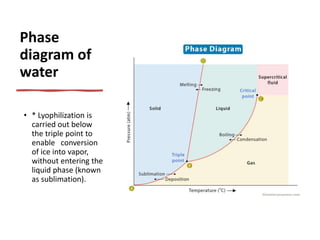
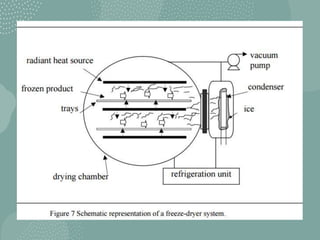
Freeze drying, also called lyophilization, is a process of removing water from materials by freezing them and then reducing pressure to allow sublimation of ice directly to water vapor. It is carried out below the triple point of water to enable direct sublimation without passing through the liquid phase. Freeze drying helps preserve nutrients, texture, flavor and appearance of foods while extending shelf life. It results in lightweight, ready-to-use products that are easy to store, transport and reconstitute.