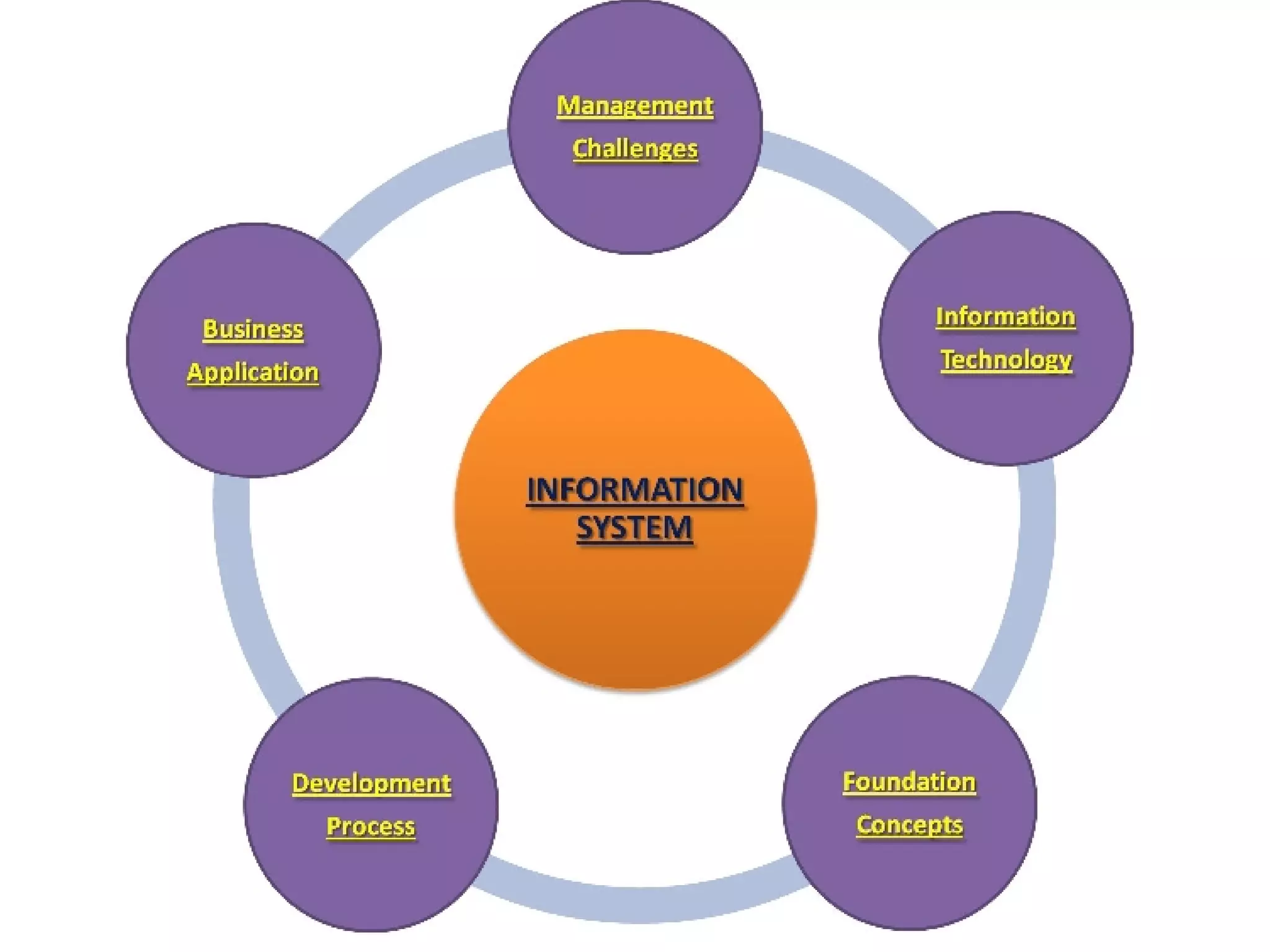
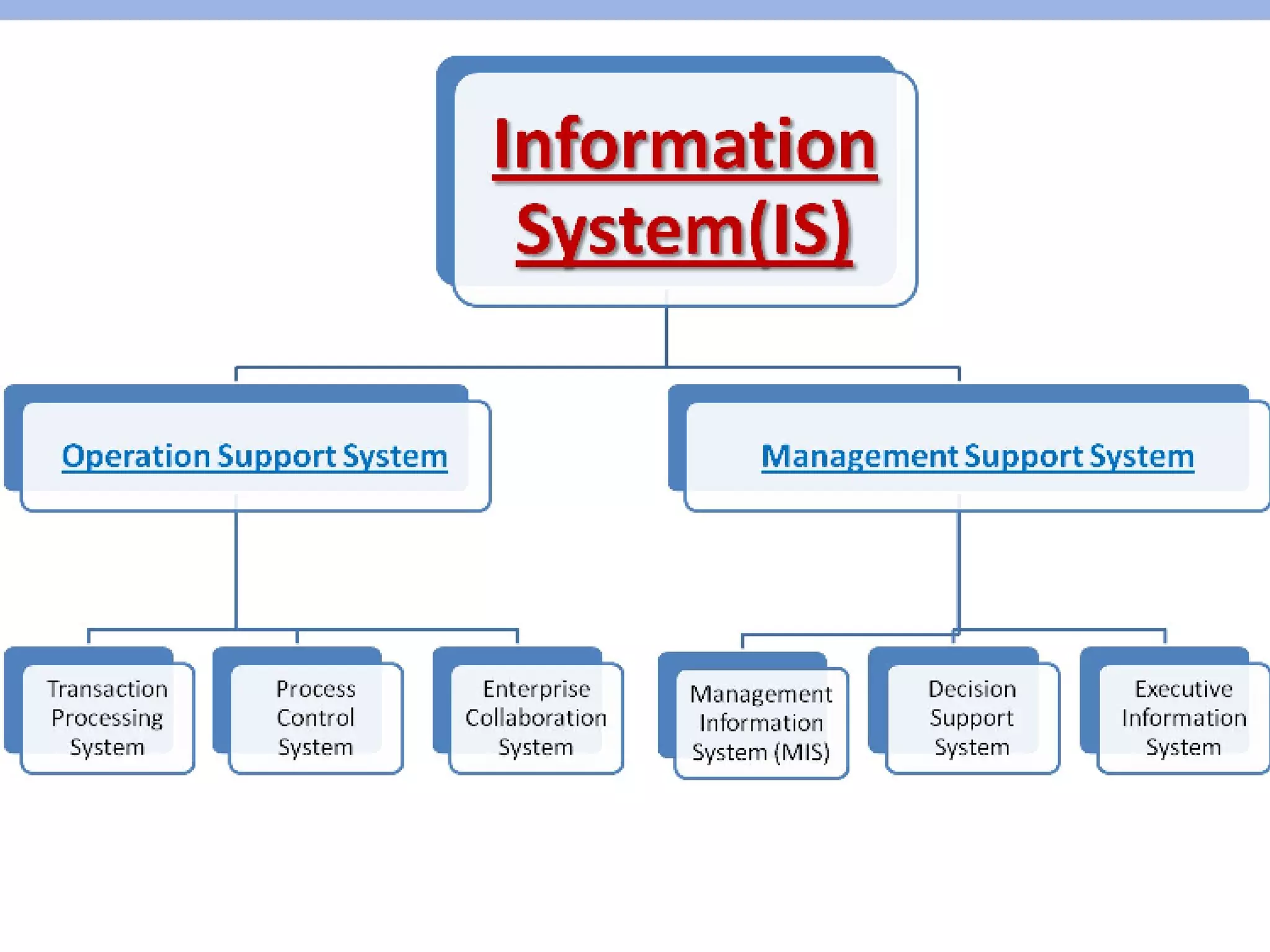
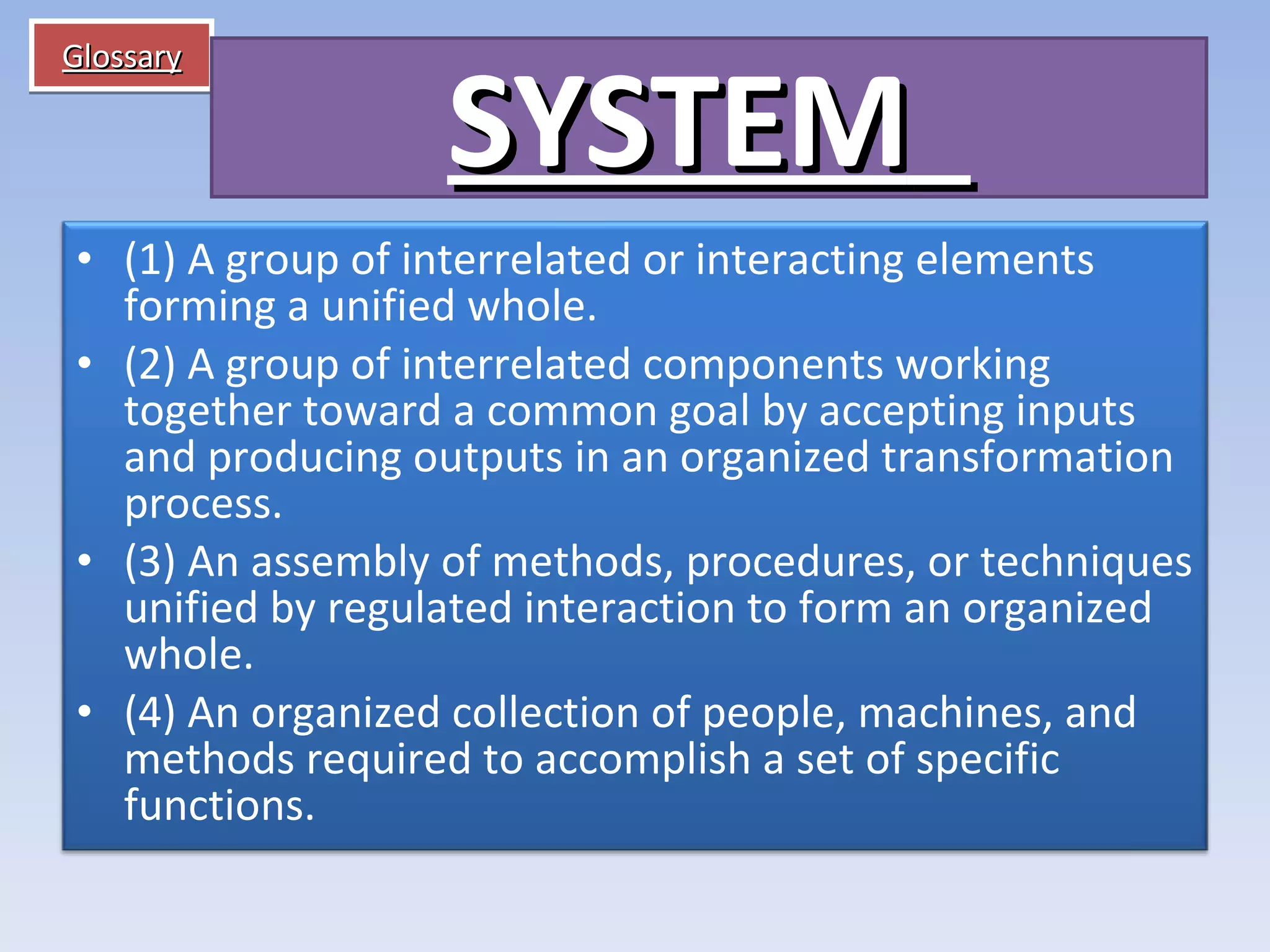
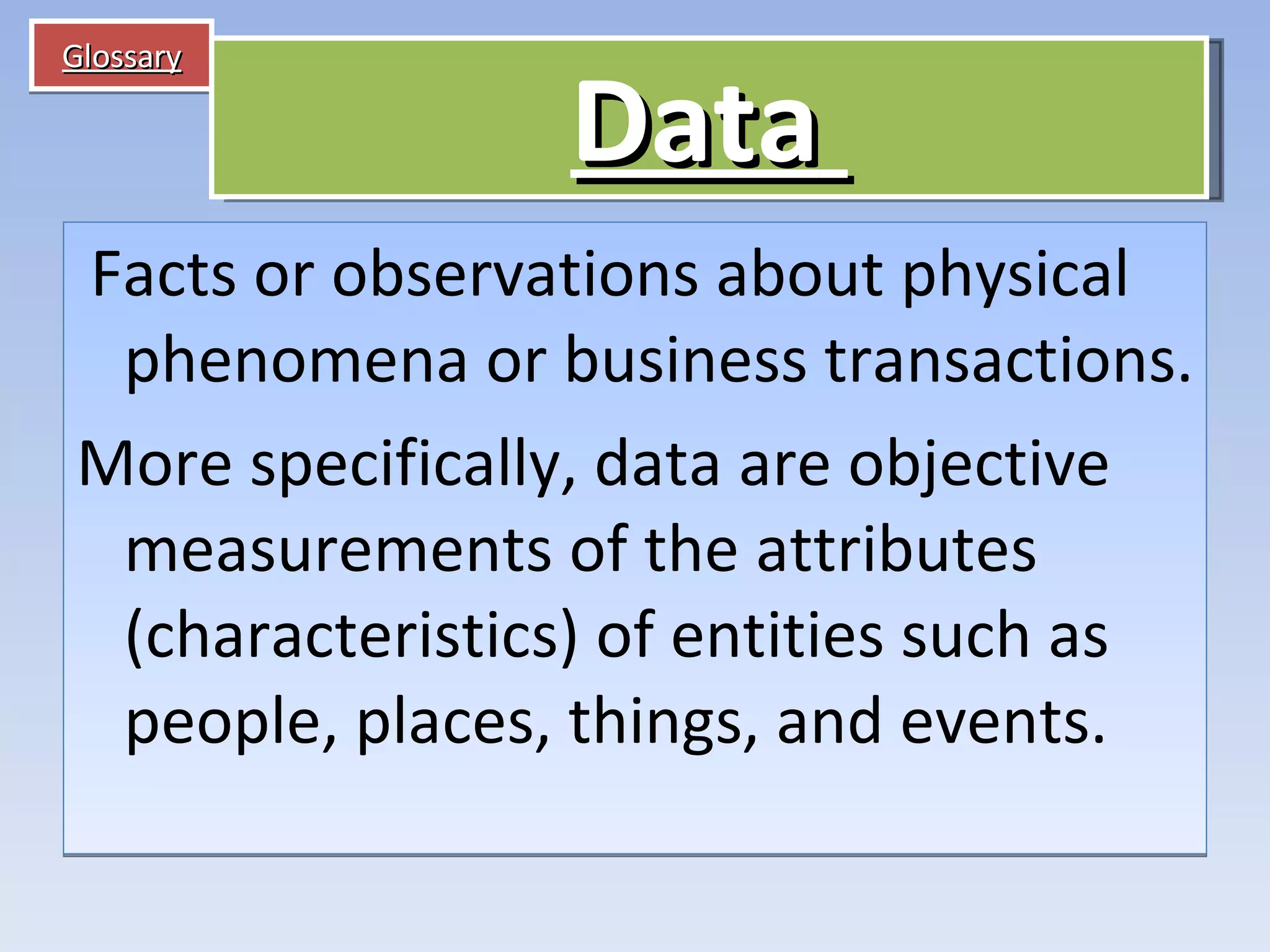
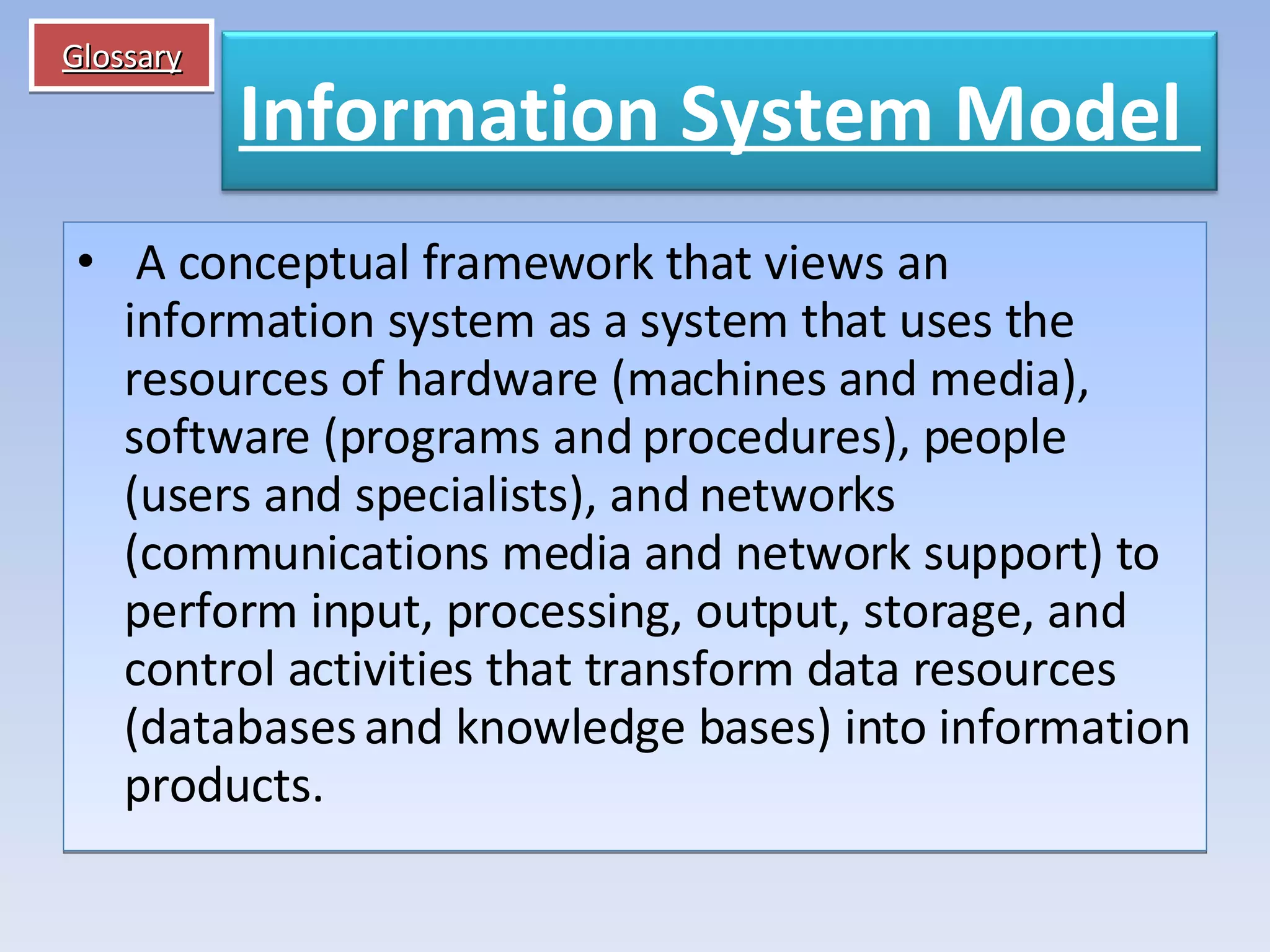
Information systems and technologies are vital for businesses to improve efficiency, effectiveness, and competitive position. They can support various business activities from product development to customer support. With Internet technologies, information systems have become necessary for business success globally. The document then outlines key concepts about information systems including components, activities, and applications for business.