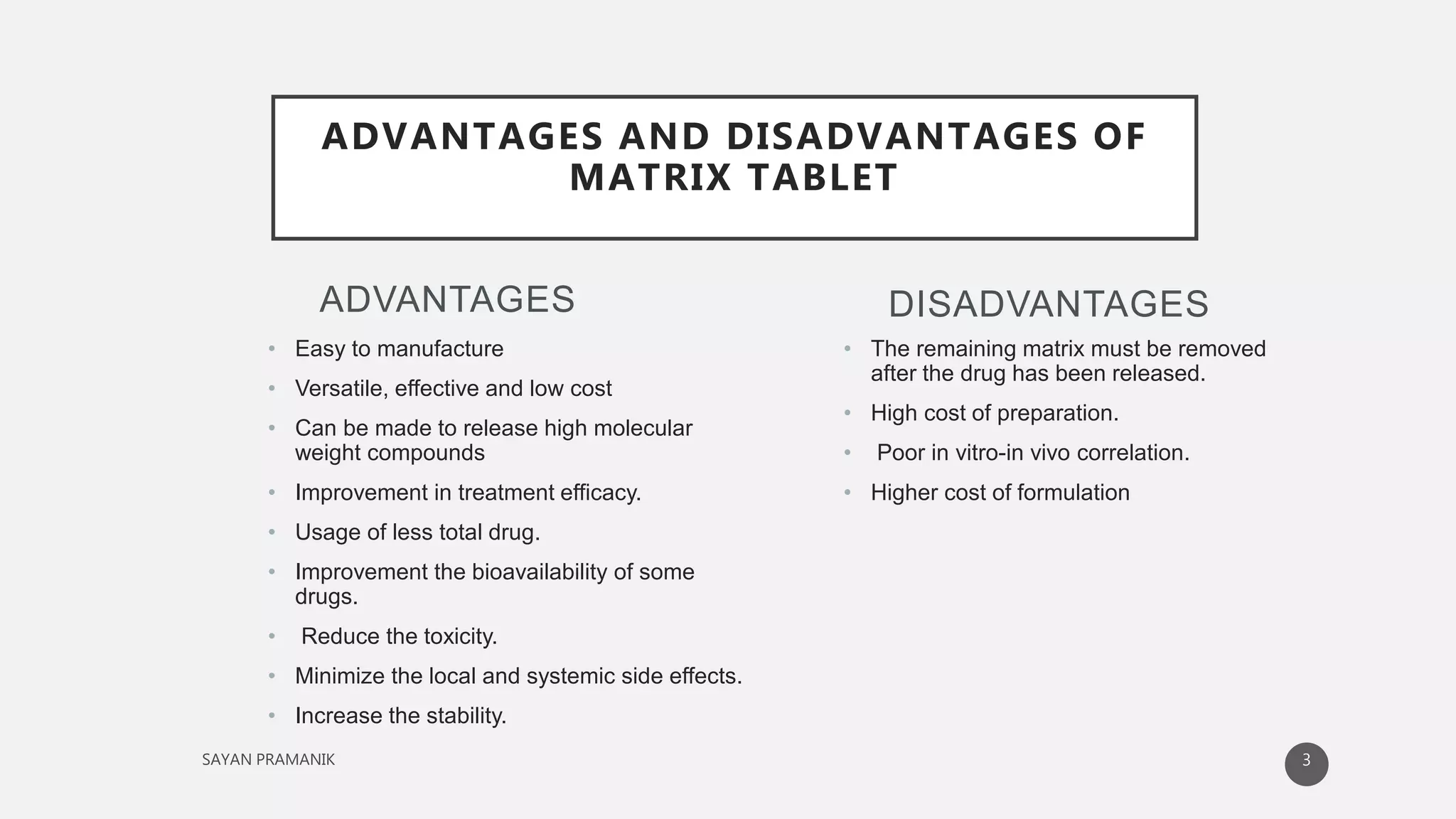
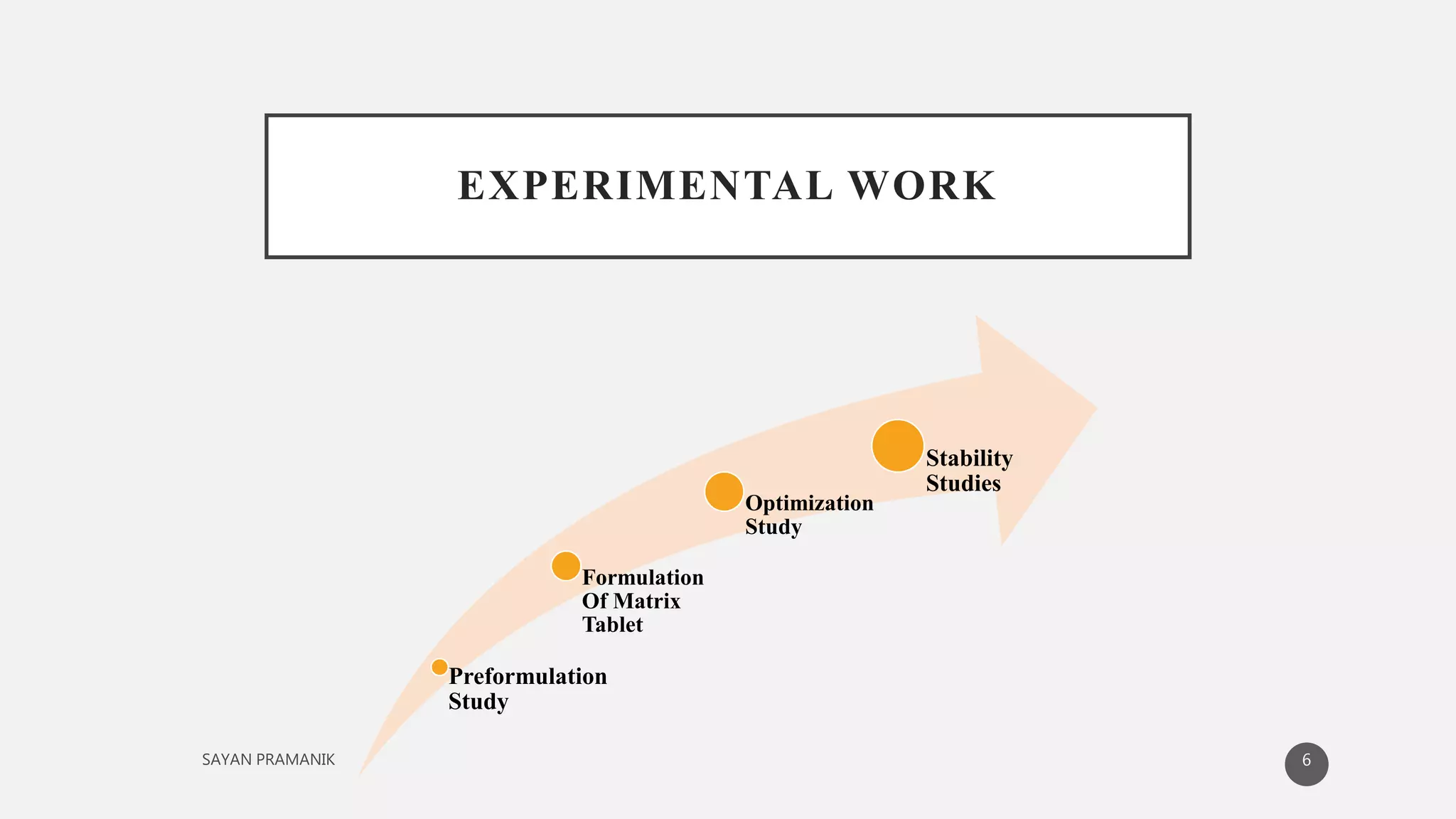
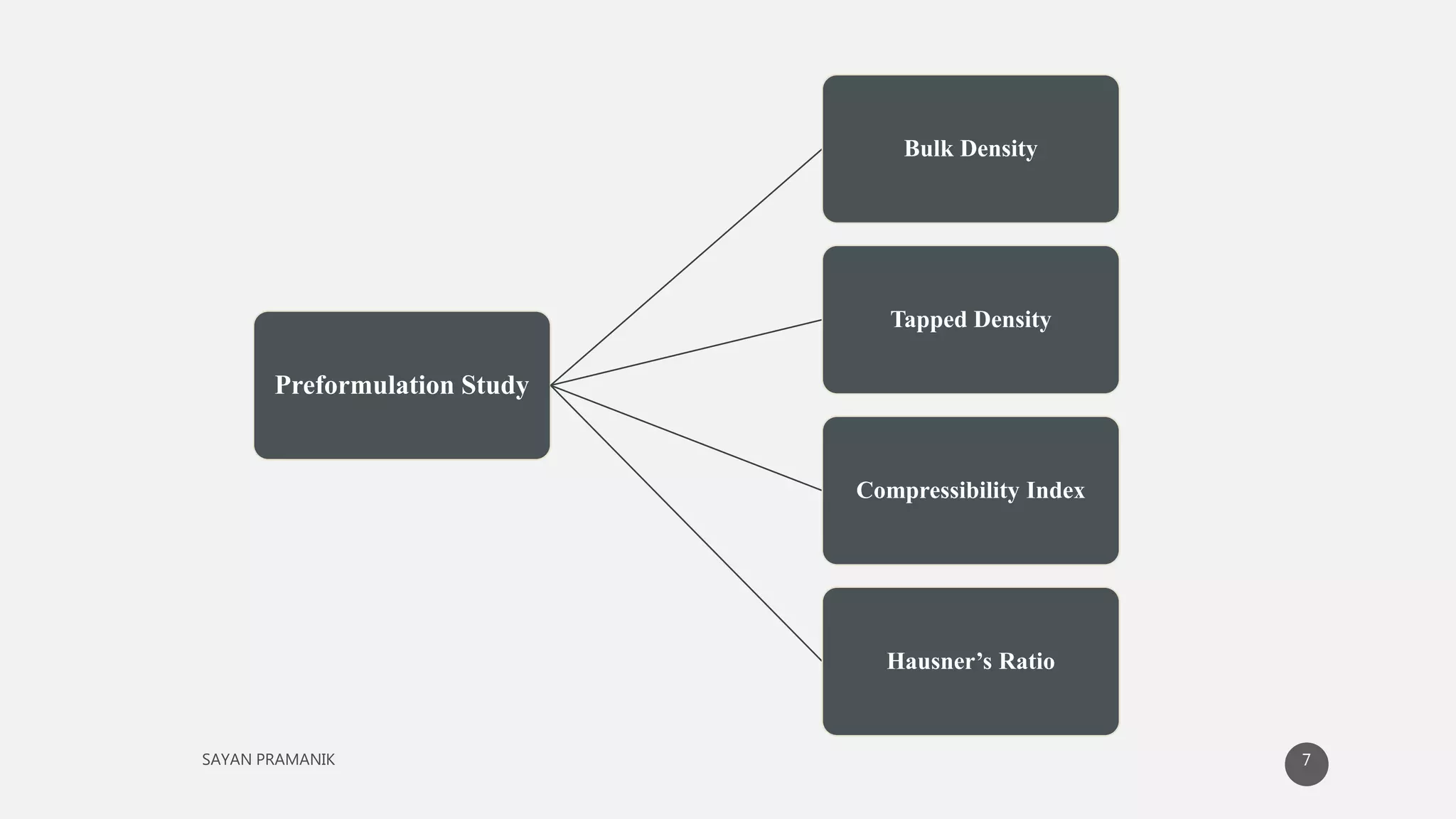
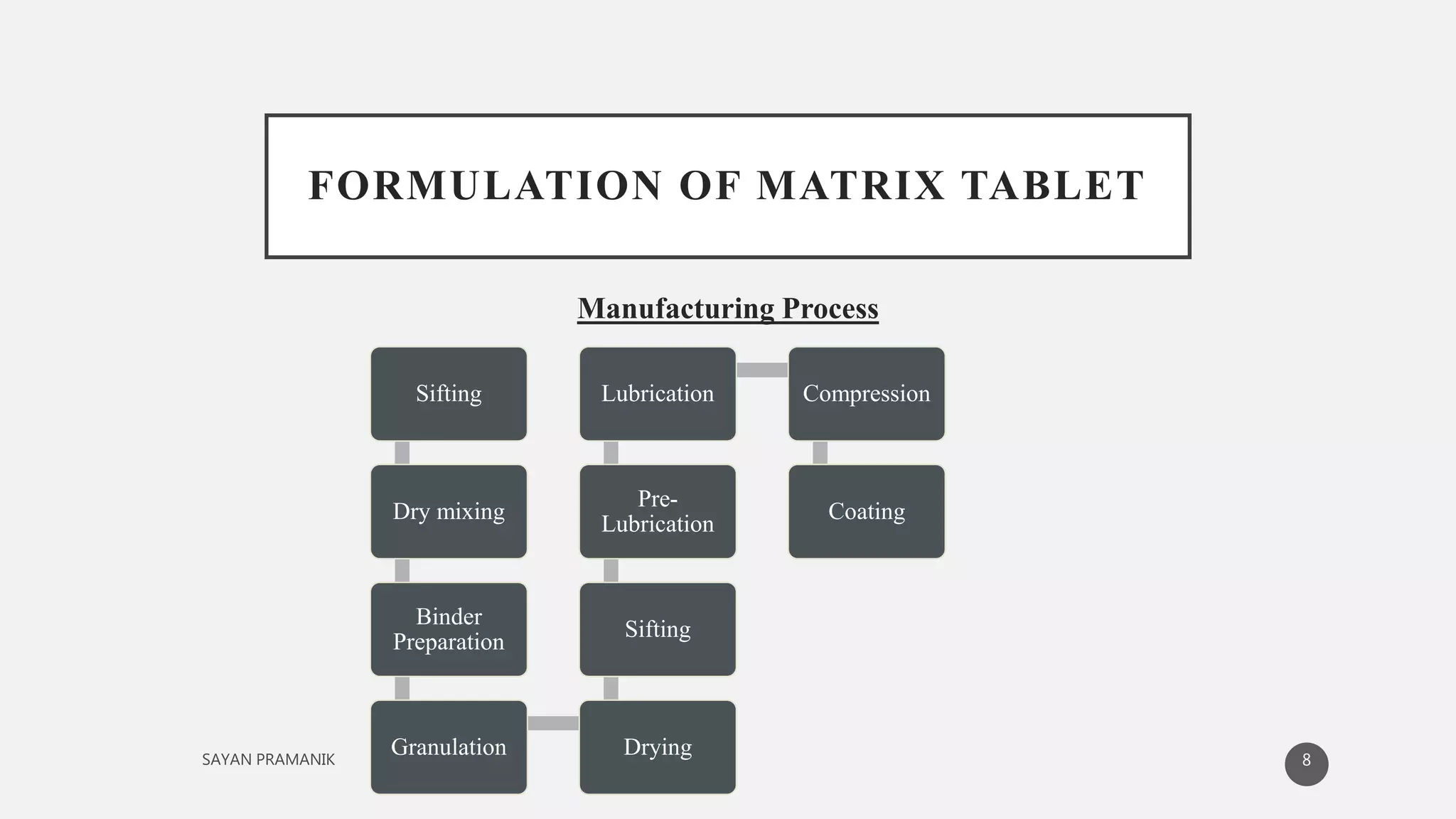
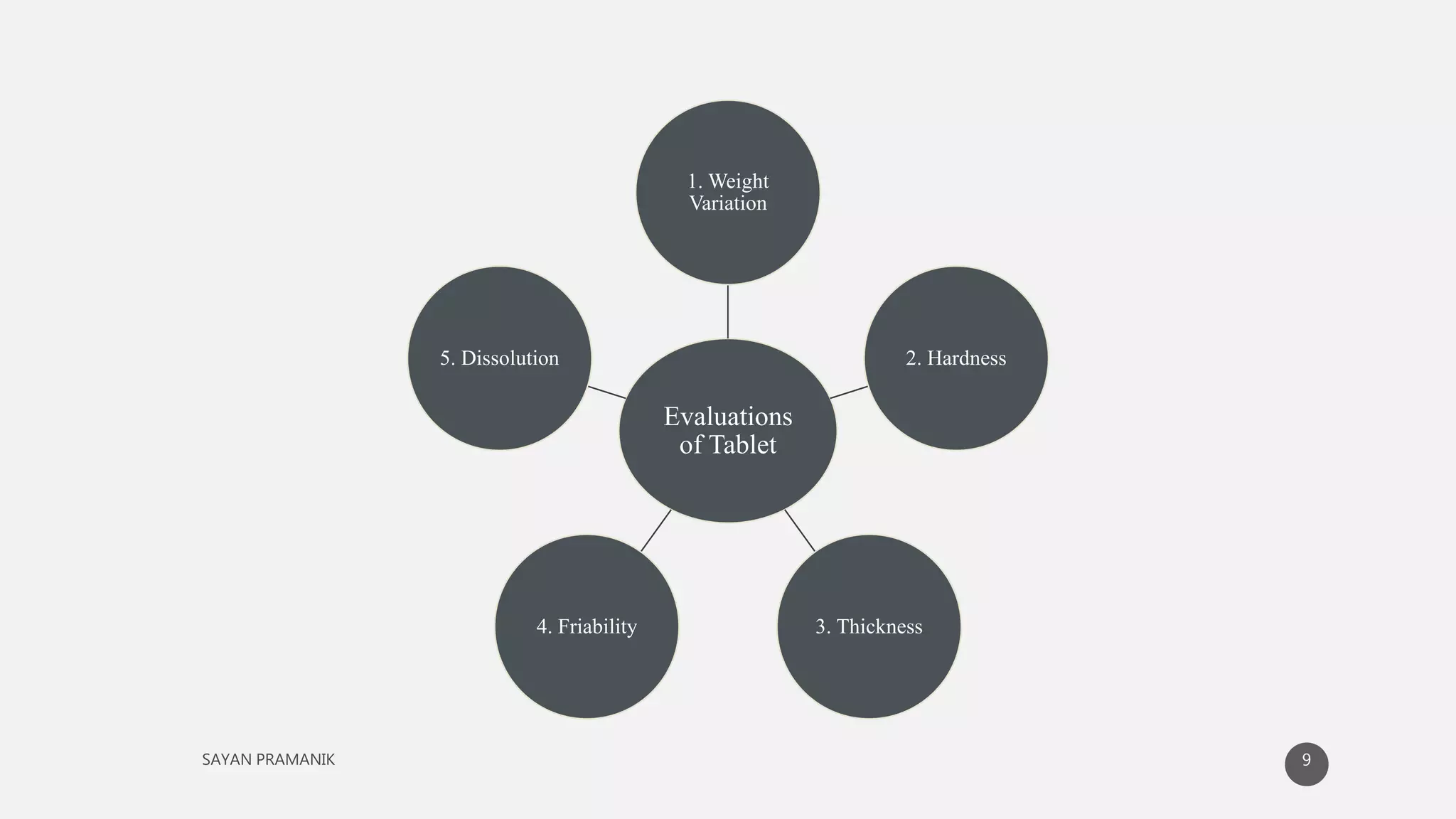
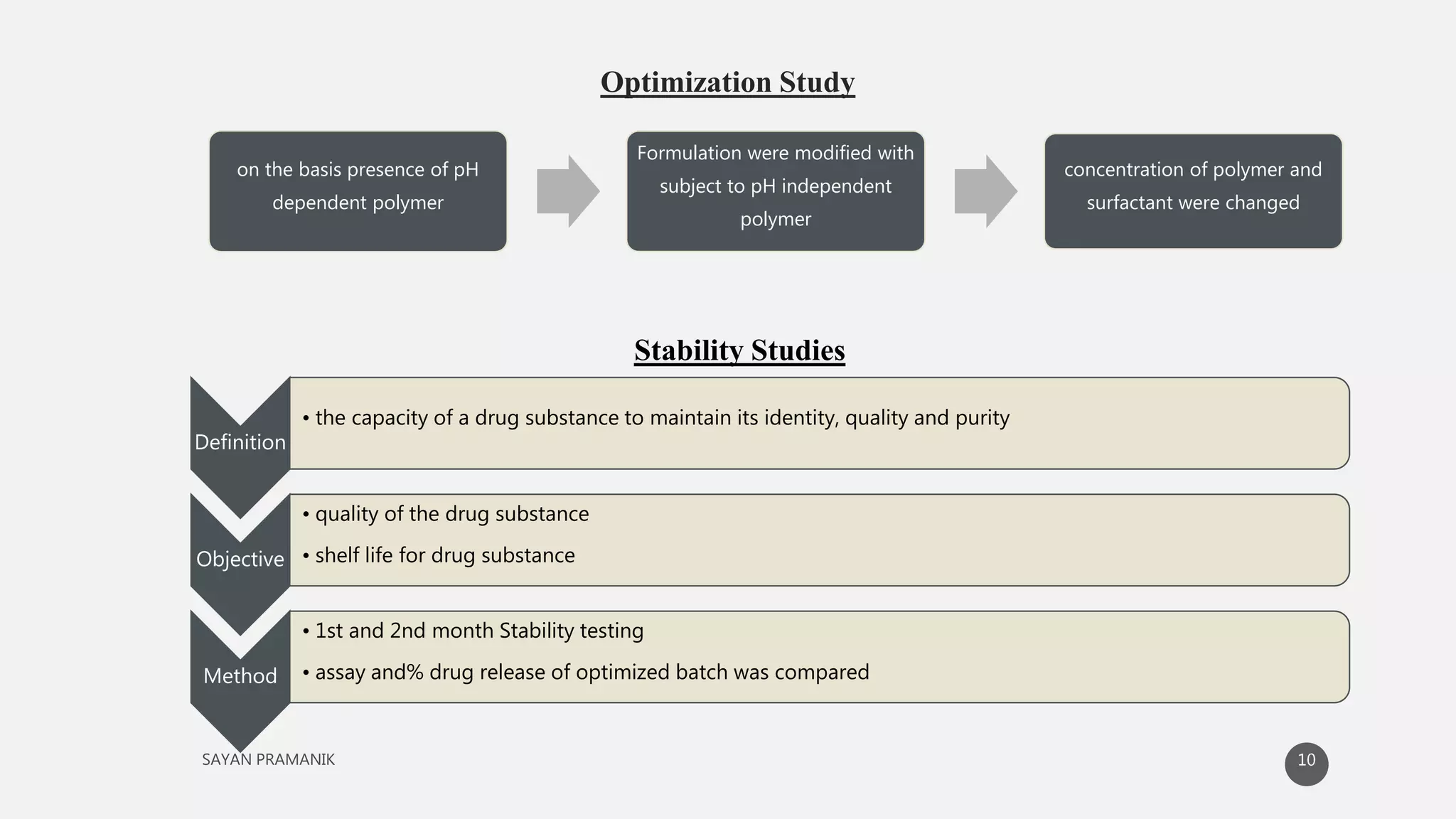
The document discusses the formulation and development of matrix tablets for controlled drug delivery, highlighting their advantages such as cost-effectiveness, improved bioavailability, and treatment efficacy, along with disadvantages like high preparation costs and poor in vitro-in vivo correlation. It classifies matrix tablets based on retardant materials and porosity, describes polymers used, and outlines the manufacturing and evaluation processes. The conclusion emphasizes the benefits of sustained-release formulations in enhancing dosage efficiency and patient compliance, particularly in antibiotics to mitigate resistance.