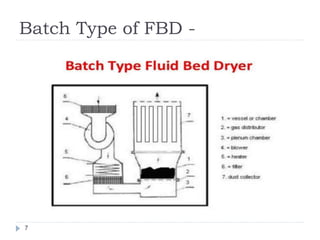
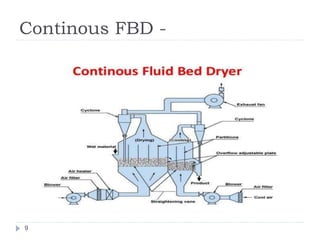
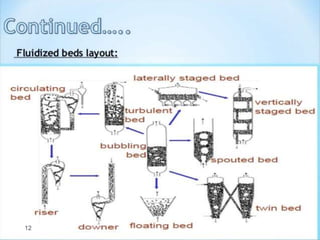
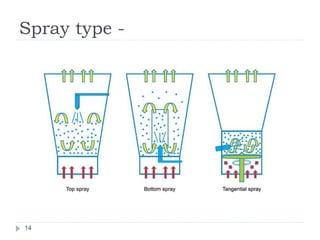
The document discusses fluidized bed drying (FBD), which uses hot air passed through granules in a container at high pressure to fluidize and dry the granules. There are two main types - batch and continuous. Batch types include vertical and rotating discharge dryers. Continuous dryers use a horizontal vibrating conveyor. Factors like particle size and density affect fluidization. FBD allows for shorter, more uniform drying times and protects thermolabile materials compared to other drying methods. However, it can cause particle attrition and electrostatic charging of some powders during drying.