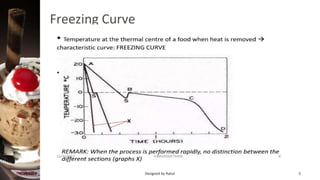
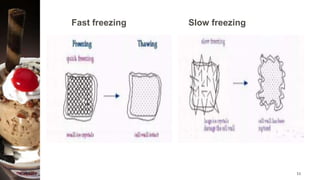
Freezing is a method of food preservation where heat is removed from food, lowering its temperature below its freezing point to solidify water inside it. There are two main types of freezing - slow freezing, which forms large ice crystals and damages cells, and fast freezing, which forms small ice crystals with minimal damage. Freezing aims to preserve taste, texture, nutrition and extend shelf life by slowing microbial growth and chemical reactions. Common freezing methods include air blast freezing, belt freezing, plate freezing and cryogenic freezing using liquid nitrogen. While freezing prevents spoilage, it can cause some quality losses through changes in volume, concentration, protein denaturation and vitamin loss.