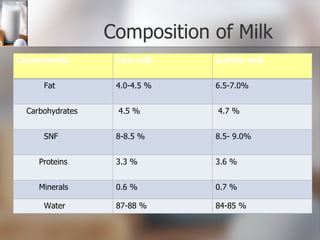
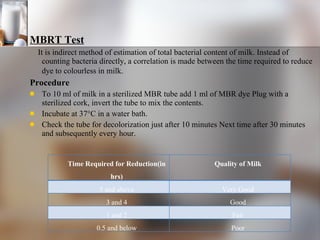
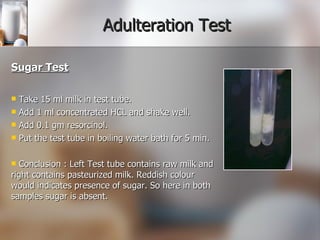
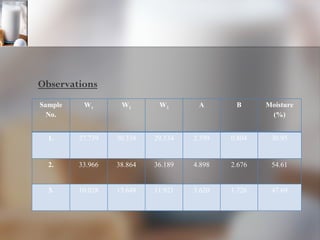
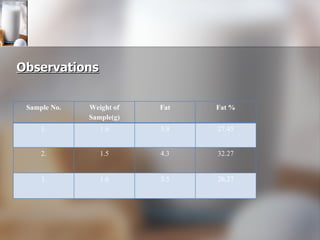
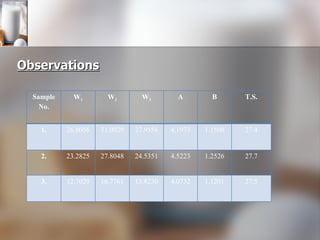
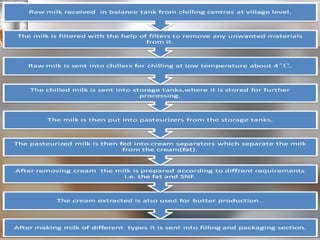
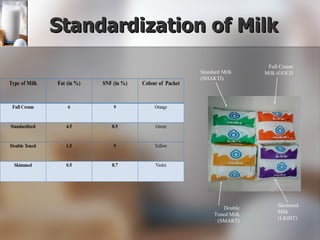
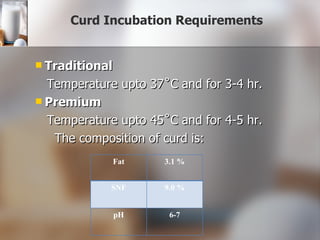
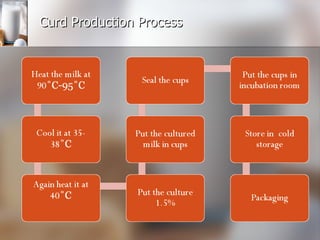
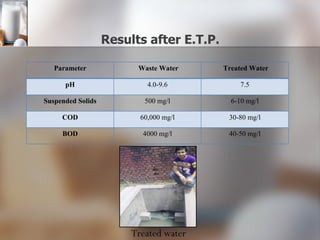
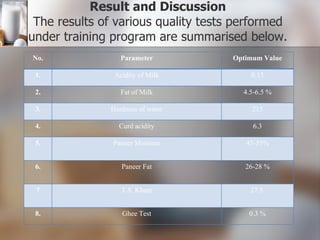
The document summarizes quality control processes at Verka Milk Plant in Mohali, India. Raw milk is received and graded before processing. Quality is ensured through various lab tests checking fat, SNF, acidity, and adulterants. Milk is pasteurized, standardized, homogenized, and packaged. Other products like curd, paneer, kheer, and lassi are also produced. Strict quality control ensures products meet standards for composition, shelf life, and safety.