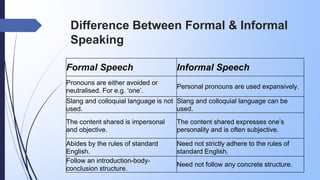
The document discusses the characteristics and appropriate uses of formal and informal speaking. Formal speaking is polite, objective, effective, uses standard English language and clarity. It is used when explaining topics to others or in academic writing. Informal speaking has a conversational tone, uses personal pronouns and contractions, informal expressions, and discusses personal feelings. Informal speaking is appropriate for sharing personal thoughts or stories. The document provides tips on what to avoid in formal speaking and the structure of a formal speech, and compares the differences between formal and informal speaking.