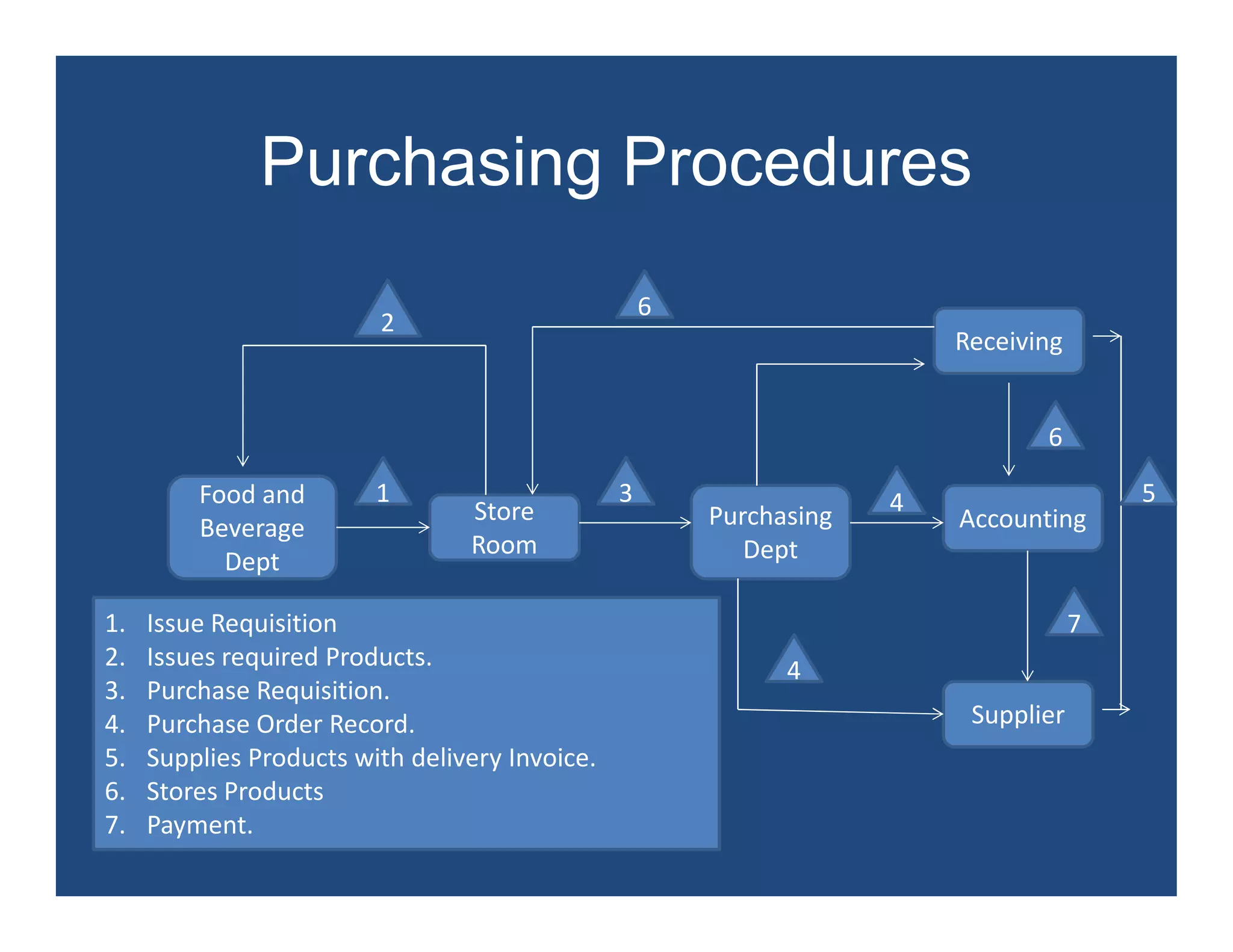
This document discusses food purchasing and receiving control in foodservice establishments. It outlines the purchasing process, including establishing quality standards, determining purchase quantities, and using a purchase order system. It also discusses selecting suppliers, reducing costs, and security concerns in purchasing and receiving. The goal is to obtain the proper quality and quantity of products at the right time and price through an efficient purchasing process.