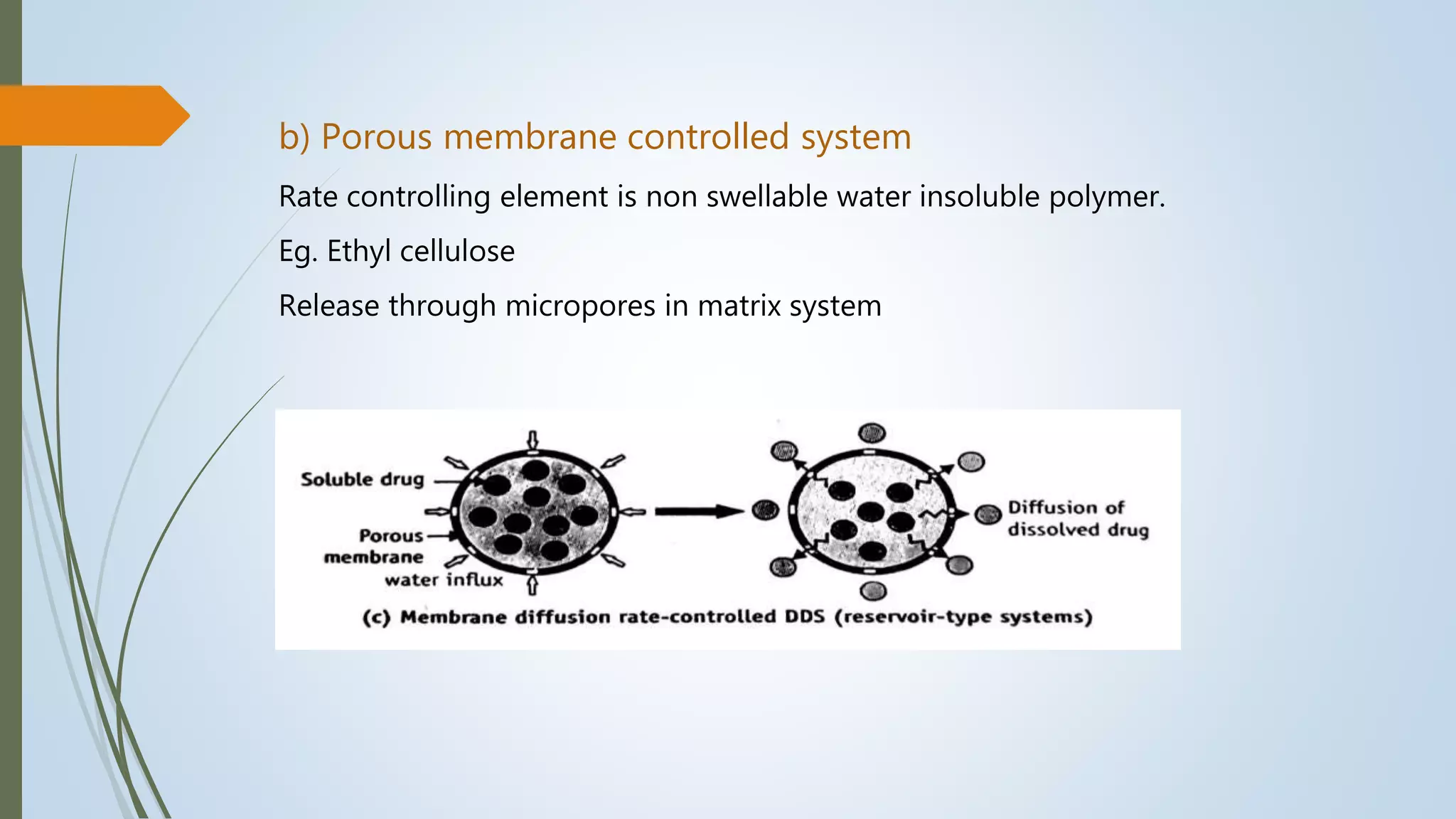
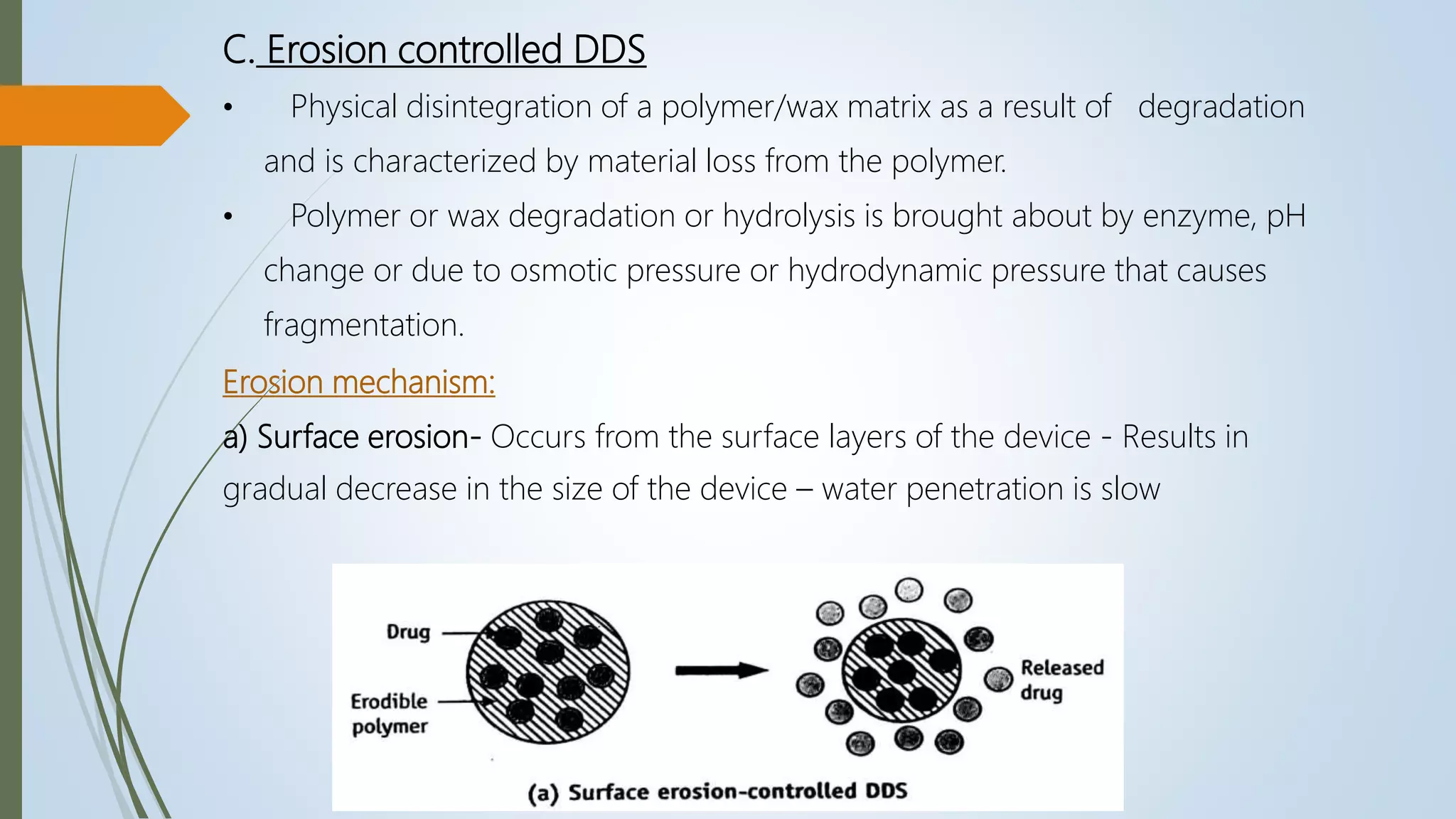
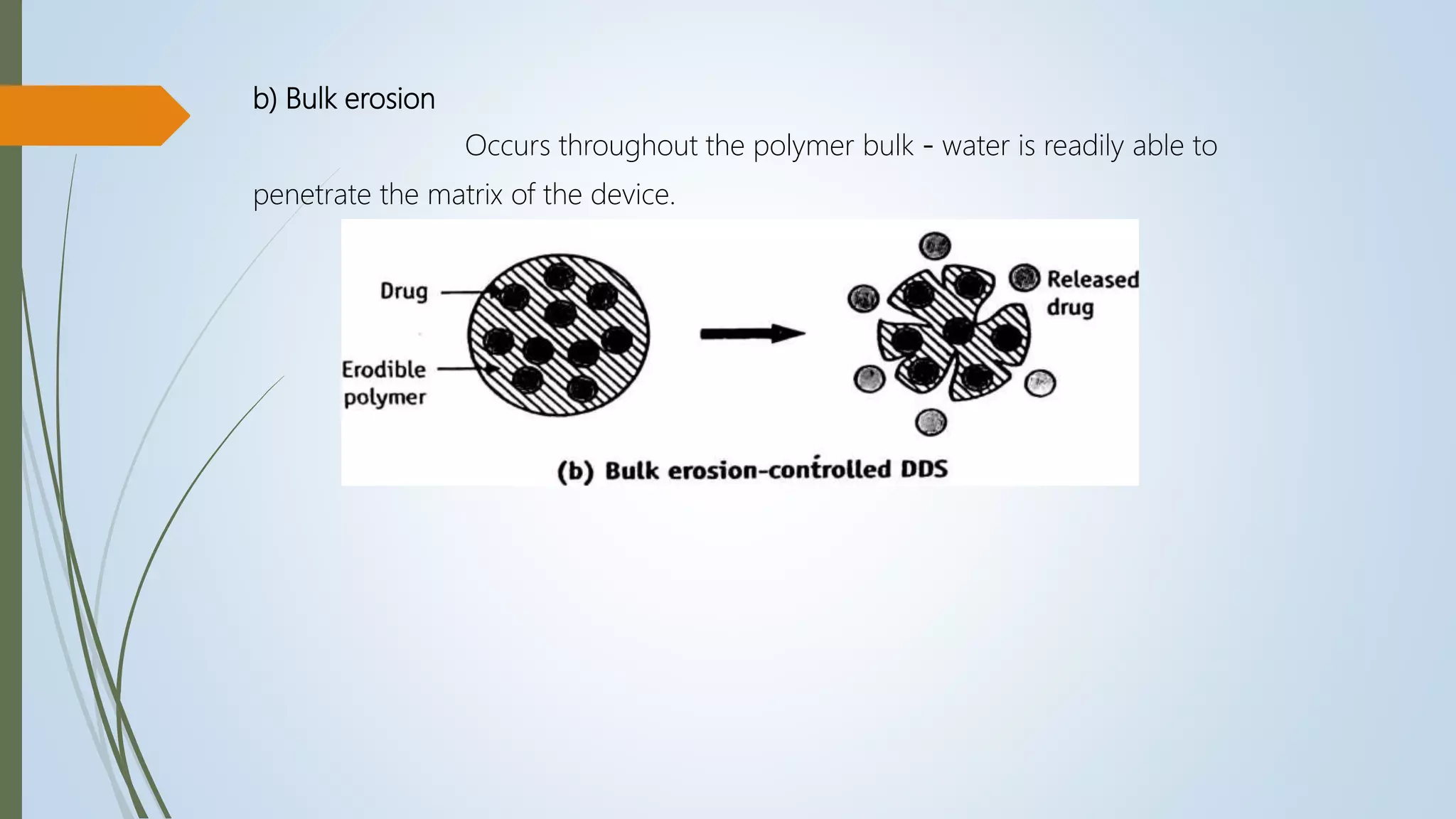
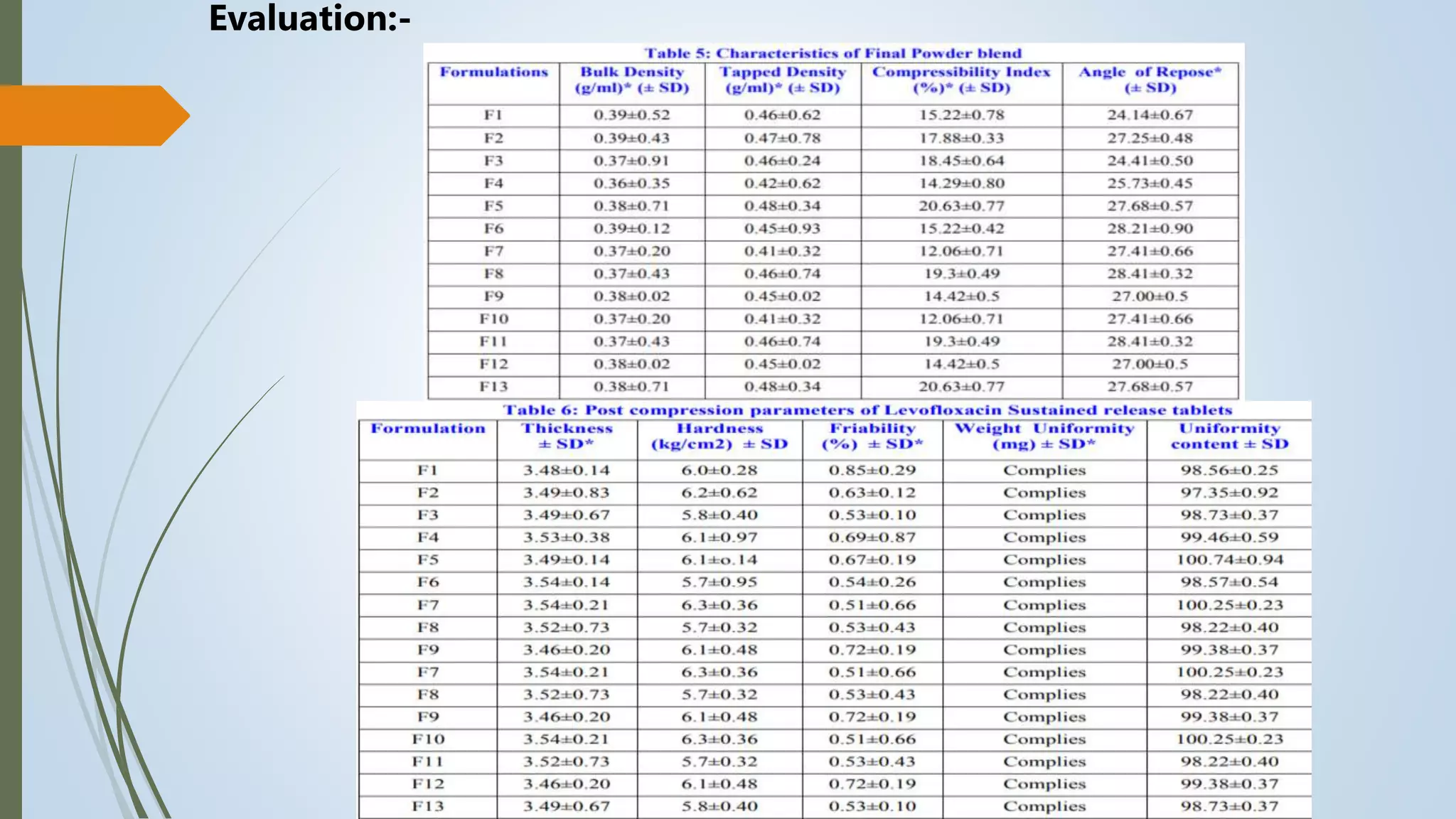
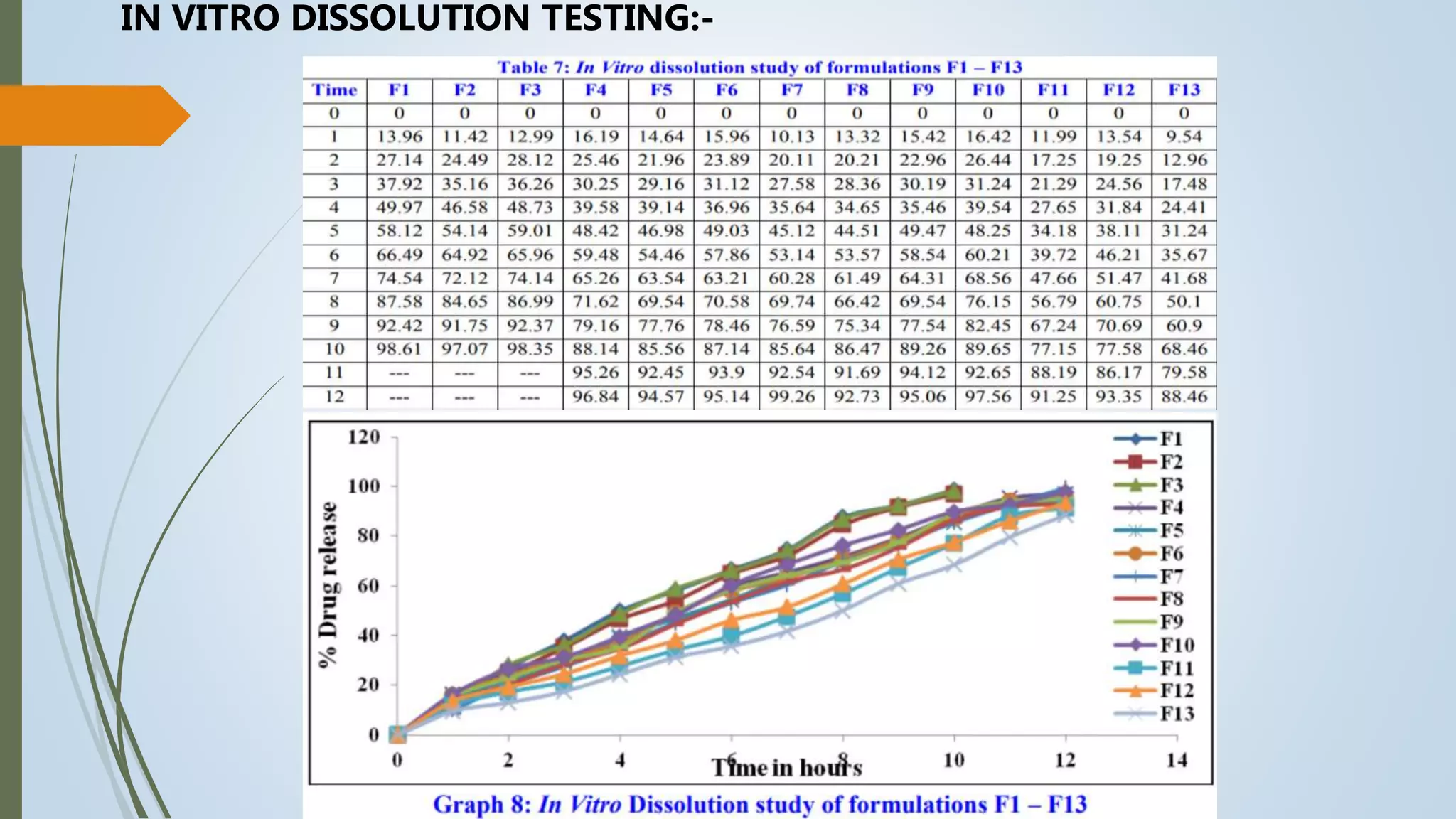
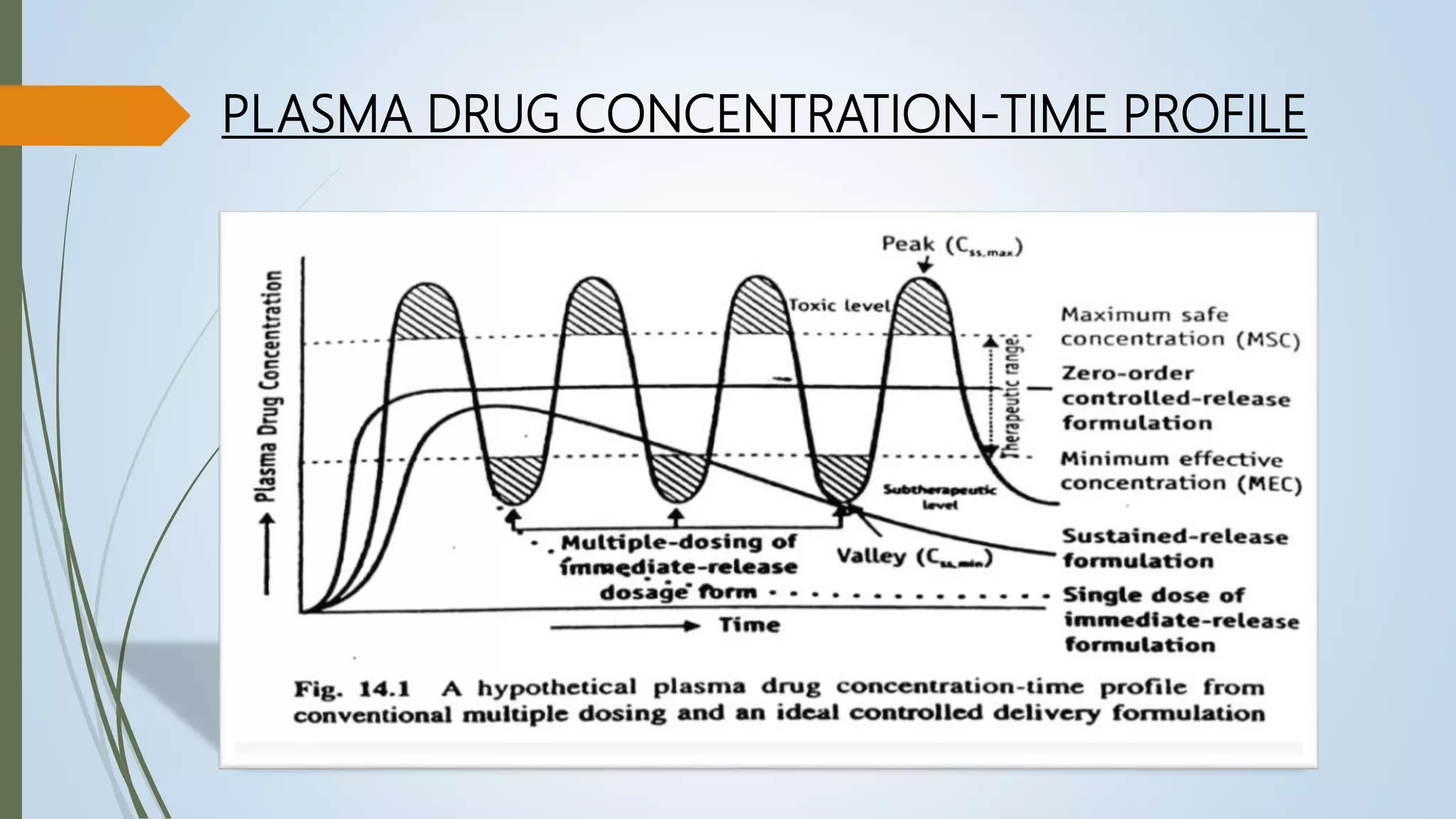
This document summarizes the formulation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets containing the drug levofloxacin. Matrix tablets were prepared using natural polymers like guar gum, karaya gum, and xanthan gum to achieve sustained release over 12 hours. Tablets were prepared by direct compression and evaluated for properties like weight variation, hardness, thickness, friability, and dissolution. Formulation F7, containing the polymers in a 40 mg ratio, provided 12 hours of drug release and was considered the optimized sustained release formulation.







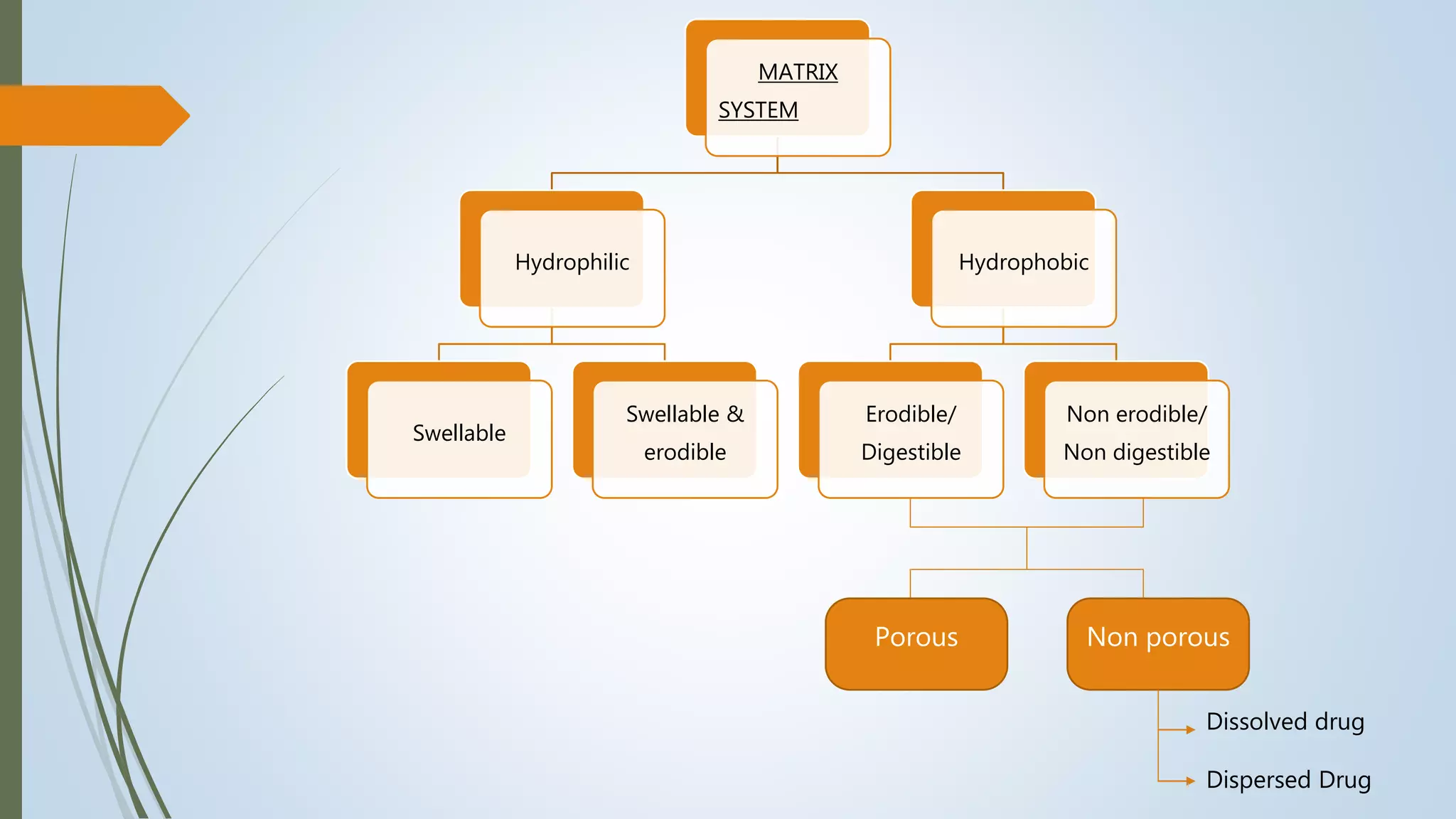
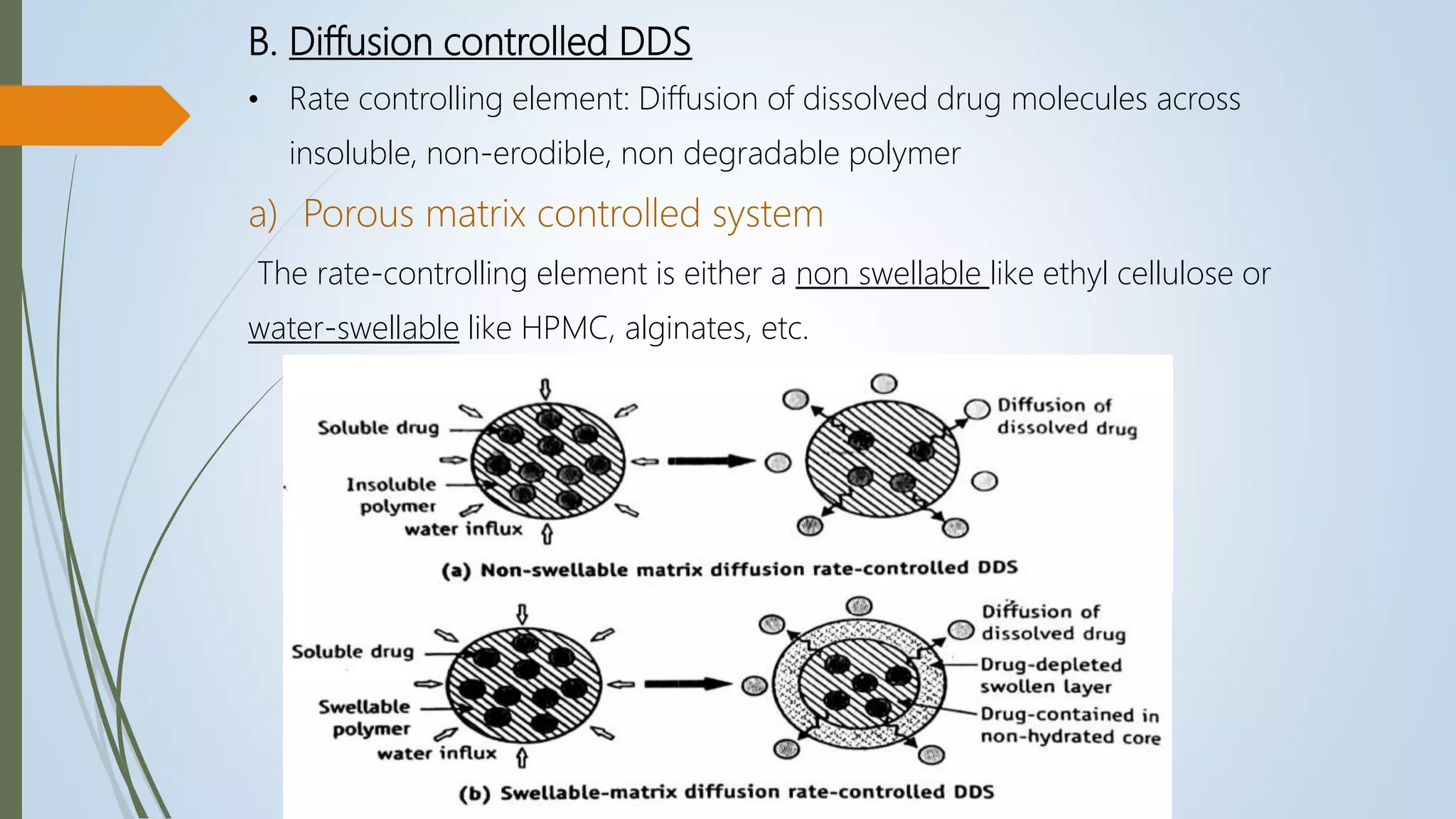
![A] Hydrophilic matrix
In this type of system the release-retarding material is water-swellable or
cum erodible hydrocolloid such as high molecular weight HPMC, HPC, HEC, xanthan gum,
alginate, etc.
Hydrophilic matrices are porous systems.
• Depending upon the swelling behaviour of hydrophilic polymer, two types of matrices are
possible-
1) Freely swellable matrix
In this type, the polymer swelling is unrestricted.
2) Restricted swelling matrix
One in which the surface of the device is partially coated with an
impermeable polymer film that restricts the hydration of swellable matrix material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formulationevaluationofsrmatrixtablet-210514024135/75/Formulation-evaluation-of-Sustained-release-matrix-tablet-11-2048.jpg)
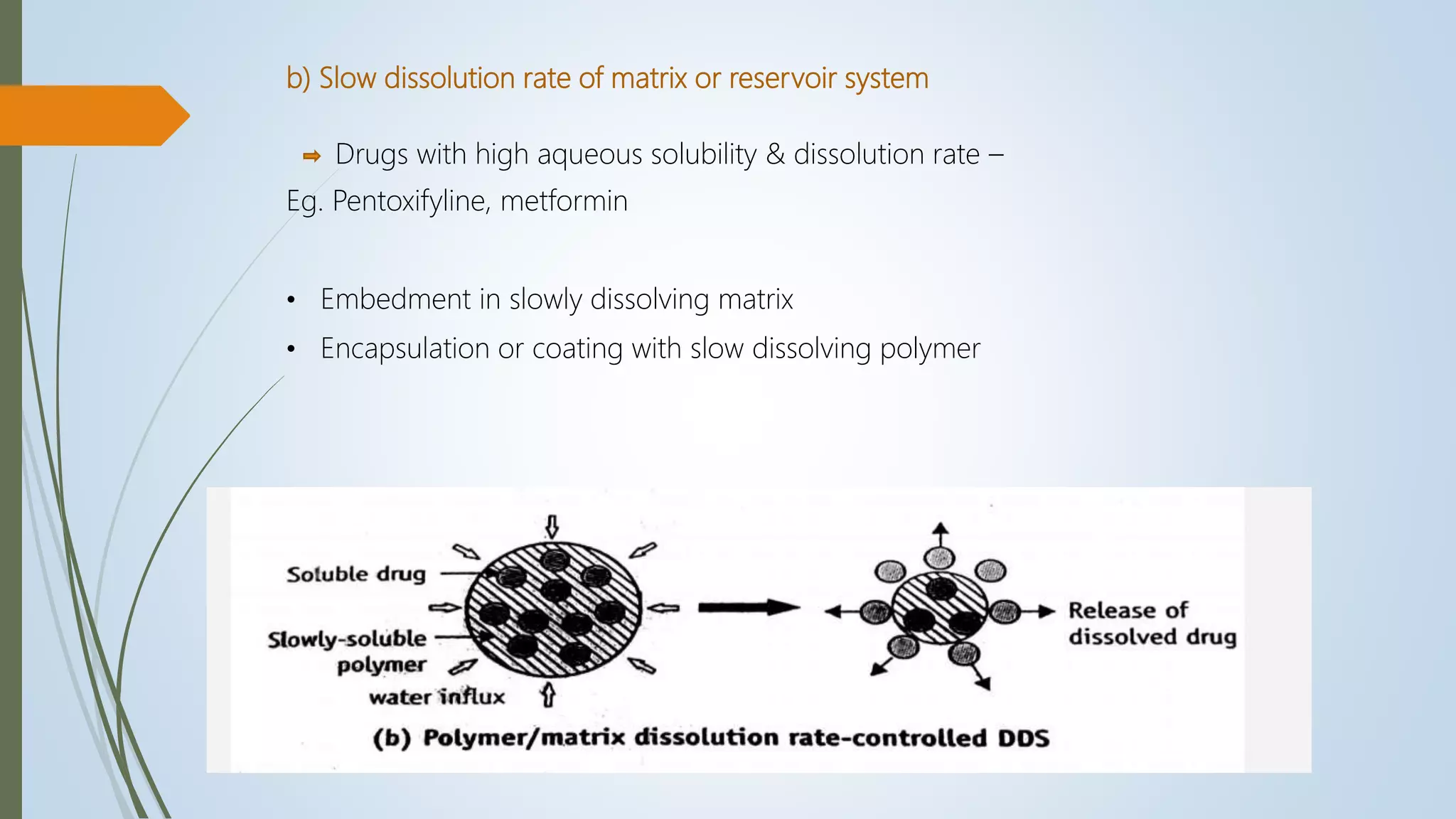
![B] Hydrophobic matrix ( plastic)
In this type of system the release-retarding material is slowly soluble, erodible or
digestible like waxes, hydrogenated vegetable oils, cetyl alcohol, etc. and insoluble or non
digestible materials like ethyl cellulose, polymethacrylates, etc.
- Depending upon the manner of incorporation of drug in the matrix, hydrophobic matrices can
be further classified as:
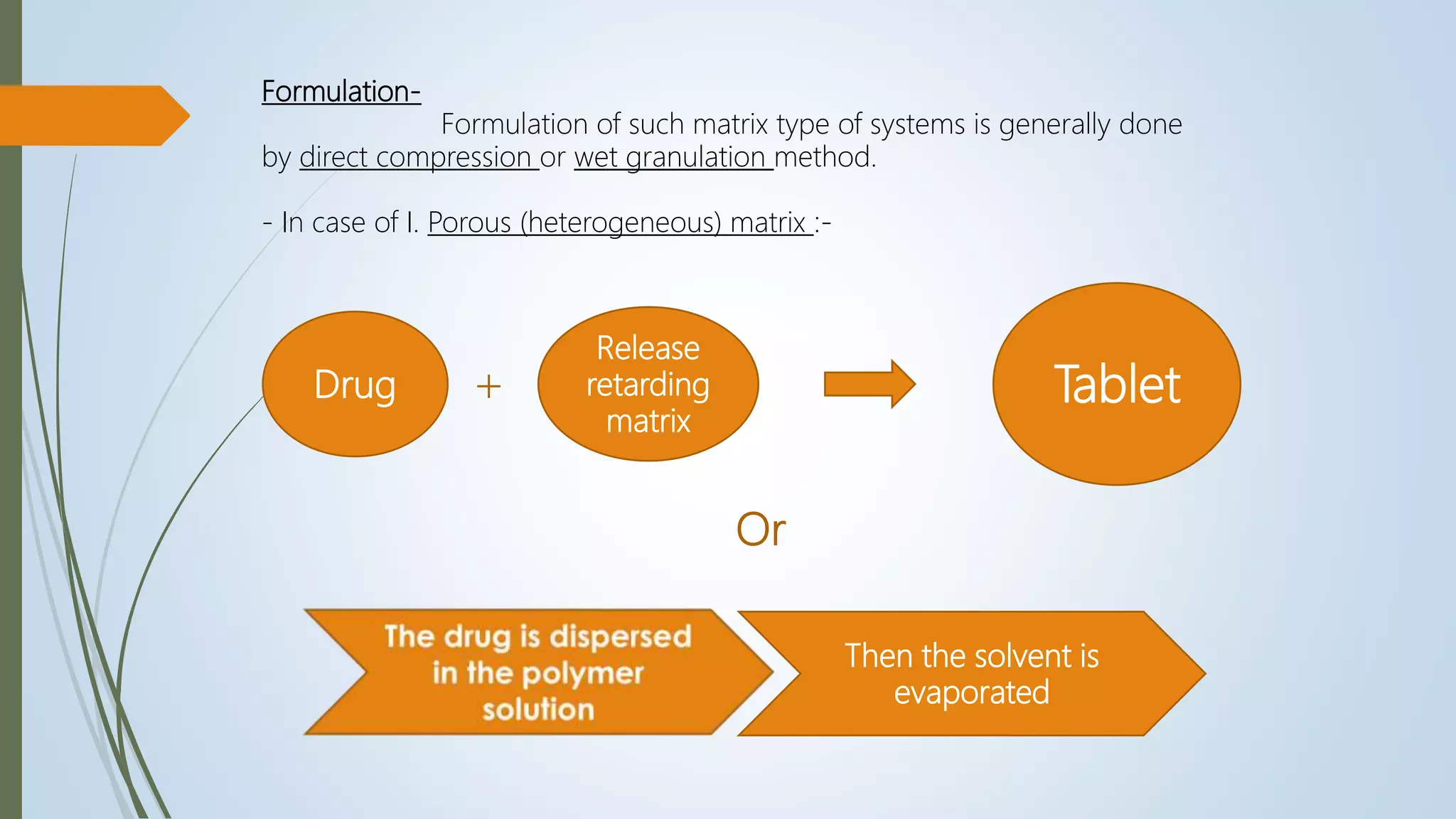
I. Porous (heterogeneous) matrix :
In these systems, the drug diffusion occurs through pores of the matrix.
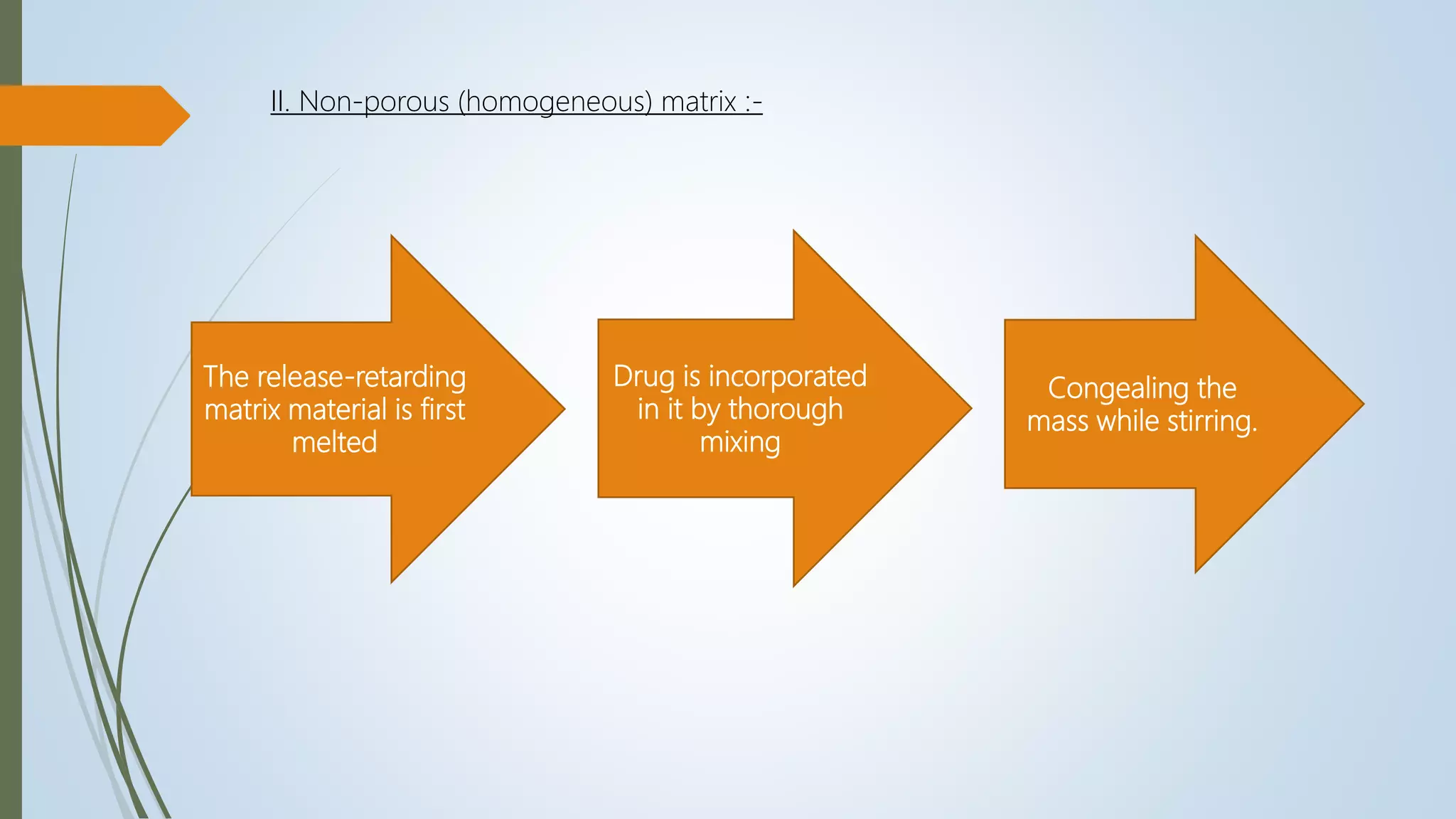
II. Non porous (homogenous) matrix :
These systems have no pores and the molecules diffuse through the network meshes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formulationevaluationofsrmatrixtablet-210514024135/75/Formulation-evaluation-of-Sustained-release-matrix-tablet-12-2048.jpg)