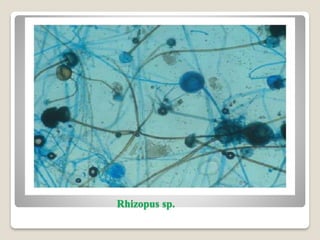
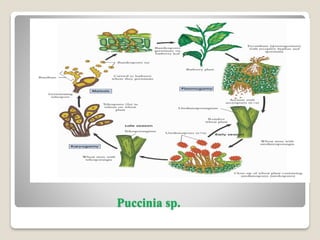
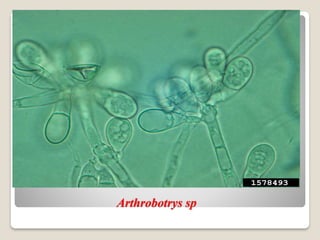
The document discusses the nutritional modes and classification of fungi, explaining that they are heterotrophic and require organic and inorganic materials for sustenance. It categorizes fungi into saprophytes, parasites, symbionts, and predacious fungi, each with distinct nutritional strategies and relationships with their hosts or environments. Additionally, it details specific mechanisms like absorptive structures and the cooperative interactions found in symbiotic relationships, such as lichens and mycorrhizae.