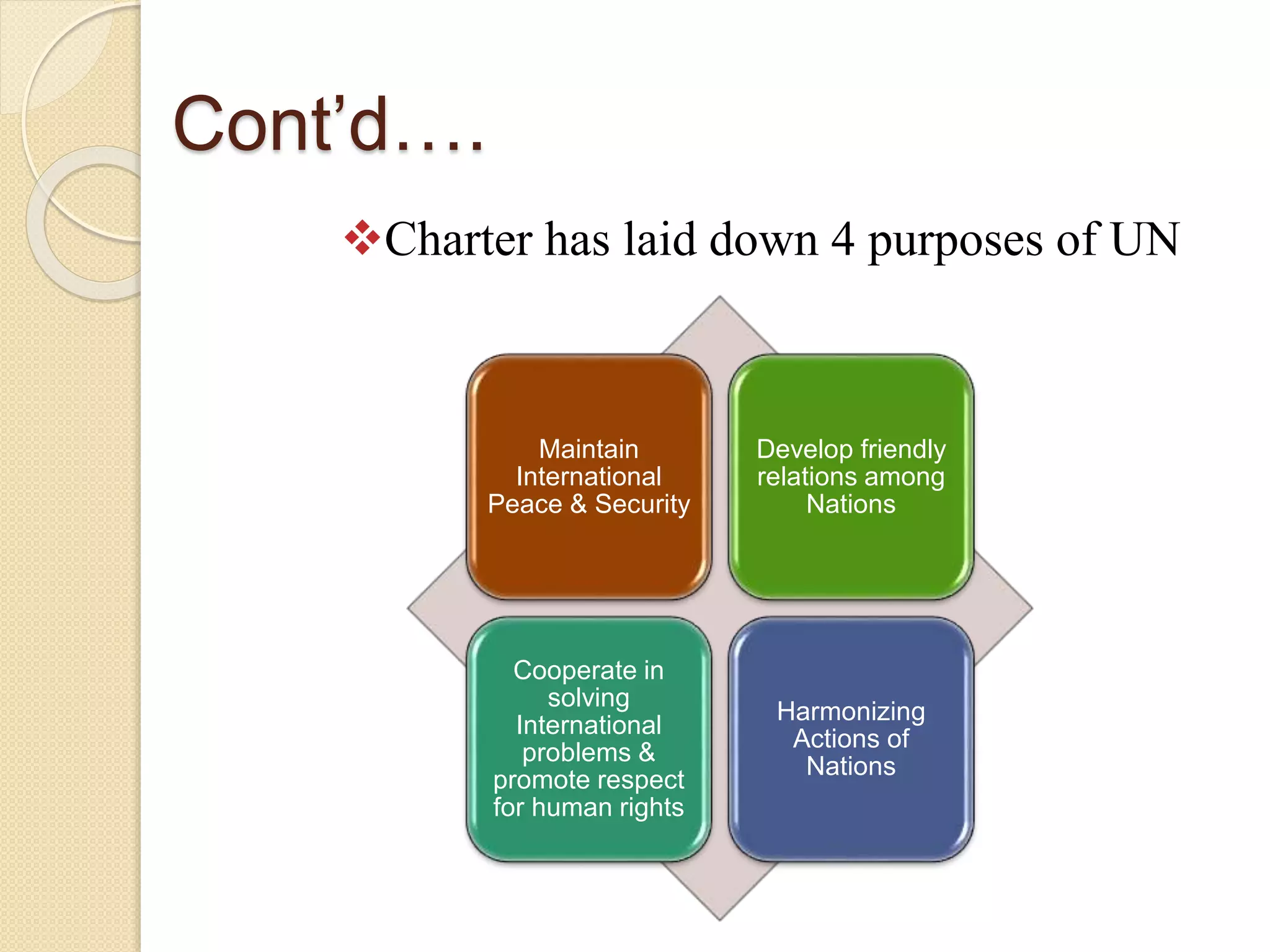
This document provides an overview of globalization and international business. It discusses the benefits of international business such as increased profits and employment opportunities. However, it also notes hurdles such as differing laws and regulations between countries. Globalization is defined as the interdependence and interrelation of the world economy. Key factors driving globalization include the fall of trade barriers, advances in telecommunications and transportation technologies, and the rise of the internet. Several global institutions that promote globalization are also discussed, including the WTO, IMF, World Bank, and UN.