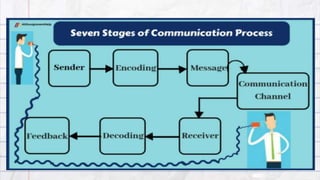
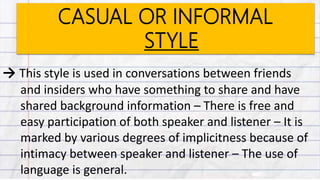
This document discusses different speech styles used in oral communication. It defines speech style as the degree of formality in language used by a speaker. There are five speech styles presented from most to least formal: frozen, formal, consultative, casual/informal, and intimate. Each style is defined based on the complexity of grammar, vocabulary, participation of the speaker and listener, and appropriate social contexts. Examples are provided to illustrate when each speech style would be used. The objectives and assignments involve identifying, applying, and presenting situations using different speech styles.