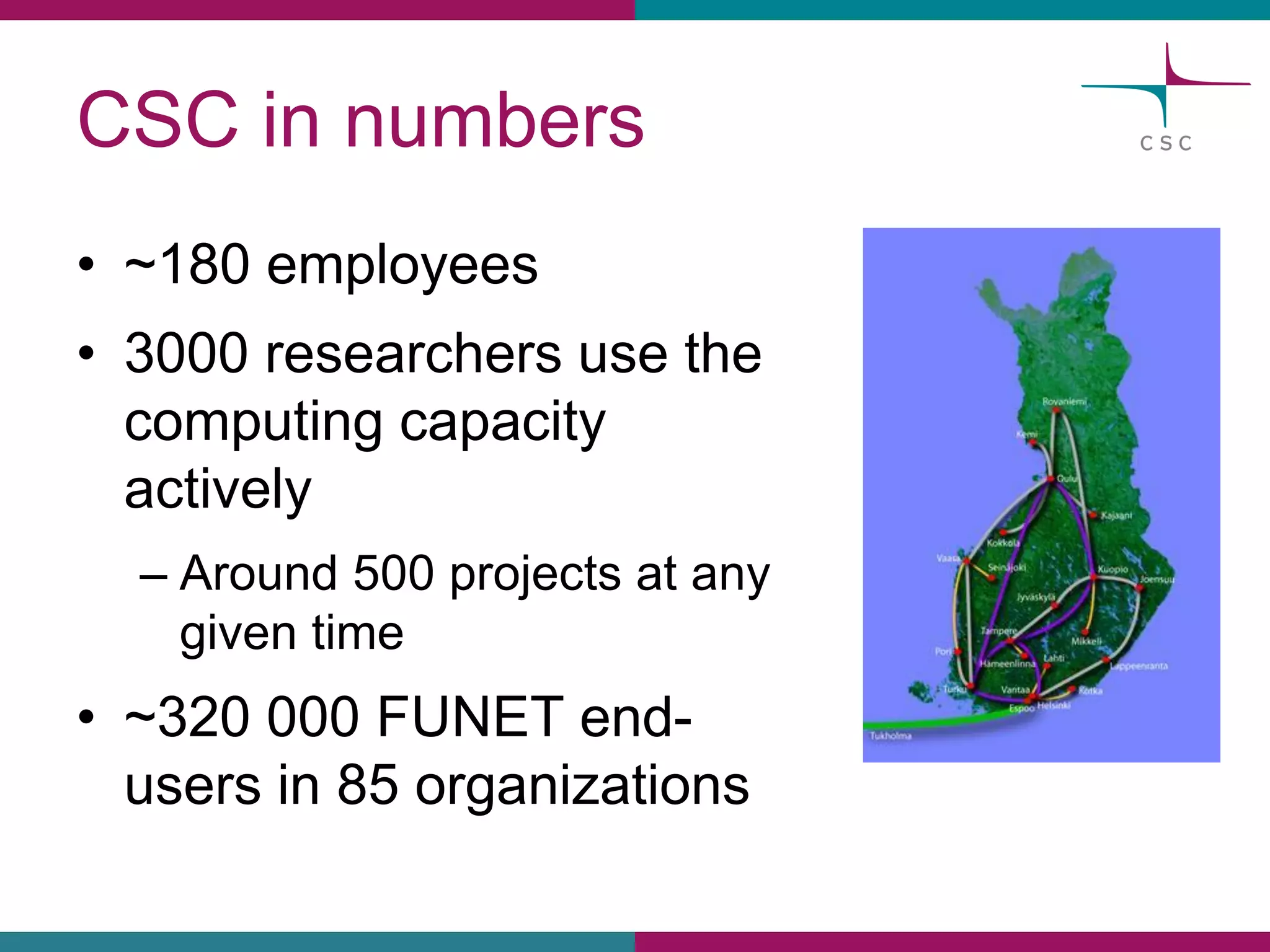
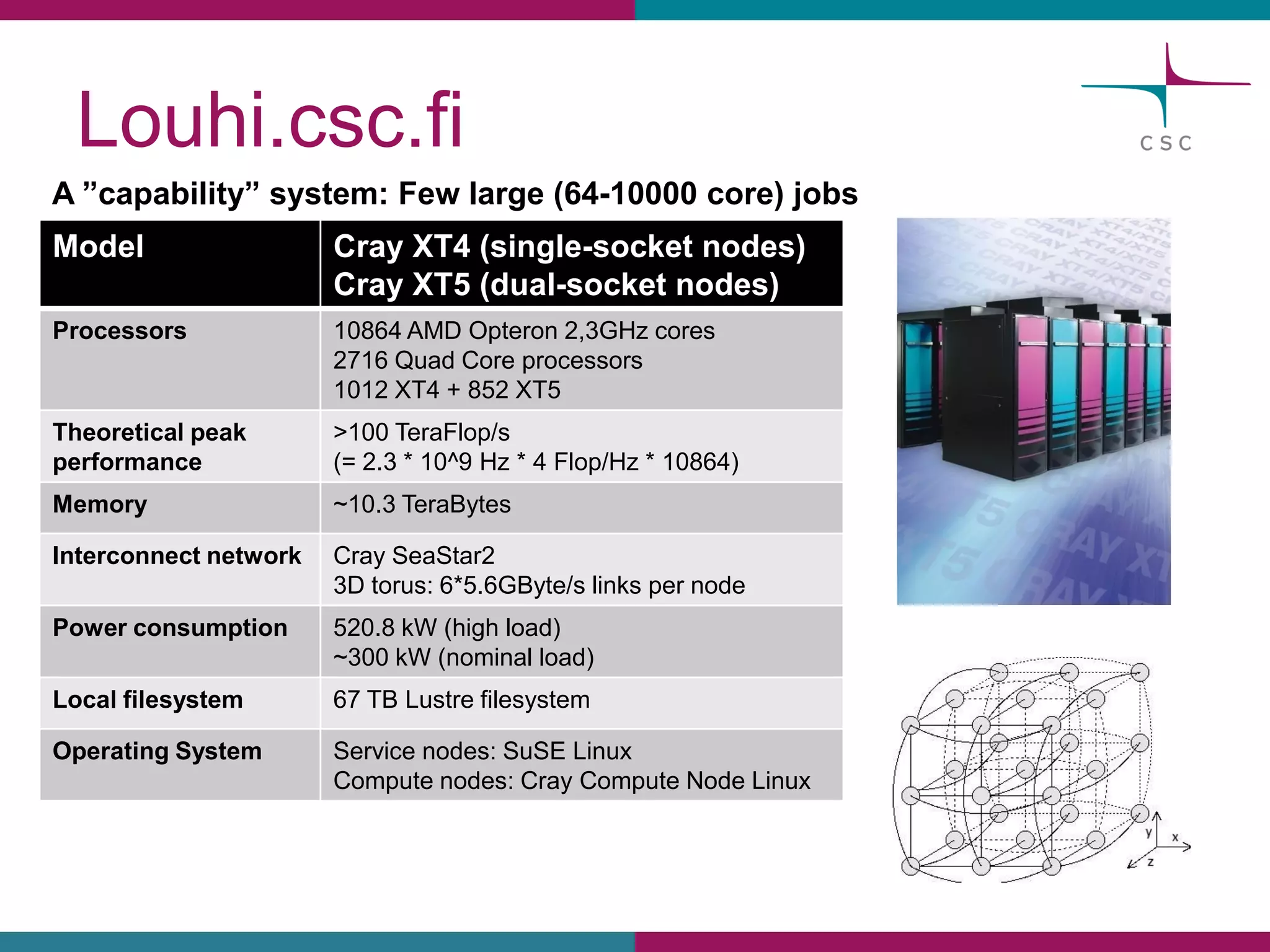
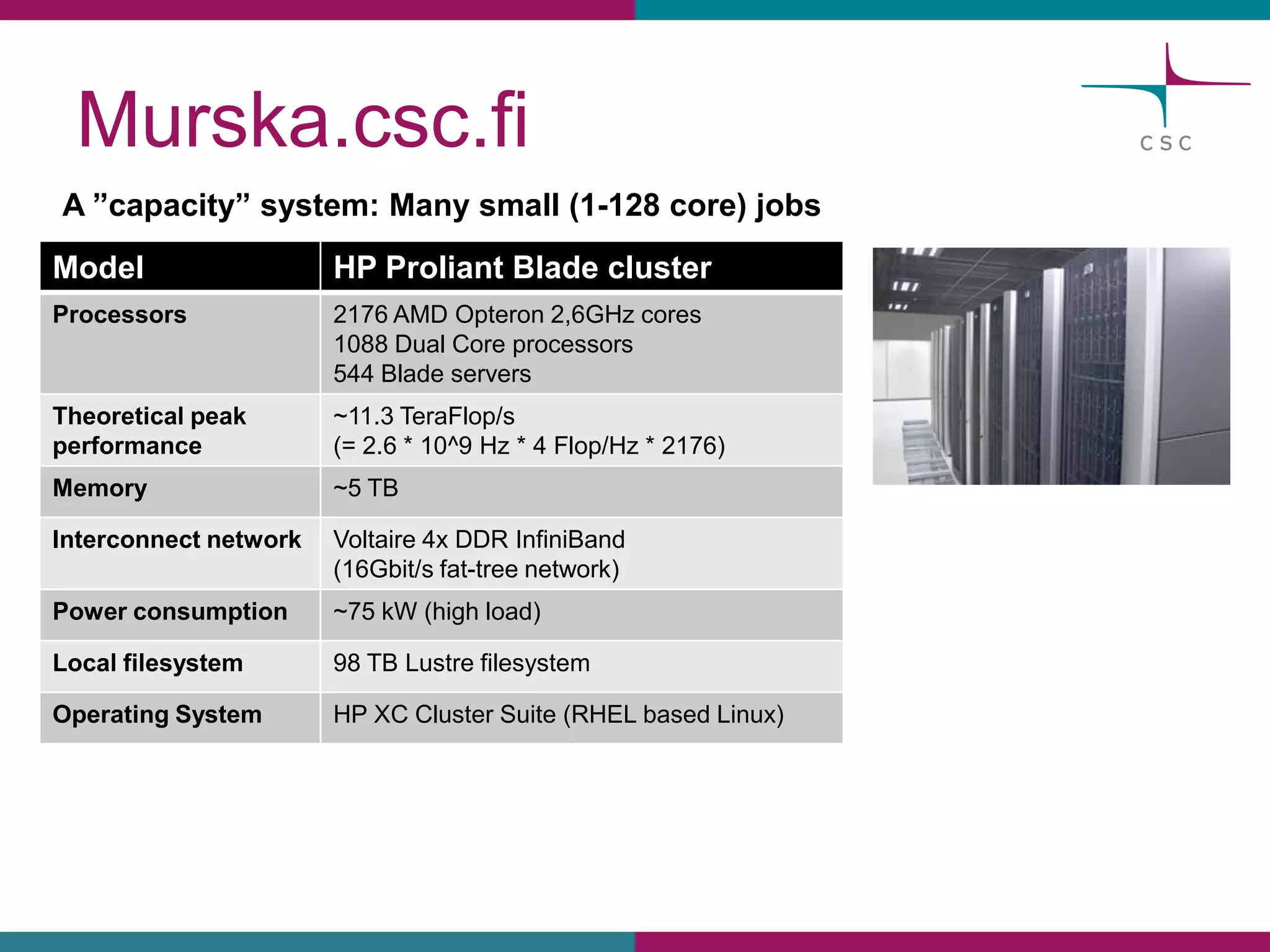
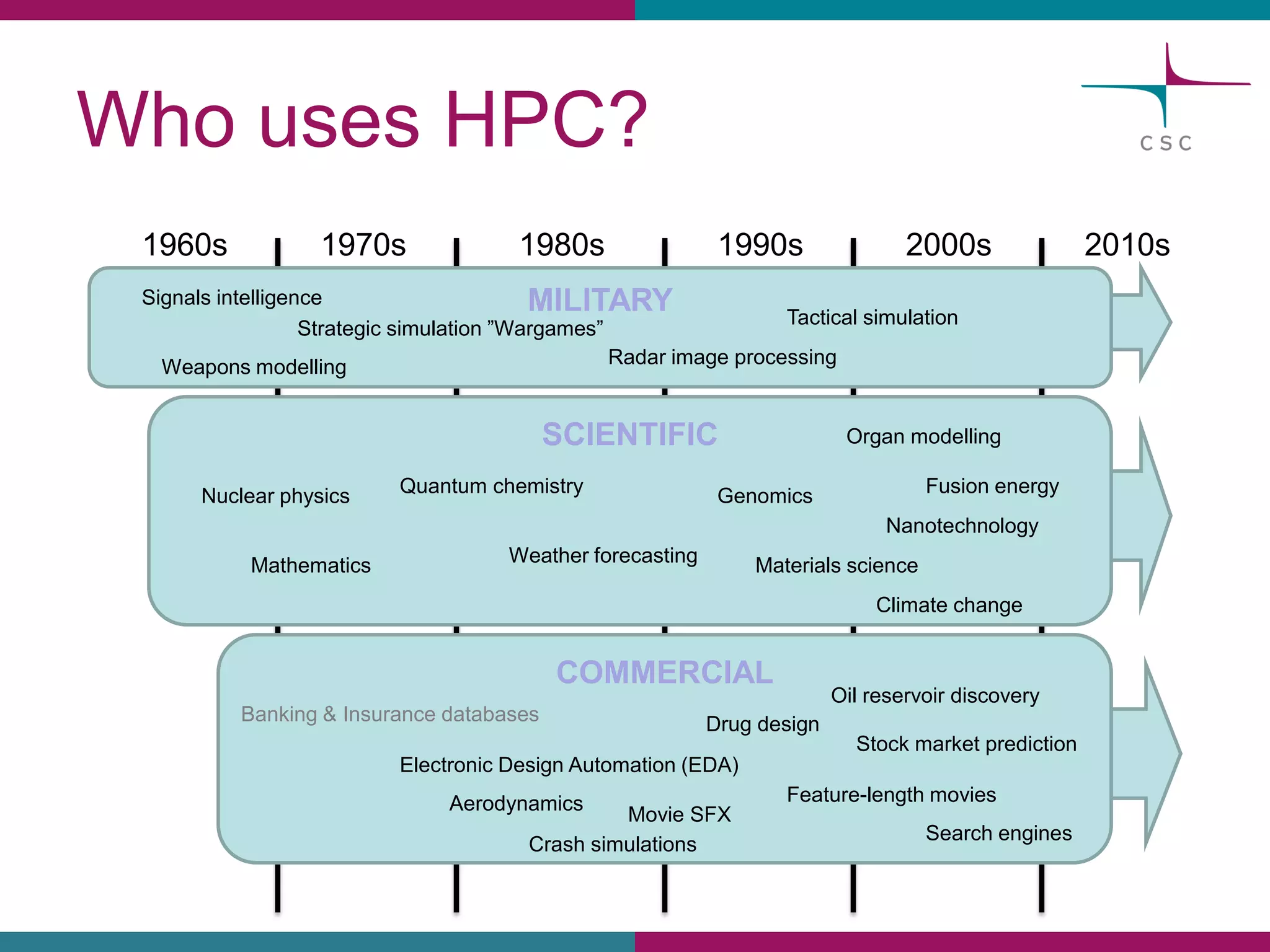
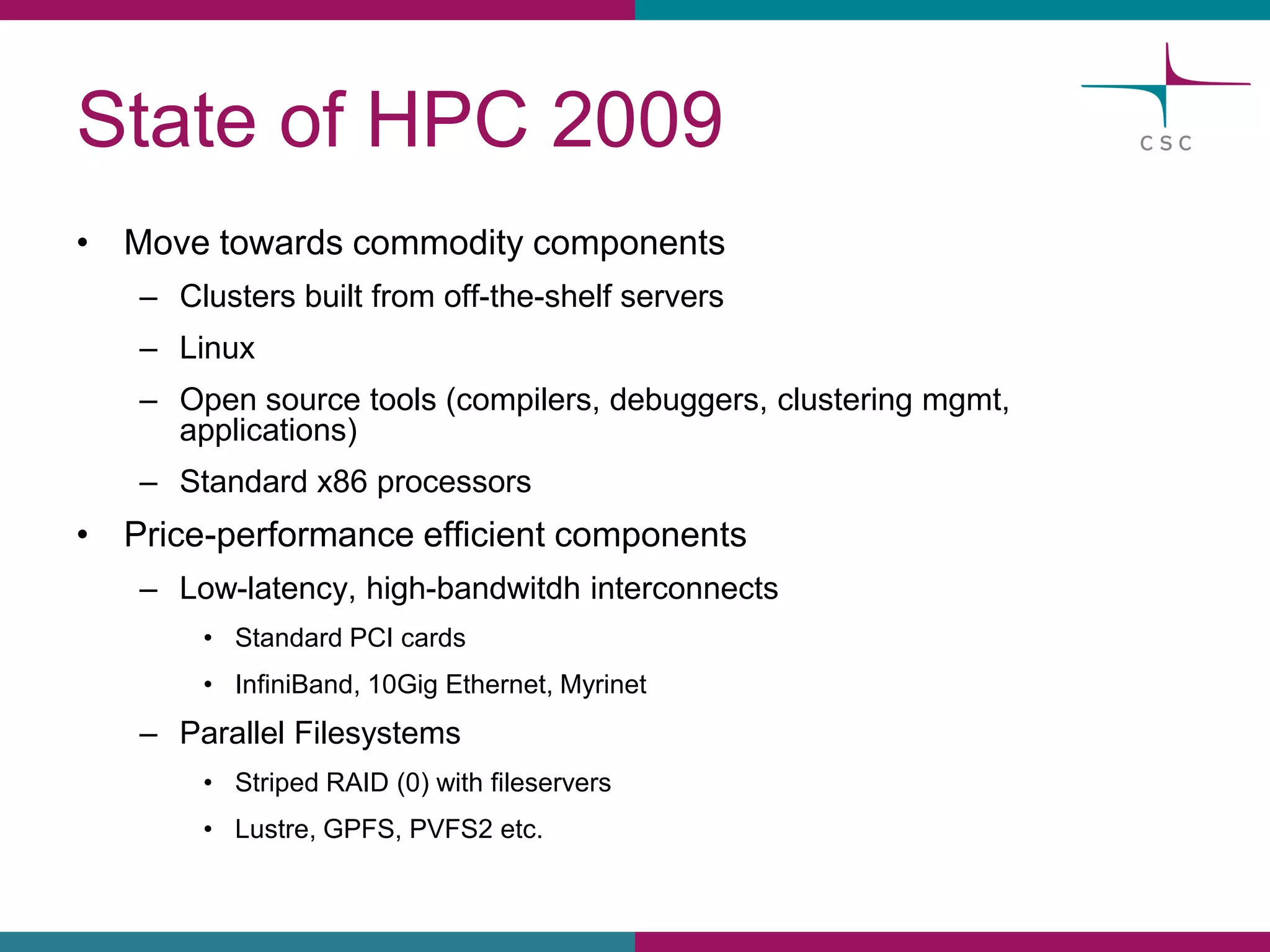
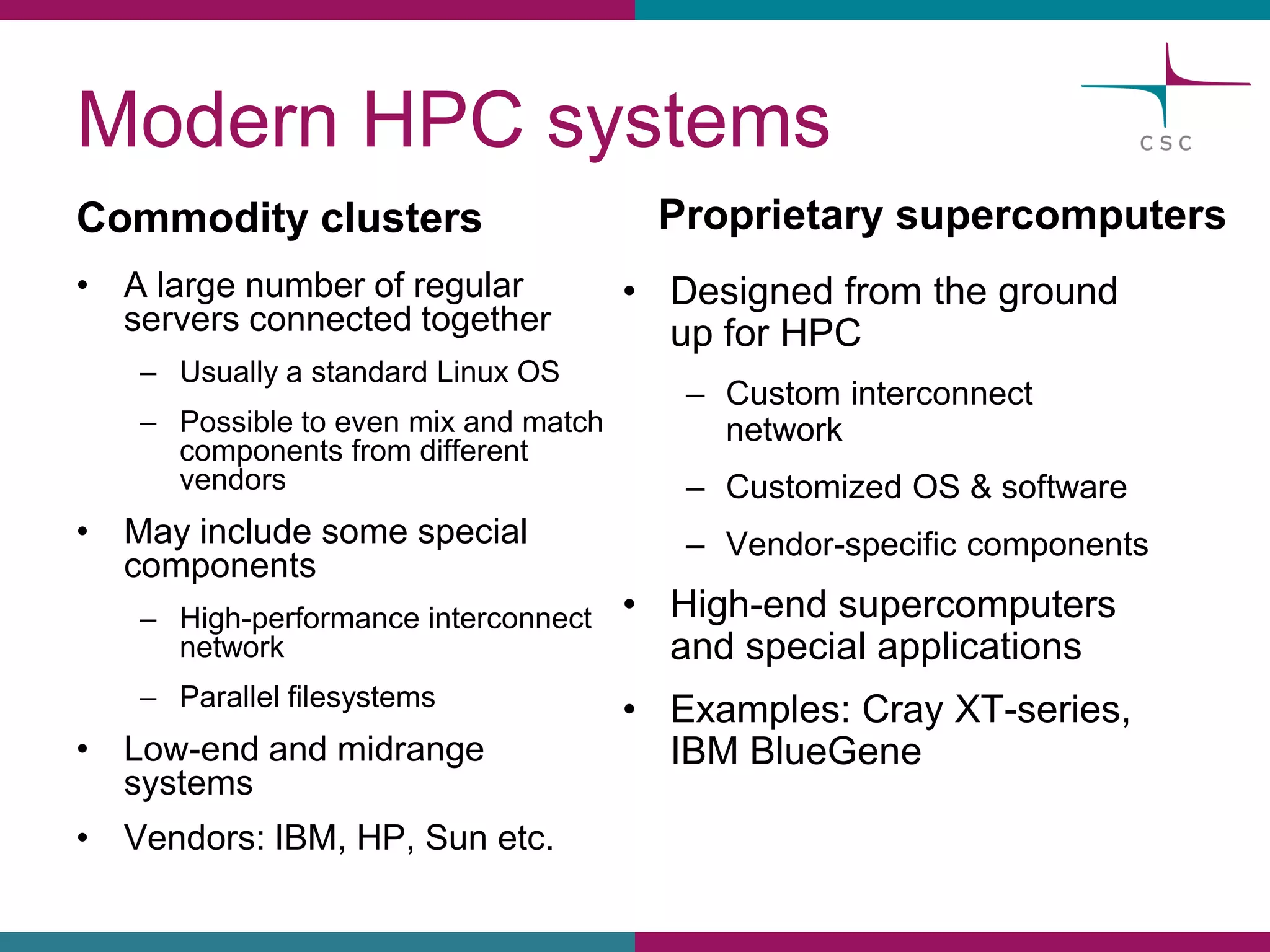
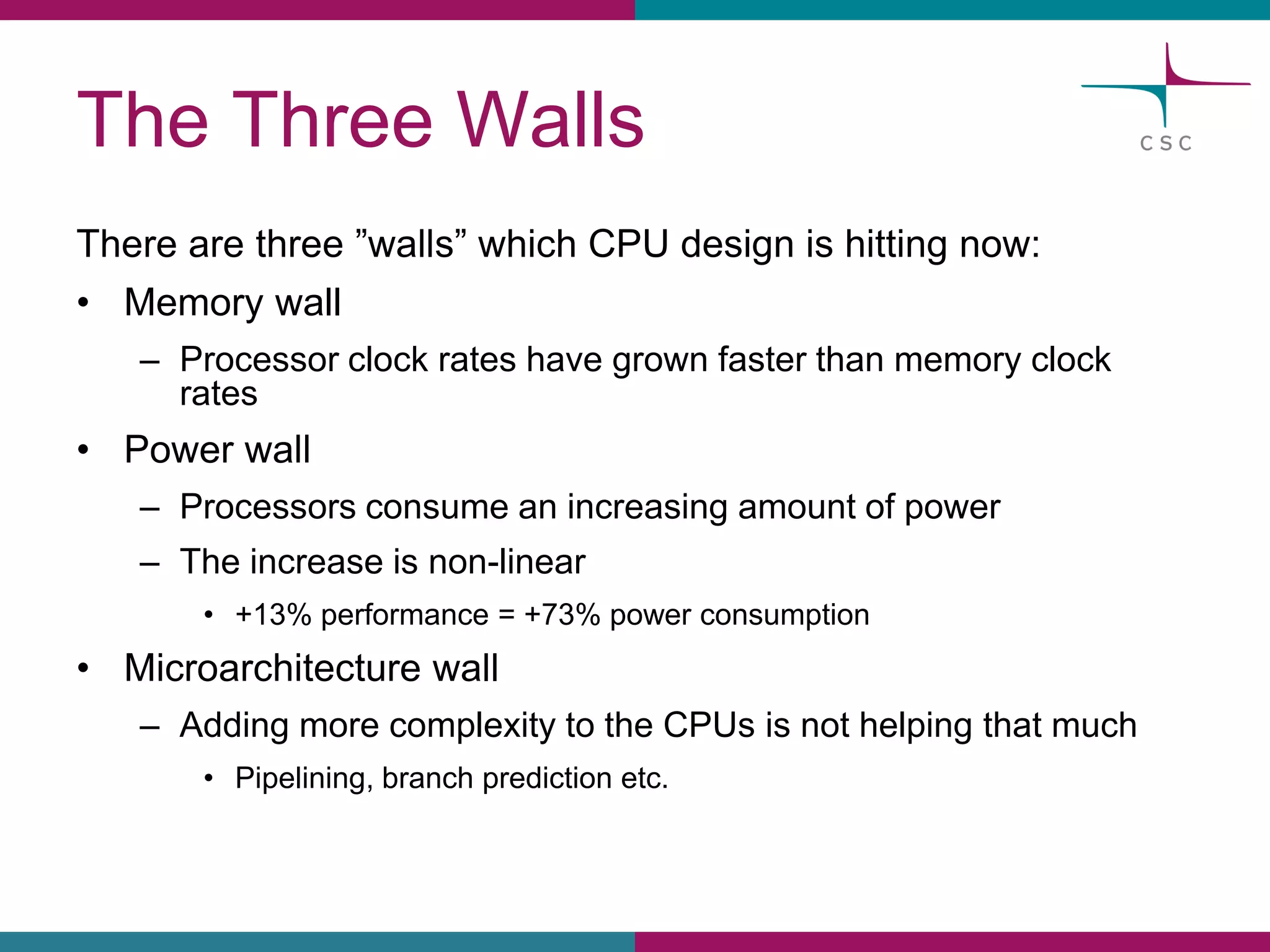
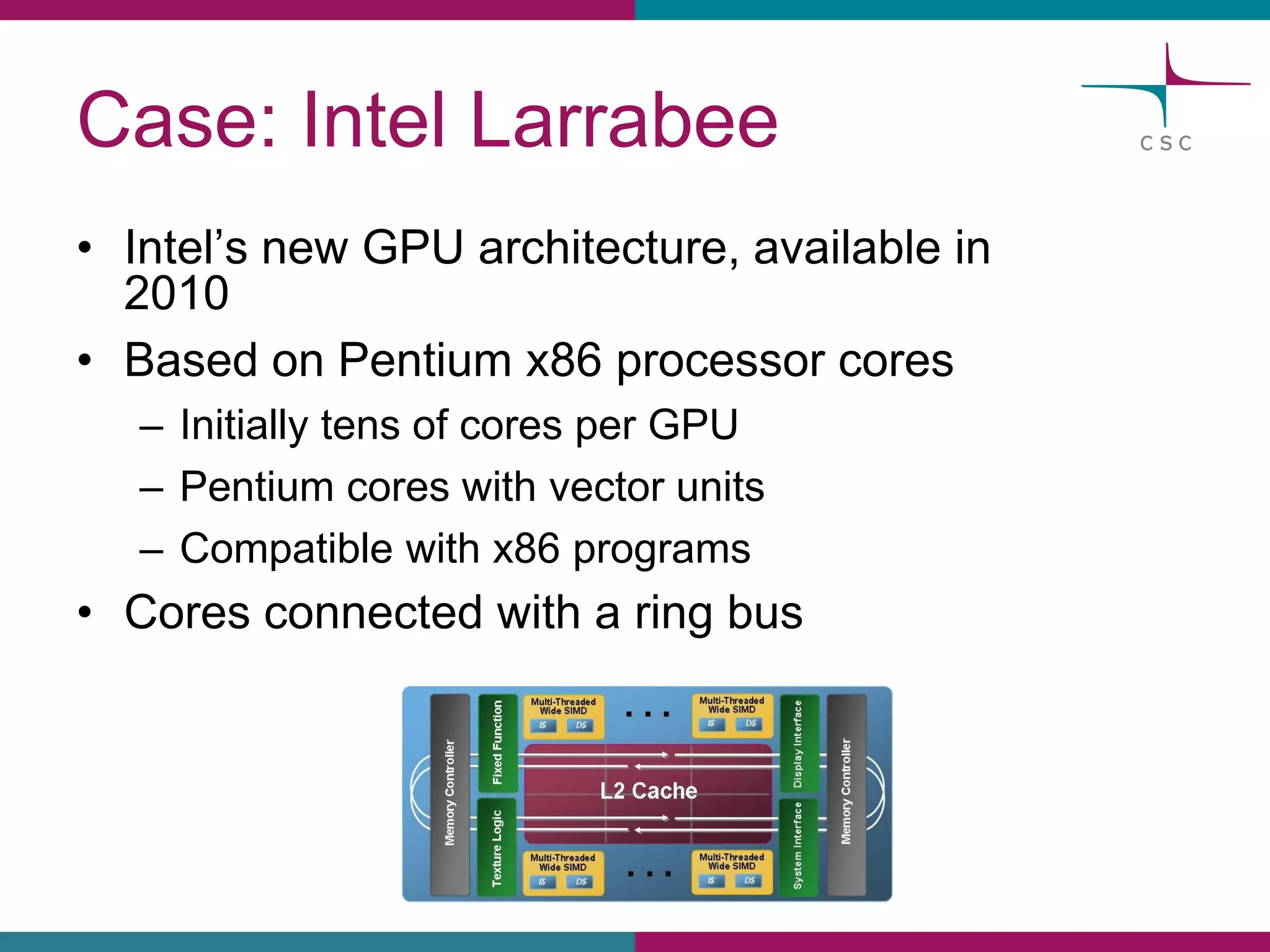
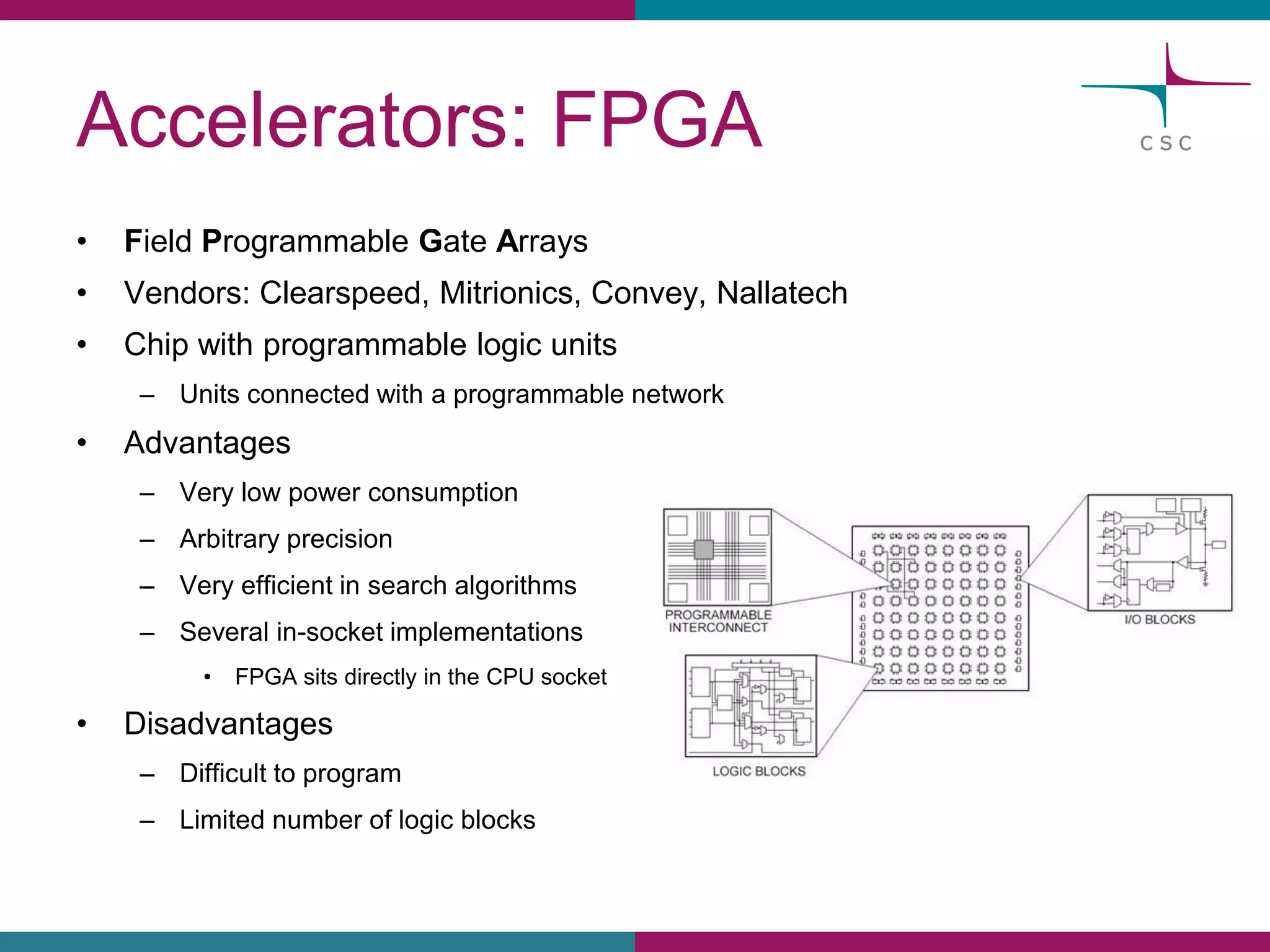
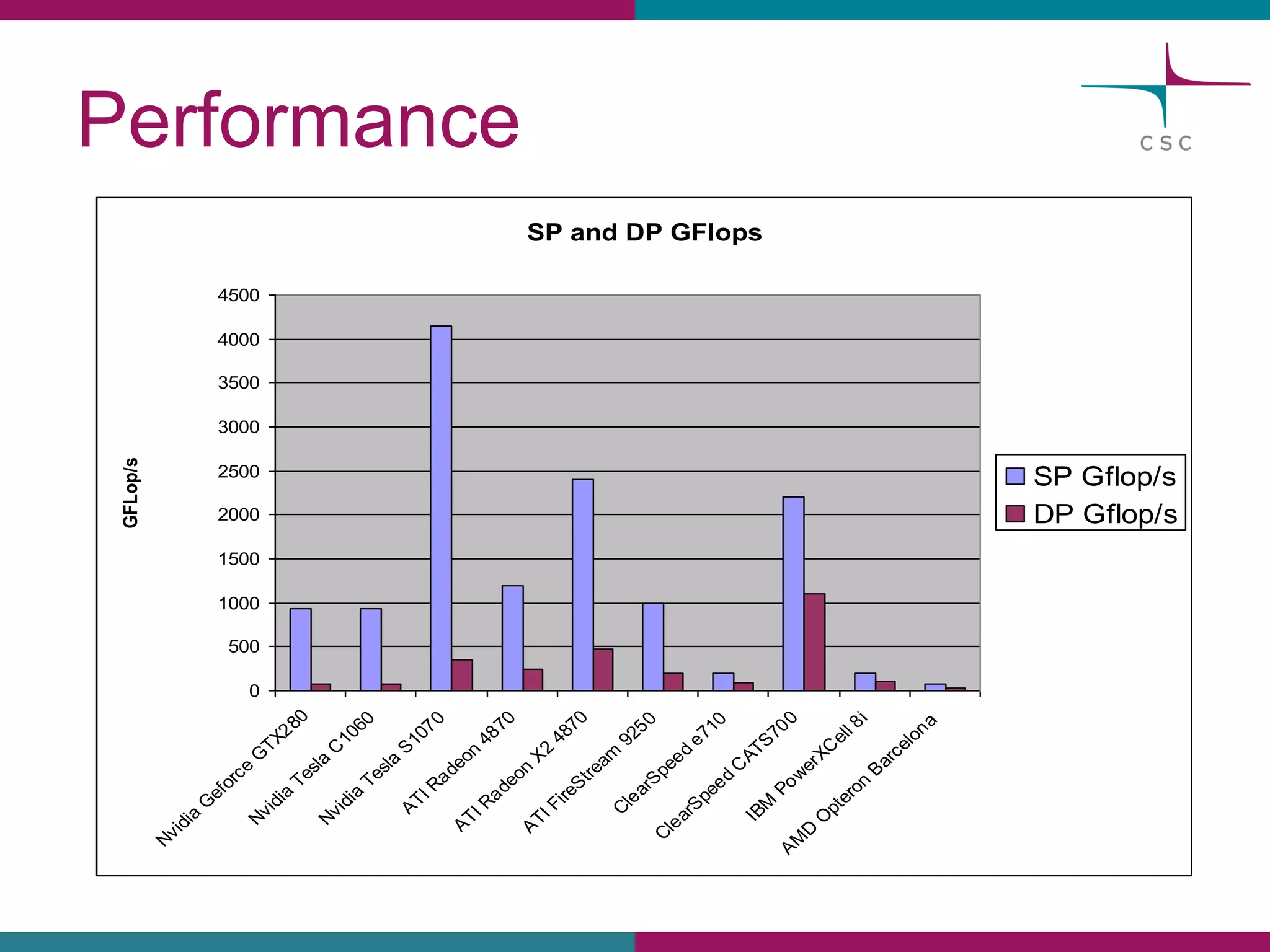
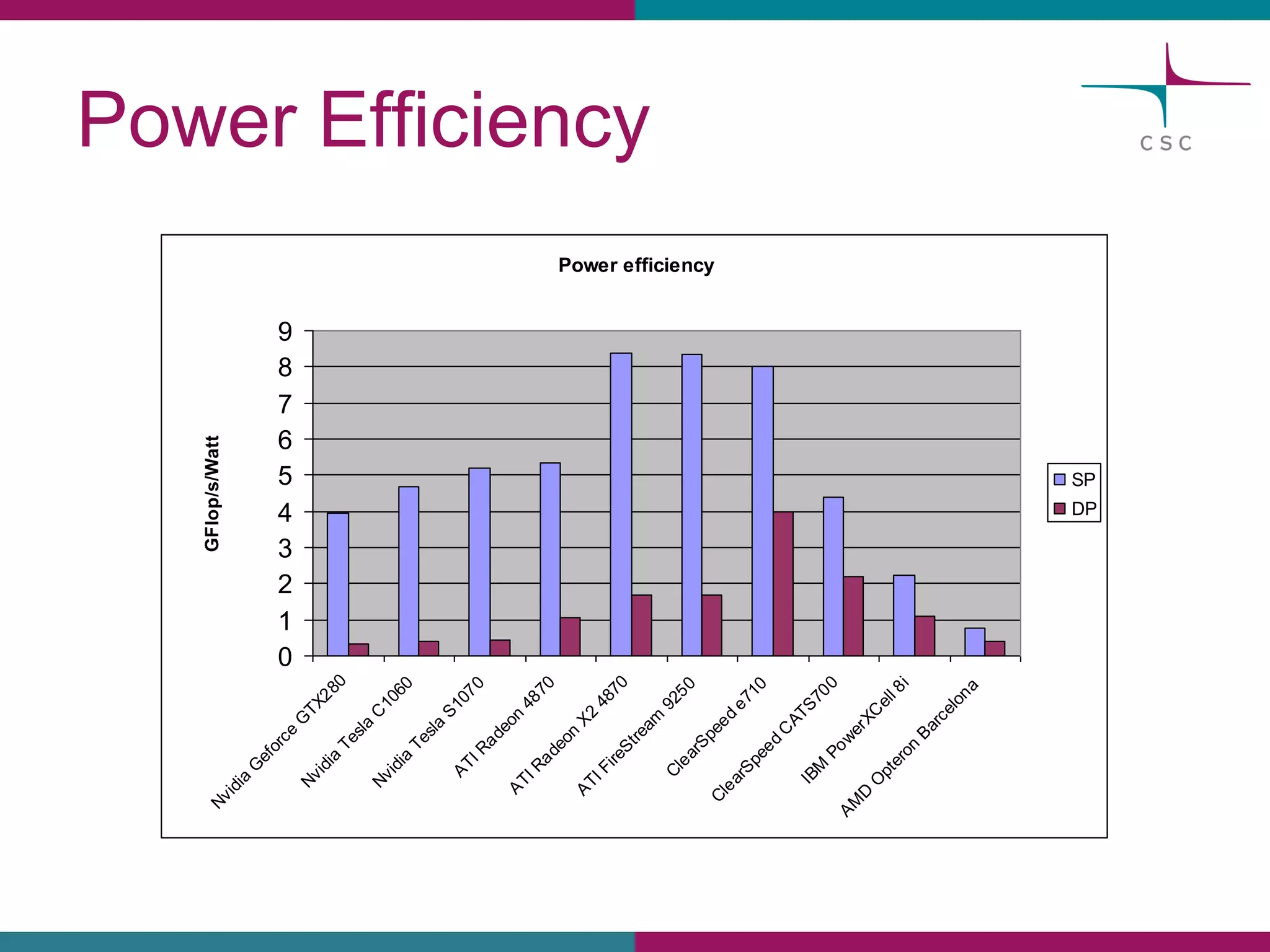
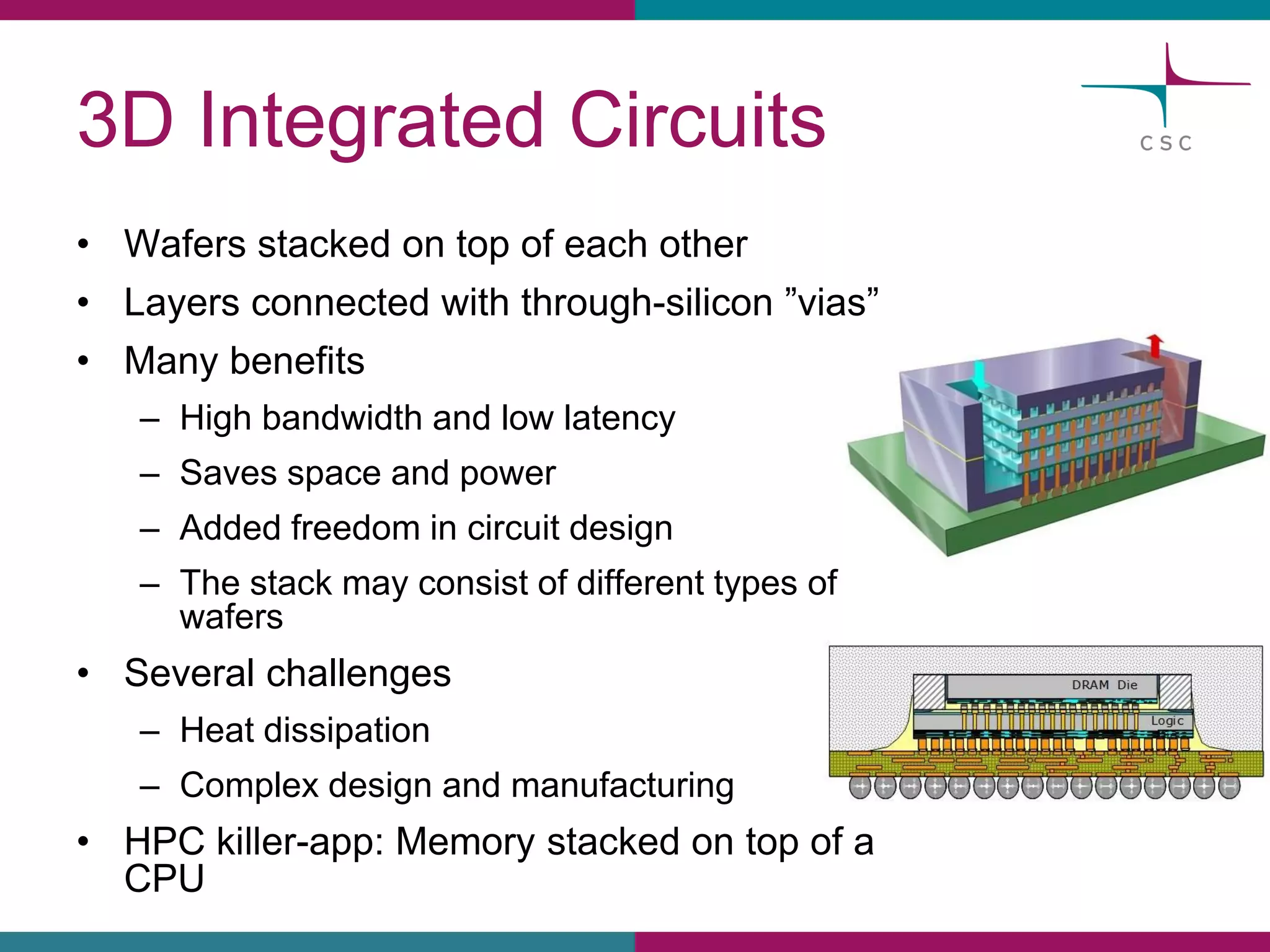
This document summarizes the state of high performance computing (HPC) and looks towards the future. It discusses how HPC systems are transitioning to use more commodity components like standard servers and processors. Reaching exascale computing power, or 1018 floating point operations per second, by 2020 will be very challenging and require major innovations in hardware, software, and programming models. Emerging technologies like accelerators, 3D chip stacking, and new memory types have potential to help overcome current barriers and improve the efficiency of future exascale systems.