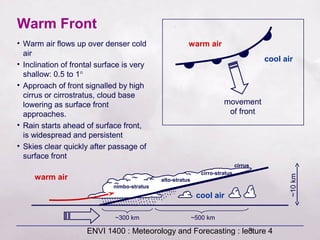
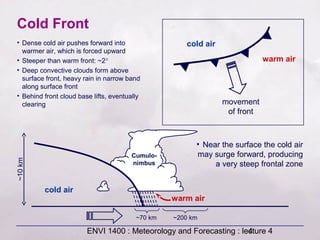
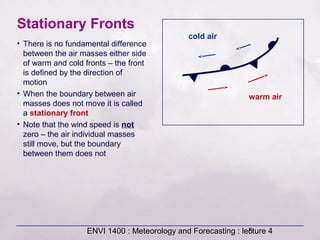
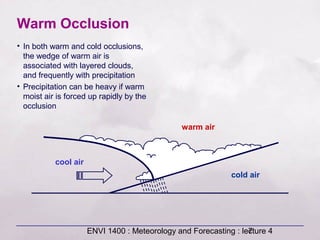
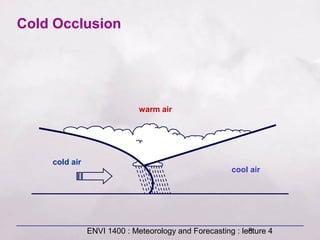
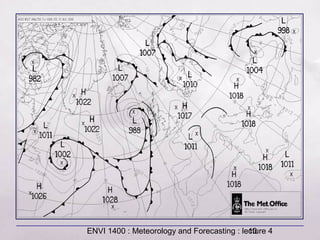
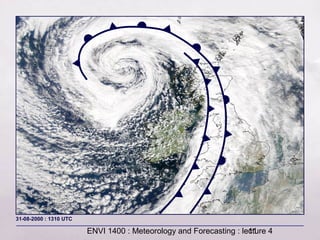
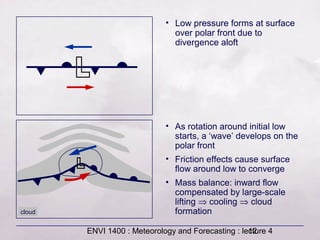
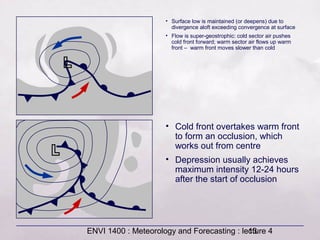
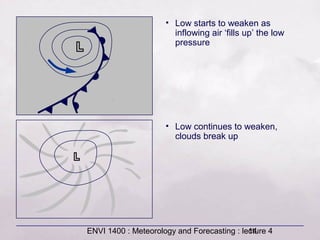
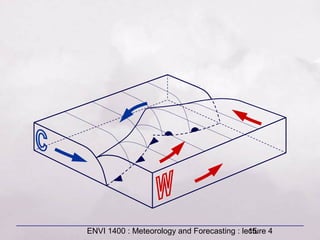
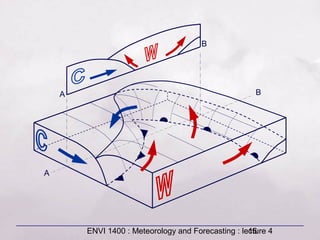
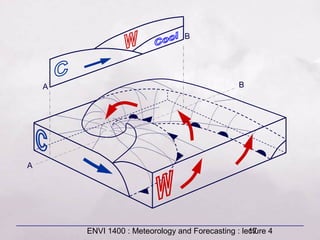
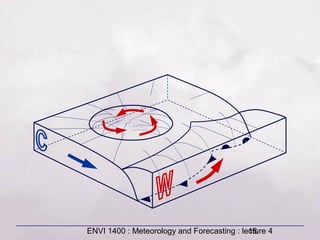
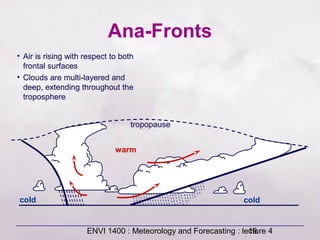
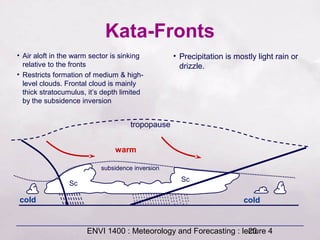
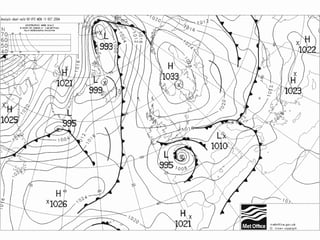
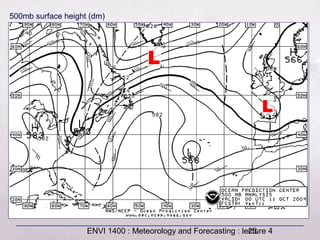
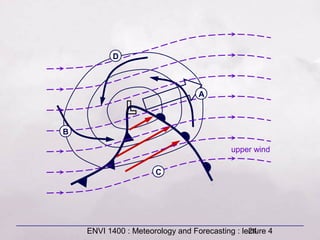
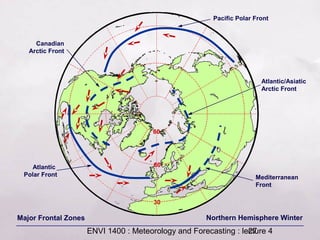
This document provides an overview of fronts and mid-latitude cyclones. It discusses the different types of fronts including warm fronts, cold fronts, stationary fronts and occluded fronts. It describes how mid-latitude cyclones form along polar fronts and the associated weather patterns. Key features of mid-latitude cyclones include the progression from warm to cold to occluded fronts as the cyclone evolves over time, bringing changing weather conditions to affected regions.