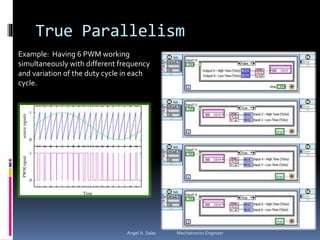
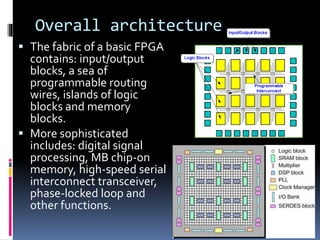
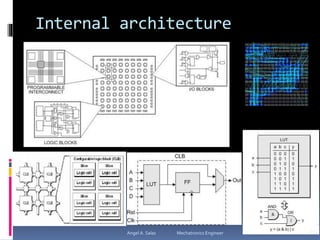
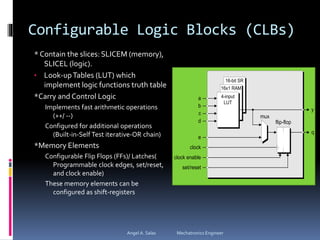
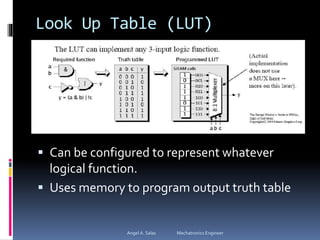
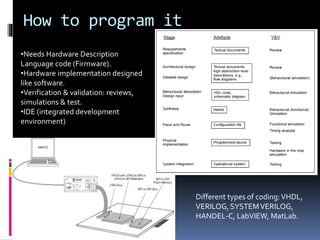
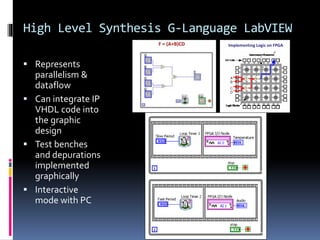
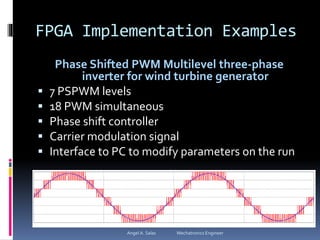
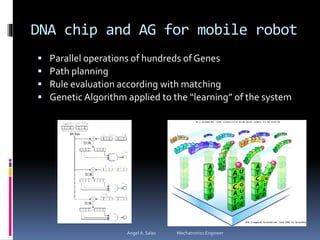
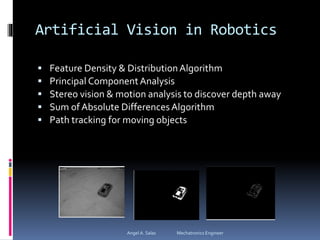
An FPGA (field programmable gate array) is a reprogrammable silicon chip that can be configured to perform different logic functions. It allows for personalized hardware design without physical chips and wiring. FPGAs offer parallel processing capabilities across different sections of the chip. They contain programmable logic blocks and routing resources that can be configured using hardware description languages. FPGAs provide advantages over processors like true parallel processing, high reliability, maintenance flexibility, and performance that exceeds DSPs. They are useful for applications like signal processing, robotics, and prototyping.