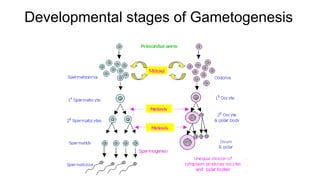
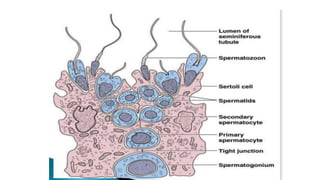
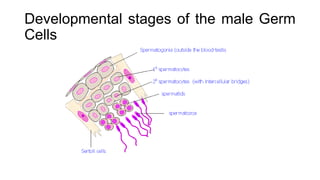
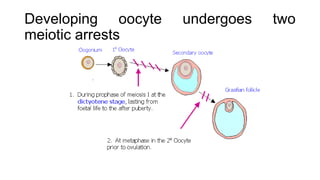
Gametogenesis is the process by which haploid gametes are formed from diploid germ cells through cell division and maturation. It occurs in four phases: primordial germ cell formation, mitotic proliferation, meiosis, and gamete maturation. In males (spermatogenesis), it occurs in the testes and produces sperm through spermatogonial mitosis and spermatocyte meiosis. In females (oogenesis), it occurs in the ovaries and arrests at two points during meiotic prophase I to produce ova.