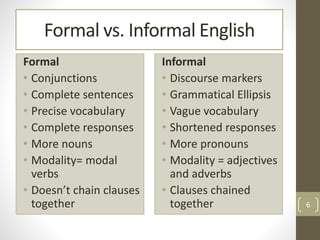
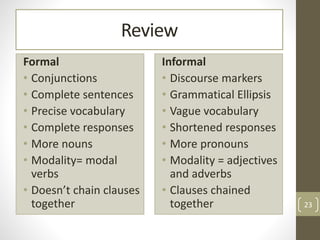
The document contrasts formal and informal English, highlighting their linguistic characteristics and contextual usage. Formal language is characterized by complete sentences, precise vocabulary, and the use of conjunctions, while informal language often features grammatical ellipsis, vague vocabulary, and a more conversational tone. Examples of varying levels of formality are included, along with tasks to practice transforming language between formal and informal styles.