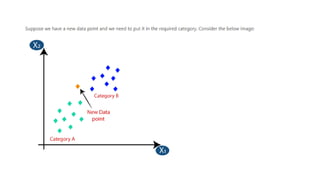
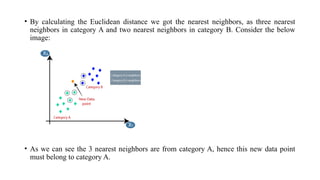
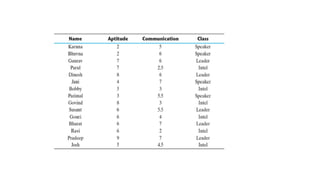
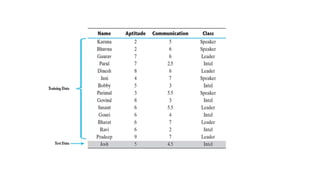
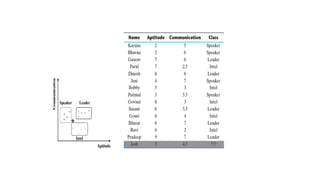
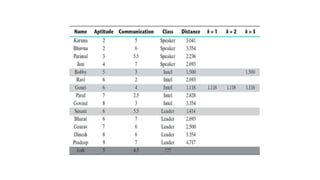
The k-nearest neighbour (k-NN) algorithm is a simple yet powerful supervised machine learning technique used for classification and regression that classifies new data points based on their similarity to existing data. It operates by storing the training data and classifying new entries based on the majority class among the k-nearest neighbors, using distance measures like Euclidean distance. While it is easy to understand and effective in certain scenarios, k-NN is considered a lazy learner as it doesn't create a predictive model and relies heavily on the training data, which can affect its performance and efficiency.