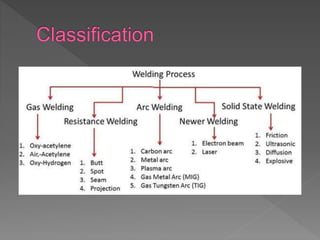
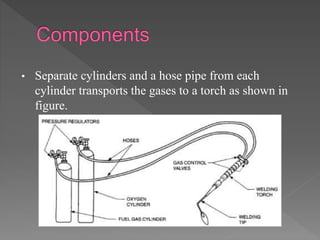
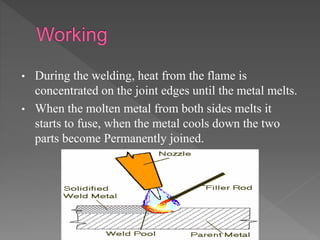
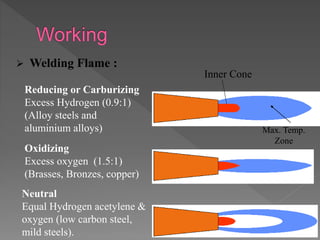
Oxy-hydrogen welding is a gas welding process that uses a torch to produce a flame from burning oxygen and hydrogen gases. The gases are supplied through separate hoses and cylinders to the welding torch, where they mix and ignite to burn at the torch nozzle. By concentrating the flame's heat on the joint edges, the metals melt and fuse together to permanently join two pieces when cooled. Different types of welding flames can be produced by varying the ratio of oxygen to hydrogen to suit materials like brass, steel, or aluminum alloys.