Embed presentation
Download to read offline



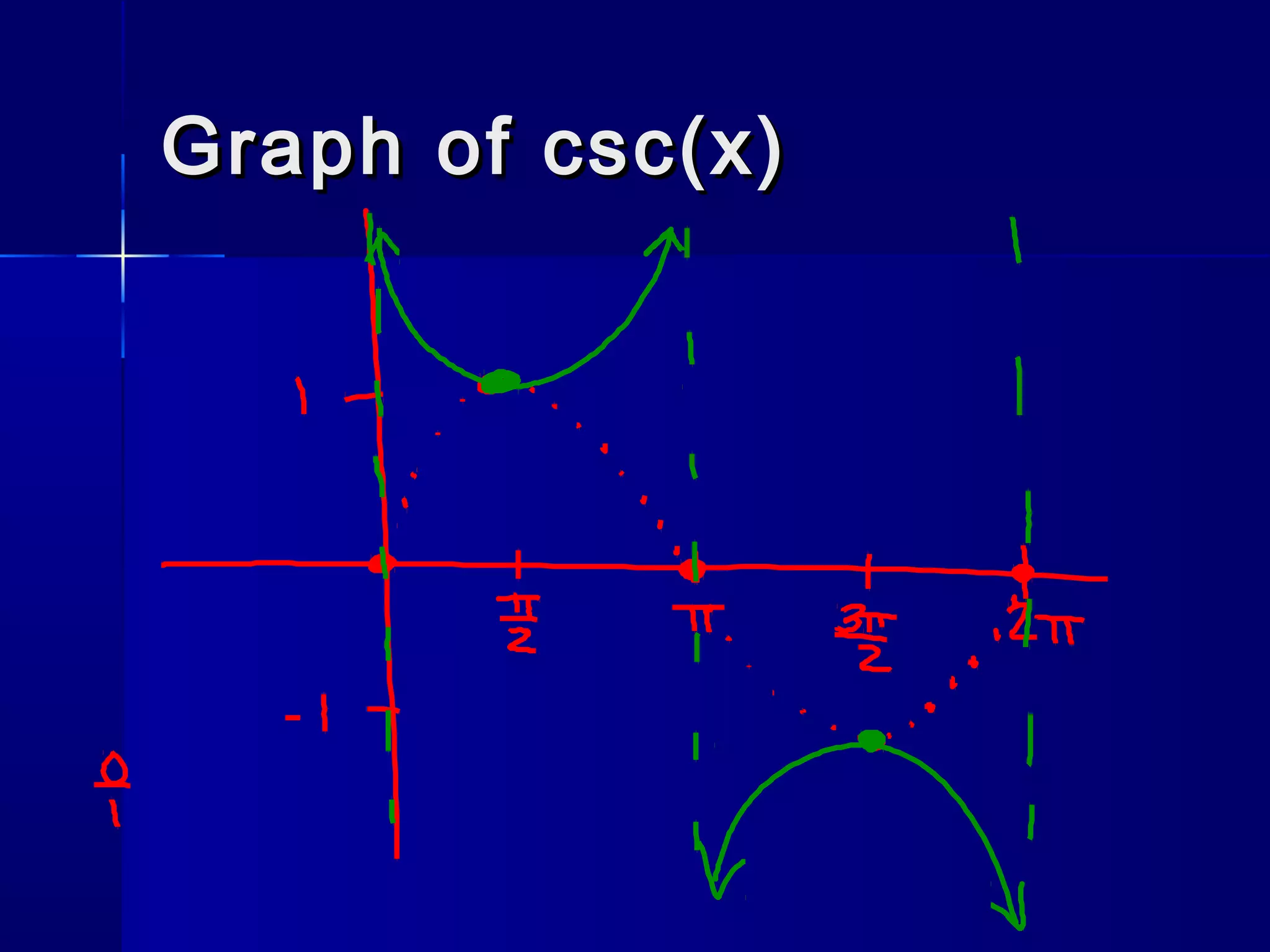
![csc (x)csc (x)
Flip of sin (x)Flip of sin (x)
PropertiesProperties
– Period: 2Period: 2
– Domain: all real numbers except nDomain: all real numbers except n
– Range: (-Range: (-∞, -1] [1, ∞)∞, -1] [1, ∞)
– No x-intNo x-int
– No y-intNo y-int
– y=1 wheny=1 when
– y=-1 wheny=-1 when
π
π
nx π
π
2
2
3
+=
nx ππ 2
2
3
+=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-161103132924/75/4-5-sec-and-csc-worked-3rd-5-2048.jpg)
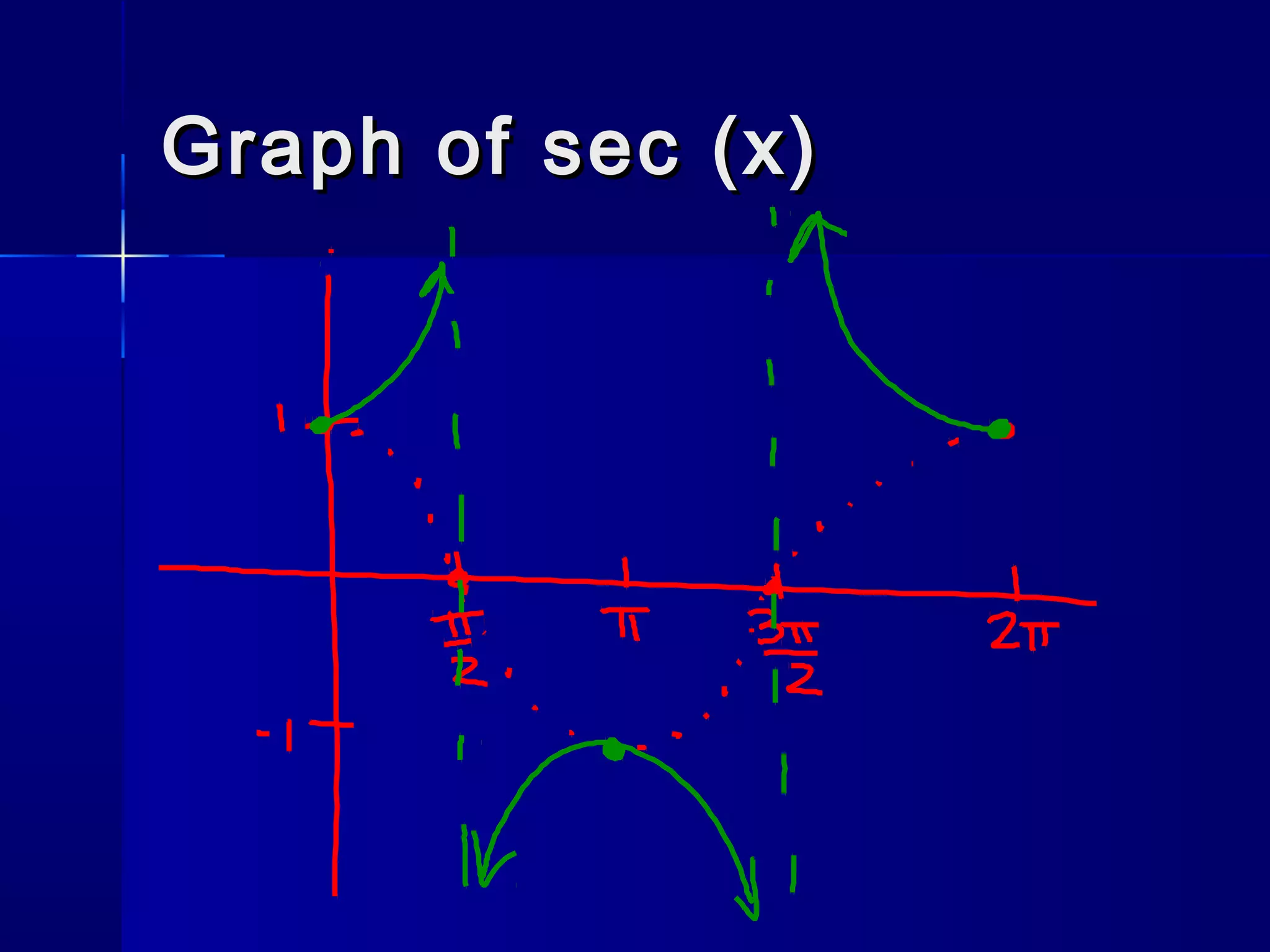
![sec (x)sec (x)
Flip of cos (x)Flip of cos (x)
PropertiesProperties
– Period: 2Period: 2
– Domain: all real numbers except n, n is oddDomain: all real numbers except n, n is odd
– Range: (-Range: (-∞, -1] [1, ∞)∞, -1] [1, ∞)
– No x-intNo x-int
– y-int = 1y-int = 1
– Asymptotes when , n is oddAsymptotes when , n is odd
– y=1 when , n is eveny=1 when , n is even
– y=-1 when , n is oddy=-1 when , n is odd
π
2
π
nx π=
nx π=
2
n
x
π
=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-161103132924/75/4-5-sec-and-csc-worked-3rd-9-2048.jpg)
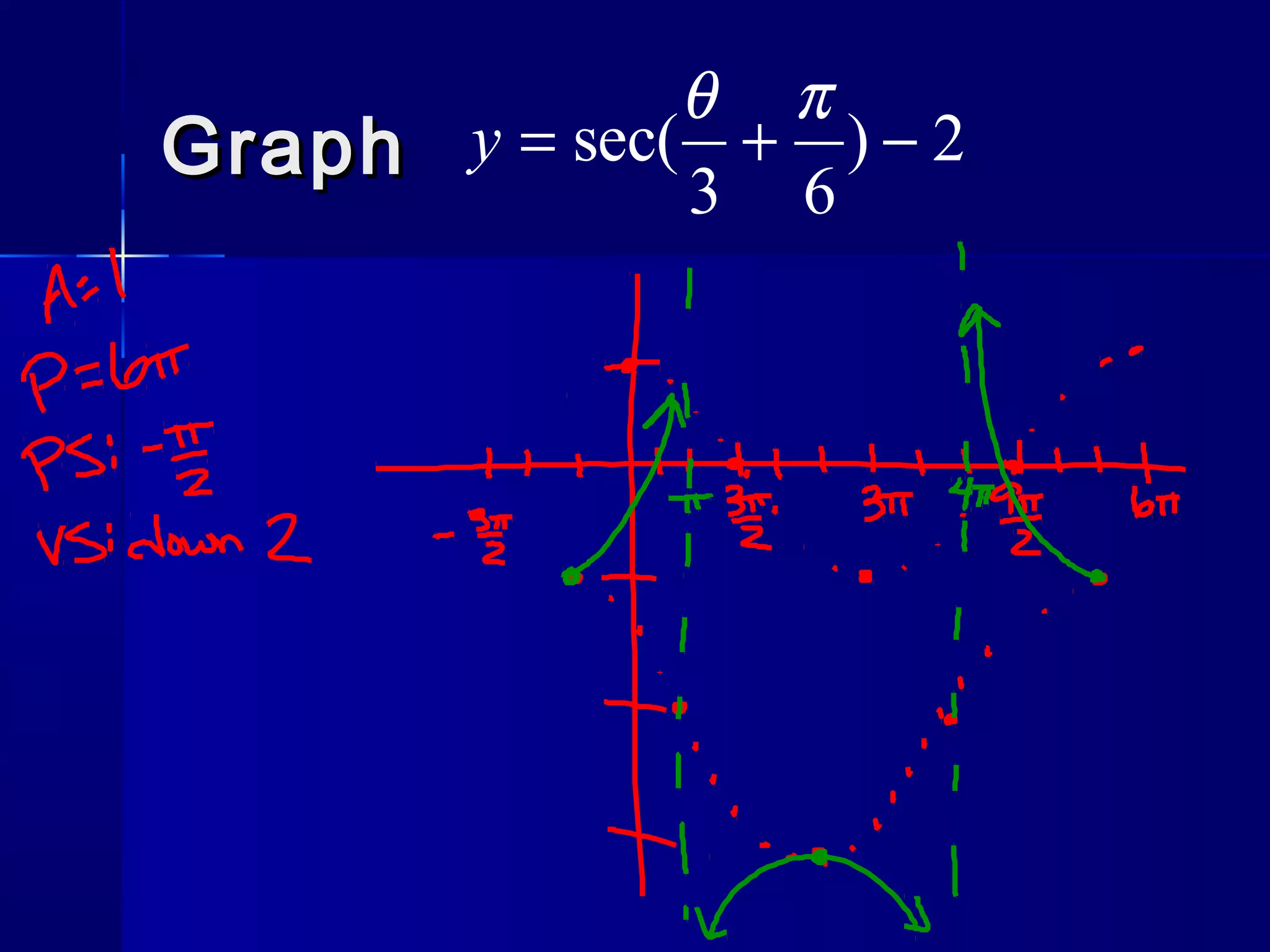
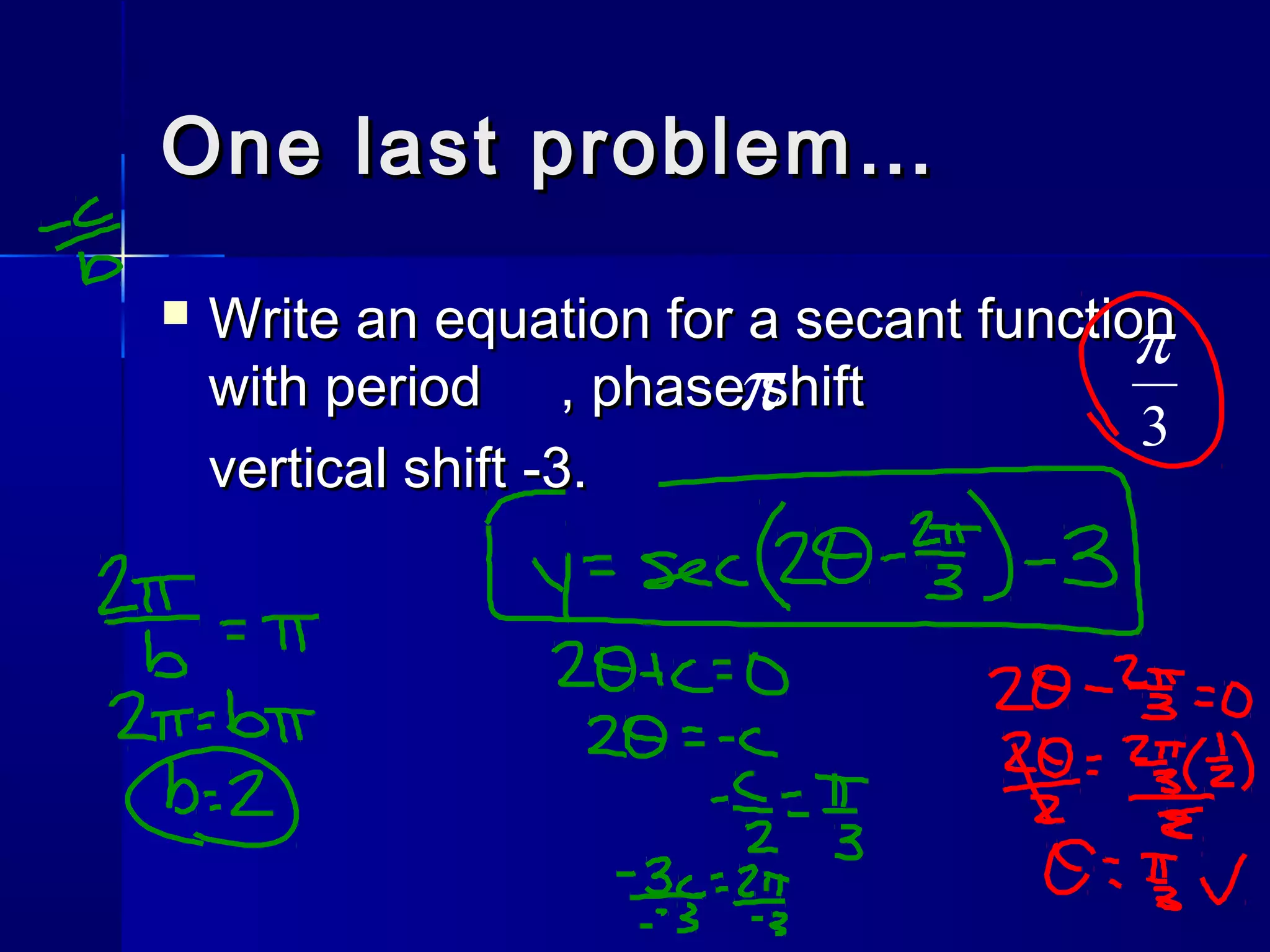

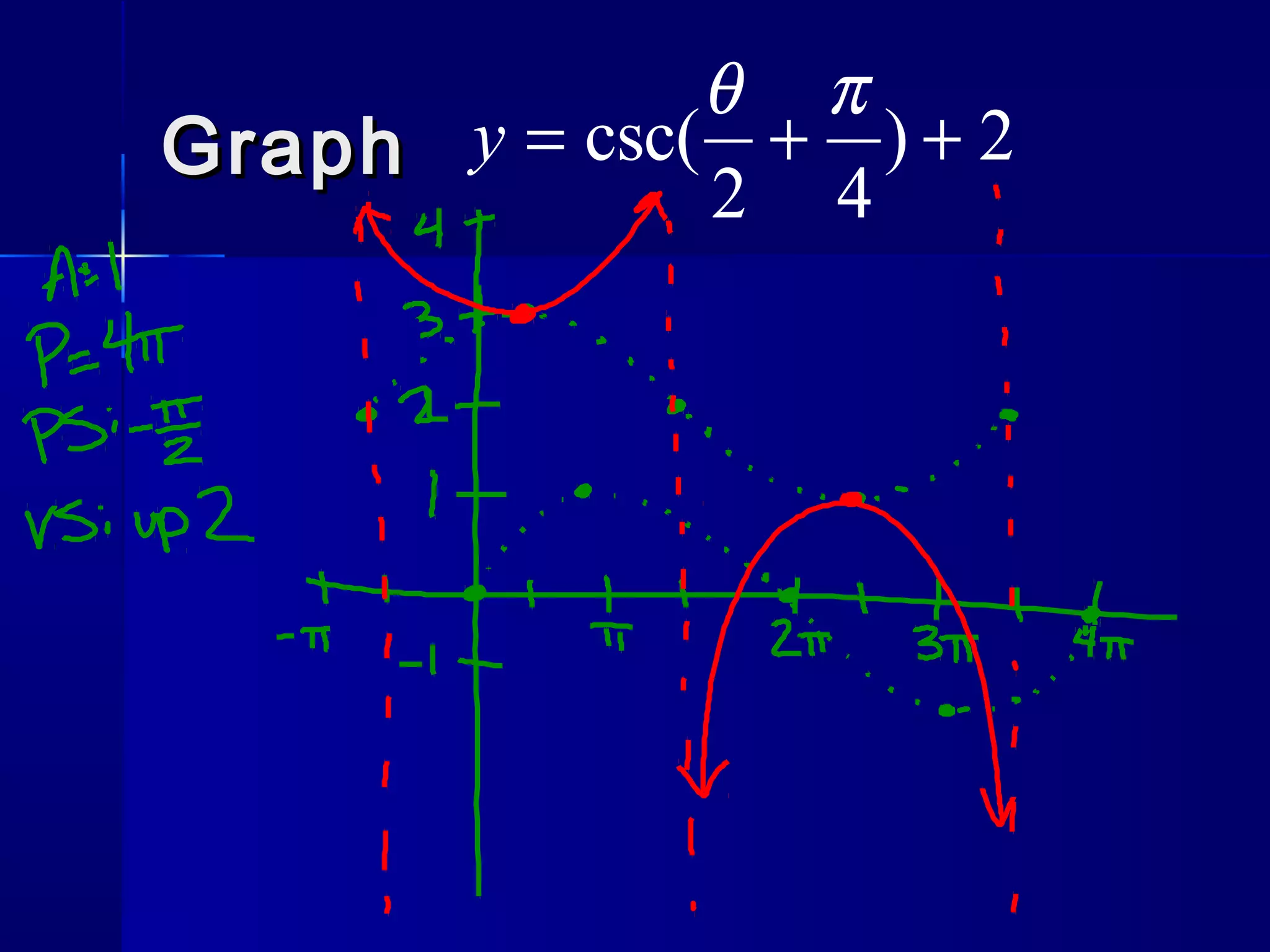
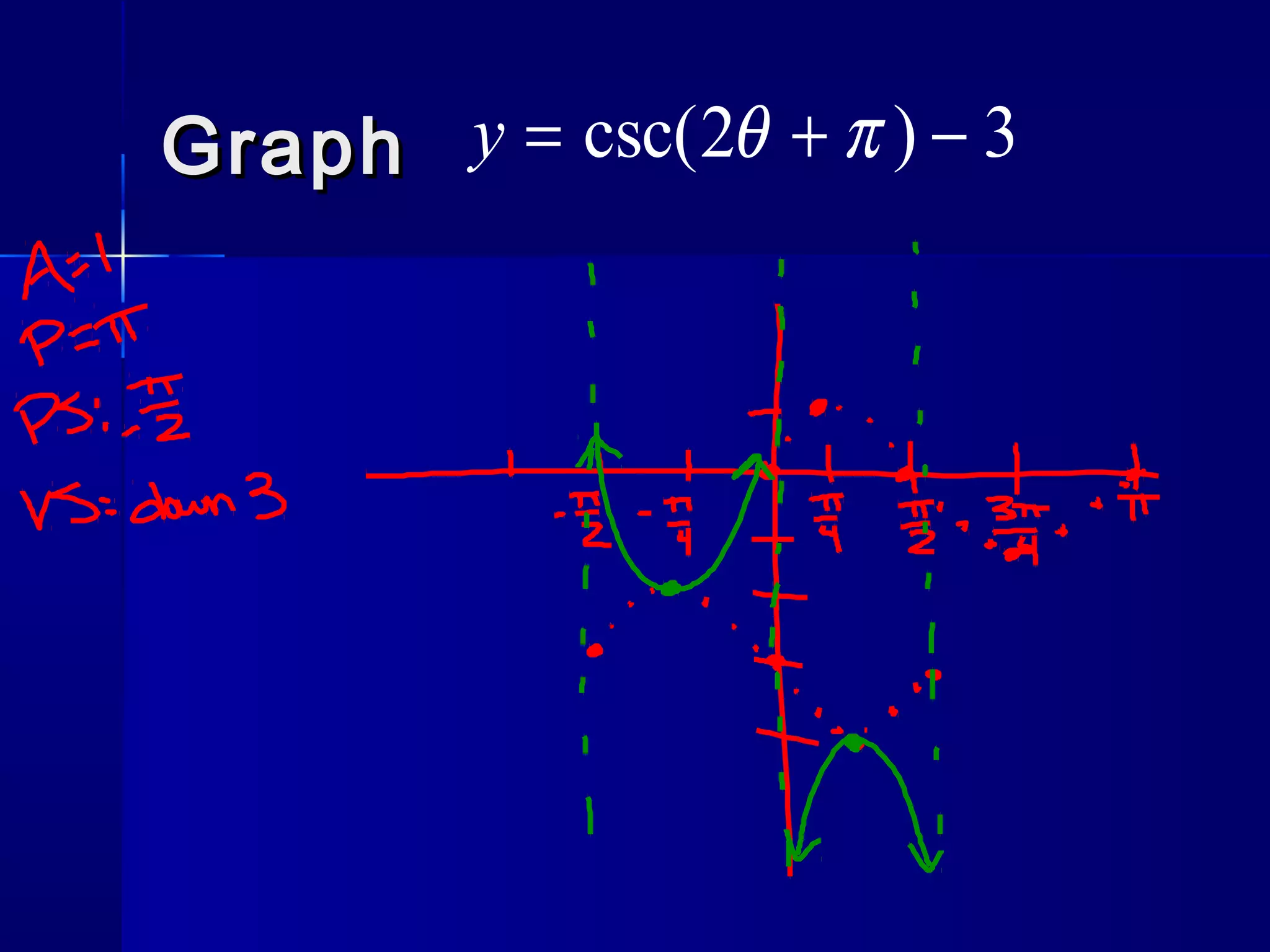
This document discusses the trigonometric functions csc(x) and sec(x). It provides properties of each function, including their period, domain, range, and any asymptotes or x-intercepts. Examples of graphs are shown for csc(x) with phase shifts of pi/2 and -pi/2. Properties of sec(x) are also described. The document concludes by assigning a worksheet on csc(x) and sec(x) and posing a problem to write an equation for a secant function with a given period, phase shift, and vertical shift.



![csc (x)csc (x)
Flip of sin (x)Flip of sin (x)
PropertiesProperties
– Period: 2Period: 2
– Domain: all real numbers except nDomain: all real numbers except n
– Range: (-Range: (-∞, -1] [1, ∞)∞, -1] [1, ∞)
– No x-intNo x-int
– No y-intNo y-int
– y=1 wheny=1 when
– y=-1 wheny=-1 when
π
π
nx π
π
2
2
3
+=
nx ππ 2
2
3
+=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-161103132924/75/4-5-sec-and-csc-worked-3rd-5-2048.jpg)



![sec (x)sec (x)
Flip of cos (x)Flip of cos (x)
PropertiesProperties
– Period: 2Period: 2
– Domain: all real numbers except n, n is oddDomain: all real numbers except n, n is odd
– Range: (-Range: (-∞, -1] [1, ∞)∞, -1] [1, ∞)
– No x-intNo x-int
– y-int = 1y-int = 1
– Asymptotes when , n is oddAsymptotes when , n is odd
– y=1 when , n is eveny=1 when , n is even
– y=-1 when , n is oddy=-1 when , n is odd
π
2
π
nx π=
nx π=
2
n
x
π
=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-161103132924/75/4-5-sec-and-csc-worked-3rd-9-2048.jpg)



