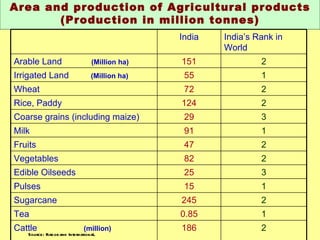
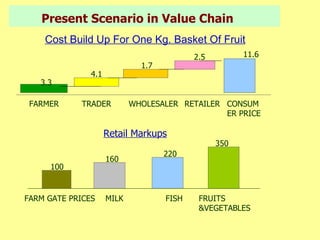
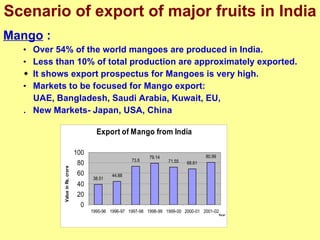
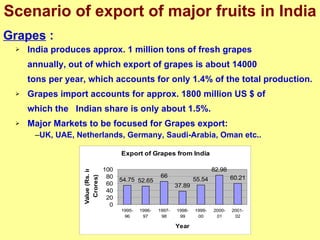
The document discusses India's advantages in agriculture such as diverse climates and abundant arable land, and its leading global production of many fruits and vegetables. It outlines issues with the current supply chain such as fragmented land holdings and lack of infrastructure and post-harvest technology. It proposes solutions like contract farming, cluster approaches, and implementing supply chain management practices to improve competitiveness through quality, cost reductions, and supplying products just in time.
![Development of Supply Chain for Fruit and Vegetable Industry Dr. D. N. Kulkarni President – Agri Food Jain Irrigation [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fruit-veg-111218235526-phpapp01/75/Fruit-veg-1-2048.jpg)