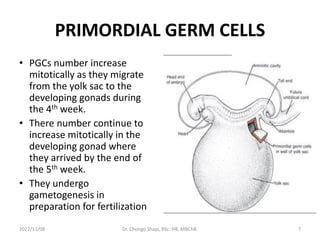
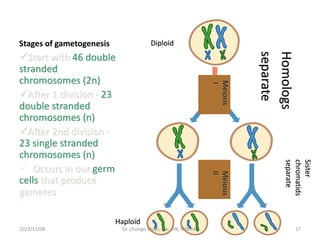
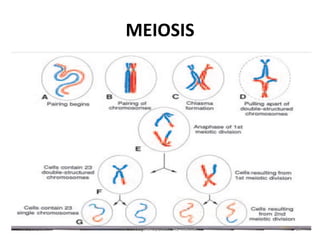
The document discusses the processes of gametogenesis, detailing the formation of sperm (spermatogenesis) and eggs (oogenesis) through meiosis in male and female gonads, respectively. It covers key stages such as the development of primordial germ cells, the distinction between somatic and germline cells, and hormonal regulation of these processes. The document highlights the intricate mechanisms and timelines involved in creating mature sex cells essential for reproduction.