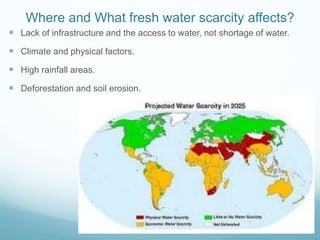
Fresh water scarcity is a growing problem, particularly in developing countries, due to increasing population and climate change factors like drought. It affects access to education, health, food, and contributes to poverty. In countries like Tanzania and Kenya, lack of infrastructure and sanitation leads to water-borne diseases. Solutions include reducing water usage, helping rural communities access clean water, and developing technologies like desalination. International cooperation via treaties and development goals also aims to address this critical issue.