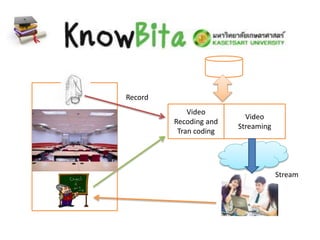
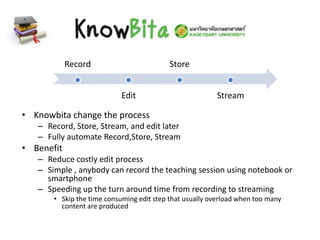
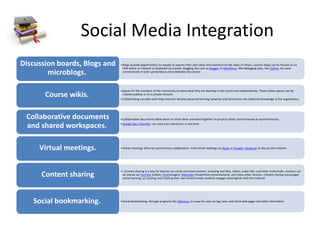
This document discusses various massive open online courses (MOOCs) platforms and providers. It begins by defining a MOOC as an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the web, using videos, readings, and problem sets along with interactive discussion forums. It notes that MOOCs are a recent development in distance education. It then discusses some key characteristics of MOOCs including being free, open to anyone with an internet connection, and having very large enrollments. The document goes on to summarize several major MOOC platforms including edX, Coursera, Udacity, Khan Academy, and a proposed local platform called Knowbita. It provides brief overviews of their approaches, features, and







![How EdX Works
• The platform uses online learning software that uses interactive
experiences.
• Each week, a new learning sequence is released in an edX course. The
learning sequence is composed of short (an average of 10 minutes each)
videos interspersed with active learning exercises where students can
immediately practice the concepts from the videos.
• They can include illustrations, often on a tablet or slide. There is a sidebar
showing the text; the student can follow the text, and scroll up or down it.
• The courses also often include tutorial videos that are similar to small-
group on-campus discussion groups, an online textbook, and an online
discussion forum where students can post and review questions and
comments to each other and teaching assistants.
• Where applicable, online laboratories are incorporated into the course.
For example, in edX's first MOOC—a circuits and electronics course—
students built virtual circuits in an online lab.[13]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mooc-140131083142-phpapp01/85/MOOC-Wunca-Talk-11-320.jpg)





![• All videos (hosted via YouTube) are available through Khan Academy's own website
– progress tracking, practice exercises, and a variety of tools for teachers in public schools.
– Logging into the site can be done via a Google or a Facebook account
– The material can also be accessed with the Khan Academy Modern UI application available free of
charge from Windows Store.
• Khan chose to avoid the standard format of a person standing by a whiteboard,
deciding instead to present the learning concepts as if "popping out of a darkened
universe and into one's mind with a voice out of nowhere" imitate when you're
watching a guy do a problem [while] thinking out loud.
• current content is mainly concerned with pre-college mathematics and physics,
Khan's long-term goal is to provide "tens of thousands of videos in pretty much
every subject”
• Khan Academy also provides a web-based exercise system
– generates problems for students based on skill level and performance.
– The exercise software is available as open source under the MIT license.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mooc-140131083142-phpapp01/85/MOOC-Wunca-Talk-19-320.jpg)