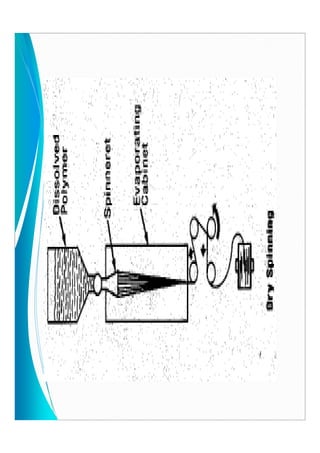
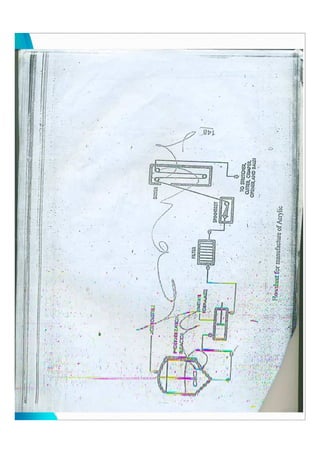
This document describes the production and properties of acrylic fibers. Acrylic is produced from acrylonitrile monomer through polymerization. It can be produced through dry or wet spinning processes where the polymer solution is extruded and dried, causing the polymer to solidify into fibers. Acrylic fibers have good tensile strength, elongation, elastic recovery and resistance to sunlight, acids and insects. Its properties make it suitable for uses such as apparel, knitwear, blankets and carpets.