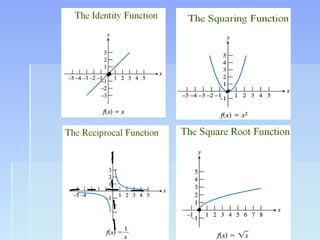
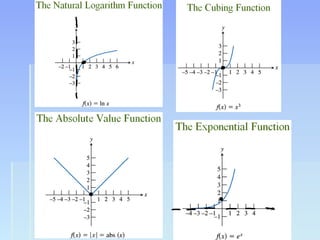
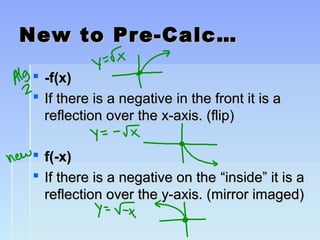
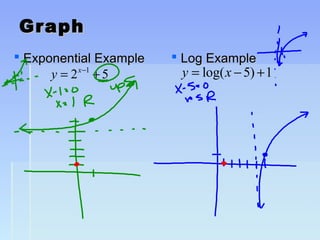
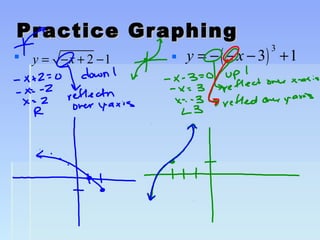
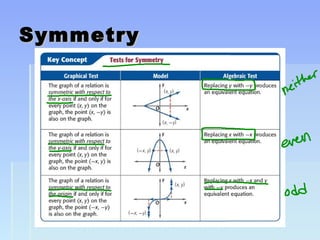
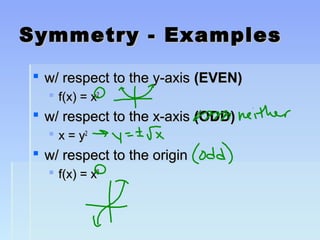
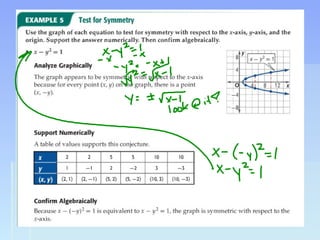
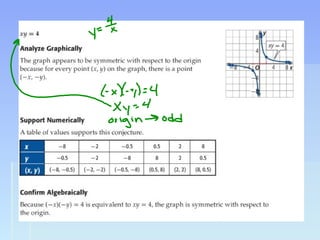
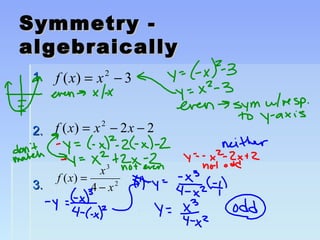
Unit 2 focuses on functions and their translations, reflections, and symmetries. Translations move the graph left/right or up/down, reflections flip or mirror the graph, and symmetries involve patterns that repeat on both sides of an axis. The document provides examples of translating and reflecting common parent functions like exponential and logarithmic functions. It also discusses symmetry in functions with respect to the y-axis (even functions), x-axis (odd functions), and origin. Homework problems are assigned from the textbook involving graphing functions and describing end behavior using limits.