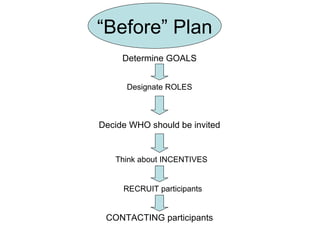
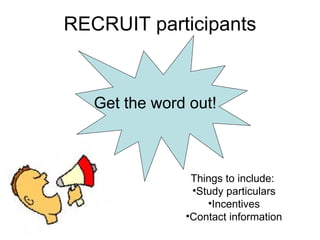
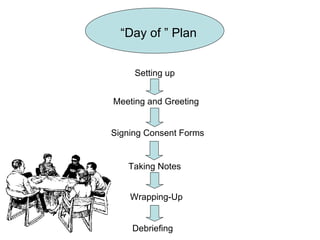
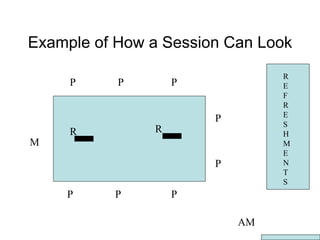
This document provides guidance for conducting a focus group in three stages: before, during, and after. It outlines steps to take such as determining goals, recruiting participants, moderating the session, and analyzing the results. Key aspects covered include selecting roles, providing incentives, contacting participants, facilitating discussion, taking notes, debriefing afterward, transcribing recordings, analyzing themes, and reporting findings.