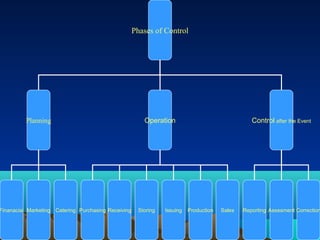
Food cost control involves setting standards for costs according to business objectives and policies. It aims to control costs related to food including cost of food cooked, wastage, spoilage, and shrinkage/pilferage. Key aspects of food cost control involve planning, operations such as purchasing and storage, and control after the event through reporting and assessment. The overall goal is to analyze income and expenses to maximize profits while maintaining quality and customer satisfaction. Factors like menu planning, purchasing, skills, and waste avoidance can impact the percentage of food costs.