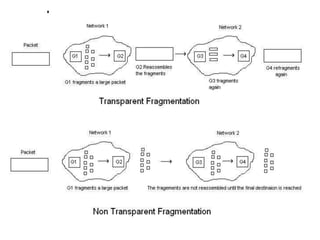
Fragmentation is the process of splitting large packets into smaller fragments to accommodate networks with smaller maximum transmission unit sizes. This allows packets to travel across multiple networks without being dropped. There are two types of fragmentation: transparent, where fragments are reassembled at exit gateways, and non-transparent, where fragments are treated as individual packets and reassembled only at the destination host, as used in the Internet Protocol. Key challenges include ensuring all fragments are received for reassembly and minimizing overhead from fragmenting and reassembling packets.