Freight transport systems can be summarized as follows:
1) Freight transport involves the movement of goods via various modes including rail, road, water, air and pipeline. Infrastructure such as roads, railways, ports and terminals enable the movement of goods.
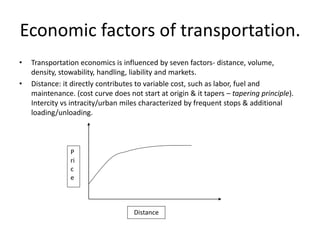
2) Key economic factors that influence transportation costs are distance, volume, density, stowability, handling requirements, liability and market conditions. Transportation costs are also impacted by variable costs, fixed costs and common costs.
3) Rates and pricing strategies aim to determine the most cost-effective way to transport goods considering classification of products, commodity specific rates, and exceptions. Documentation such as bills of lading are also used to track shipments and