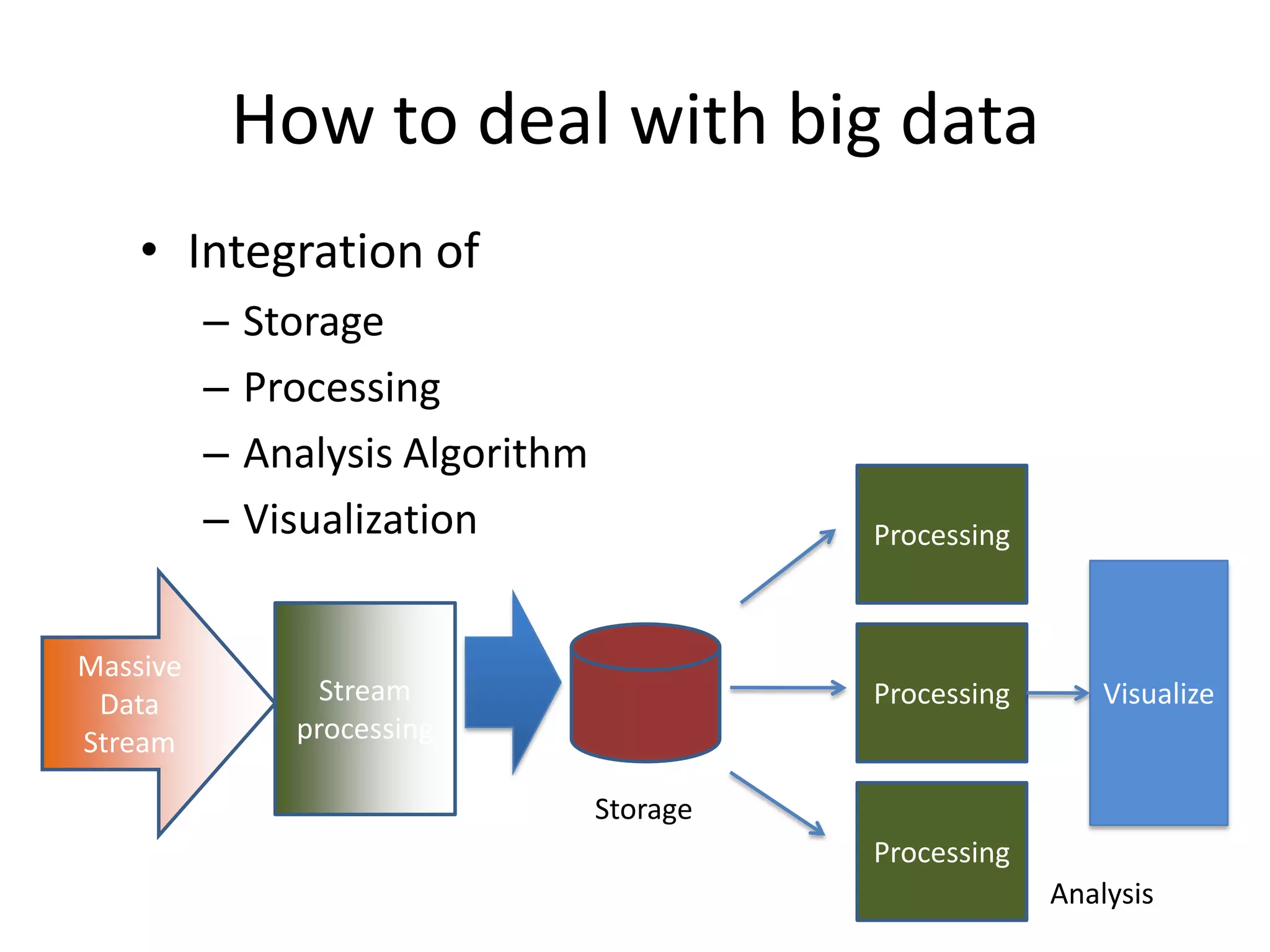
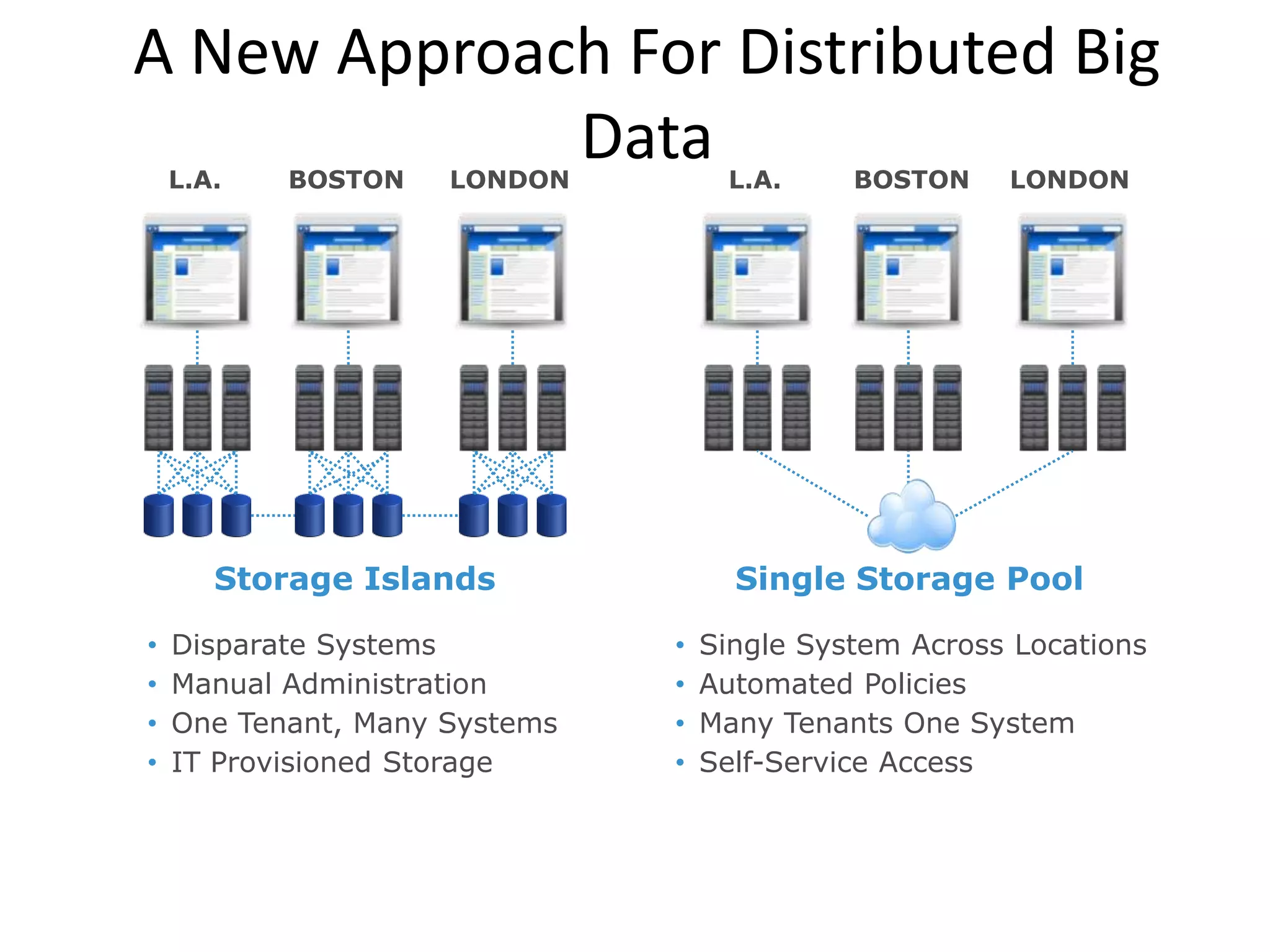
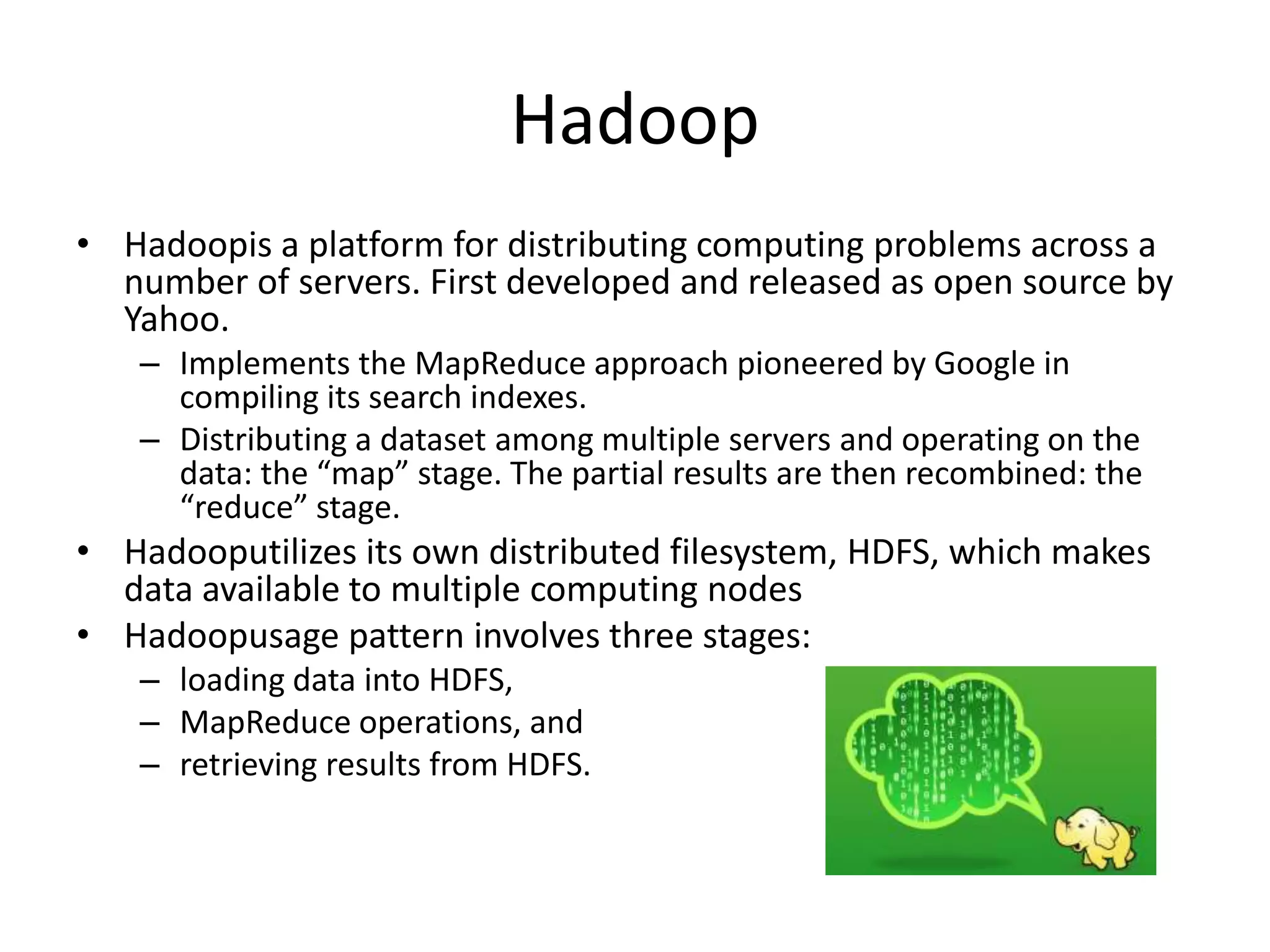
Big data refers to large volumes of diverse data that traditional database systems cannot effectively handle. With the rise of technologies like social media, sensors, and mobile devices, huge amounts of unstructured data are being generated every day. To gain insights from this "big data", alternative processing methods are needed. Hadoop is an open-source platform that can distribute data storage and processing across many servers to handle large datasets. Facebook uses Hadoop to store over 100 petabytes of user data and gain insights through analysis to improve user experience and target advertising. Organizations must prepare infrastructure like Hadoop to capture value from the growing "data tsunami" and enhance their business with big data analytics.