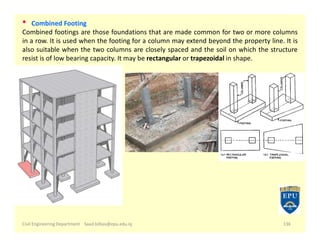
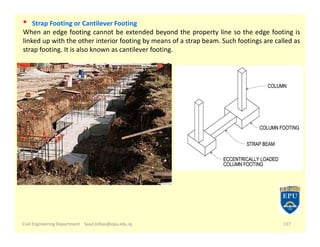
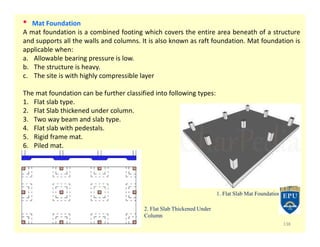
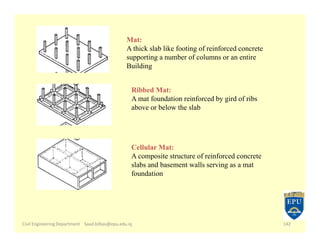
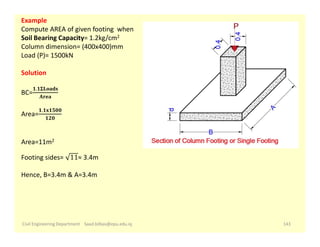
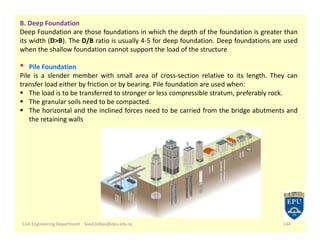
The document provides an overview of foundations in civil engineering, defining foundations as structures that transmit loads to the ground and outlining their types, including shallow foundations such as wall and column footings, and deep foundations like pile and pier foundations. The purposes of foundations include load distribution, stability enhancement, and prevention of lateral movement. Additionally, it details various foundation designs, their applications, and calculations for determining size based on soil bearing capacity and structural load.