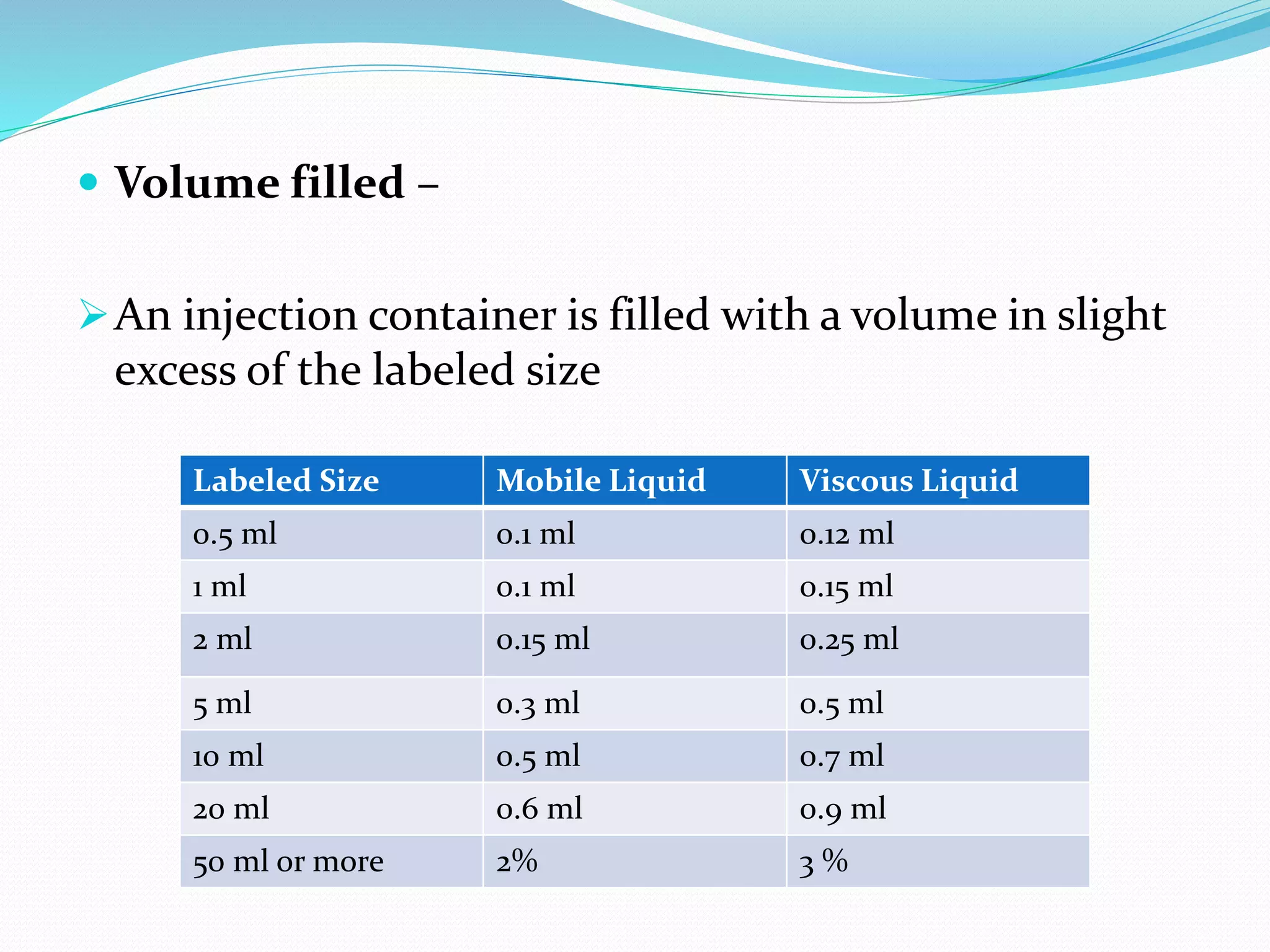
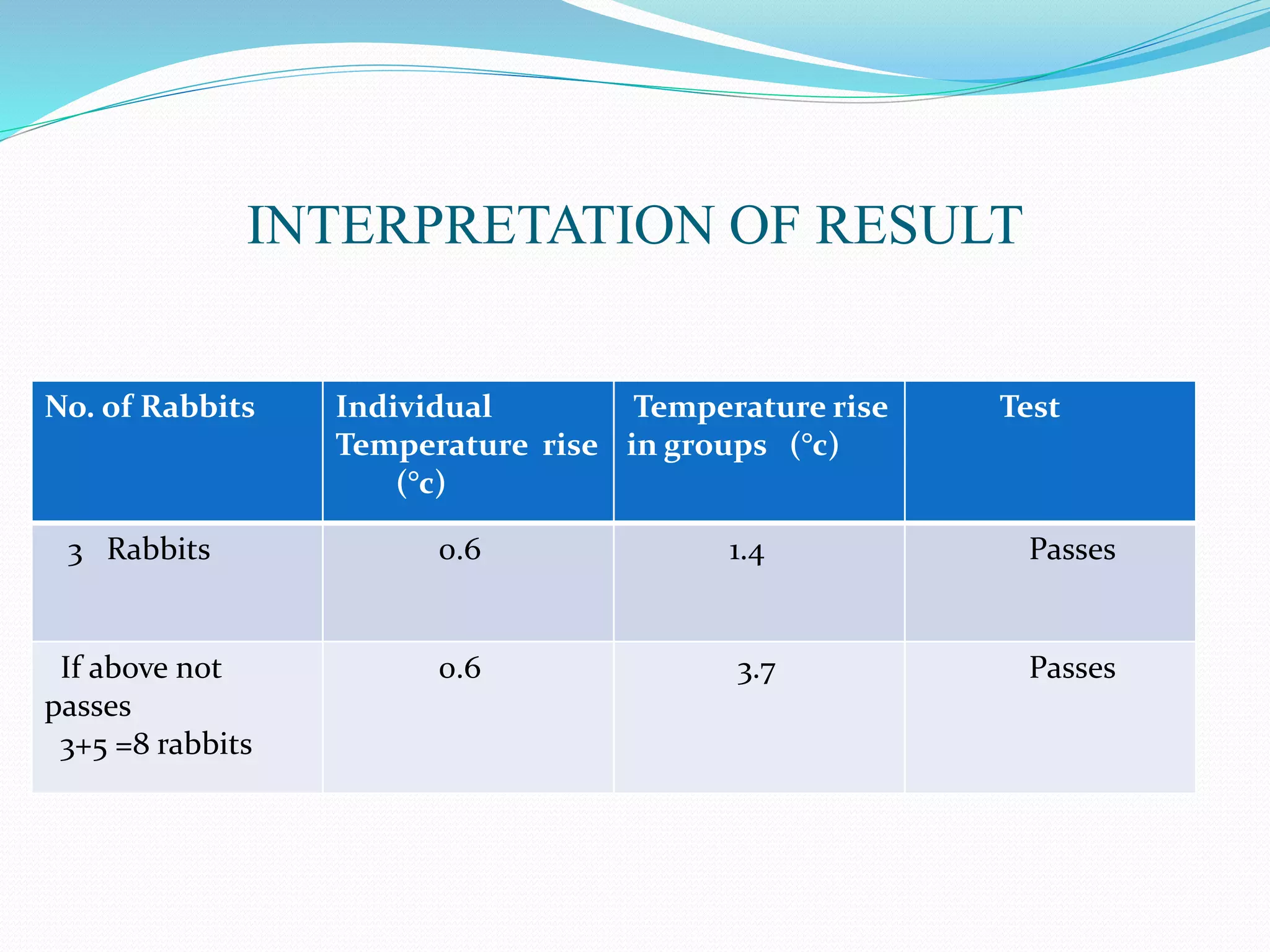
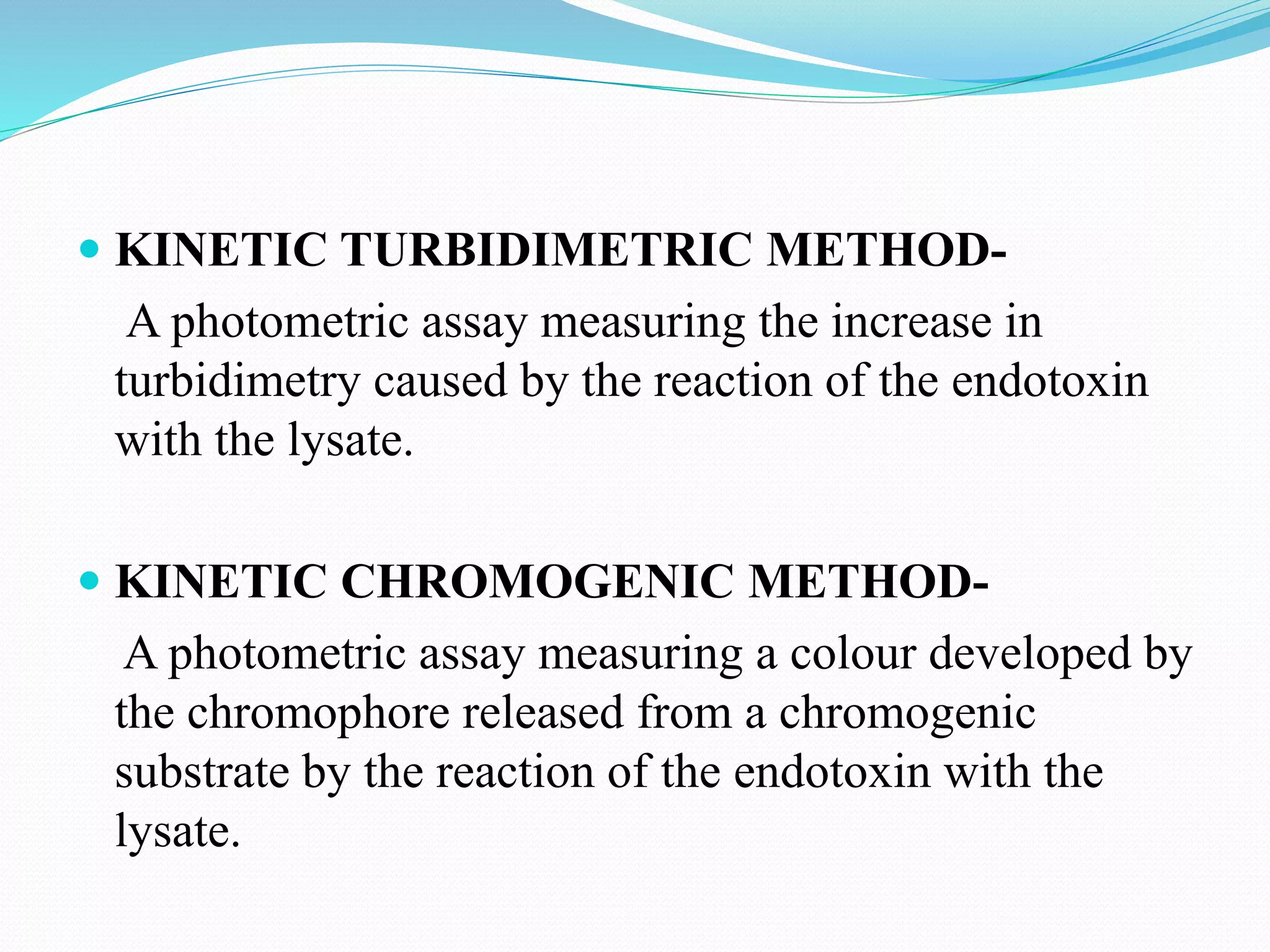
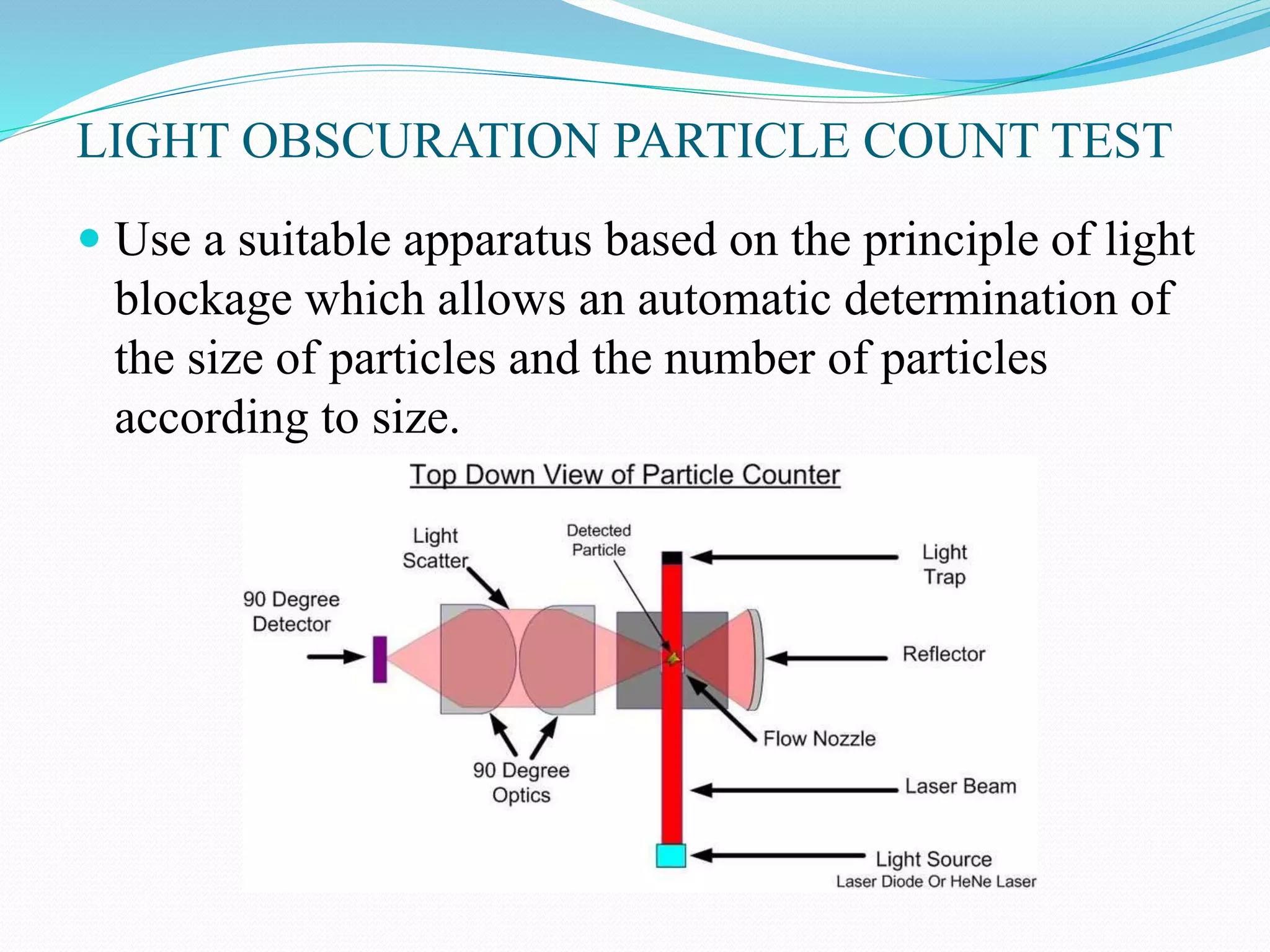
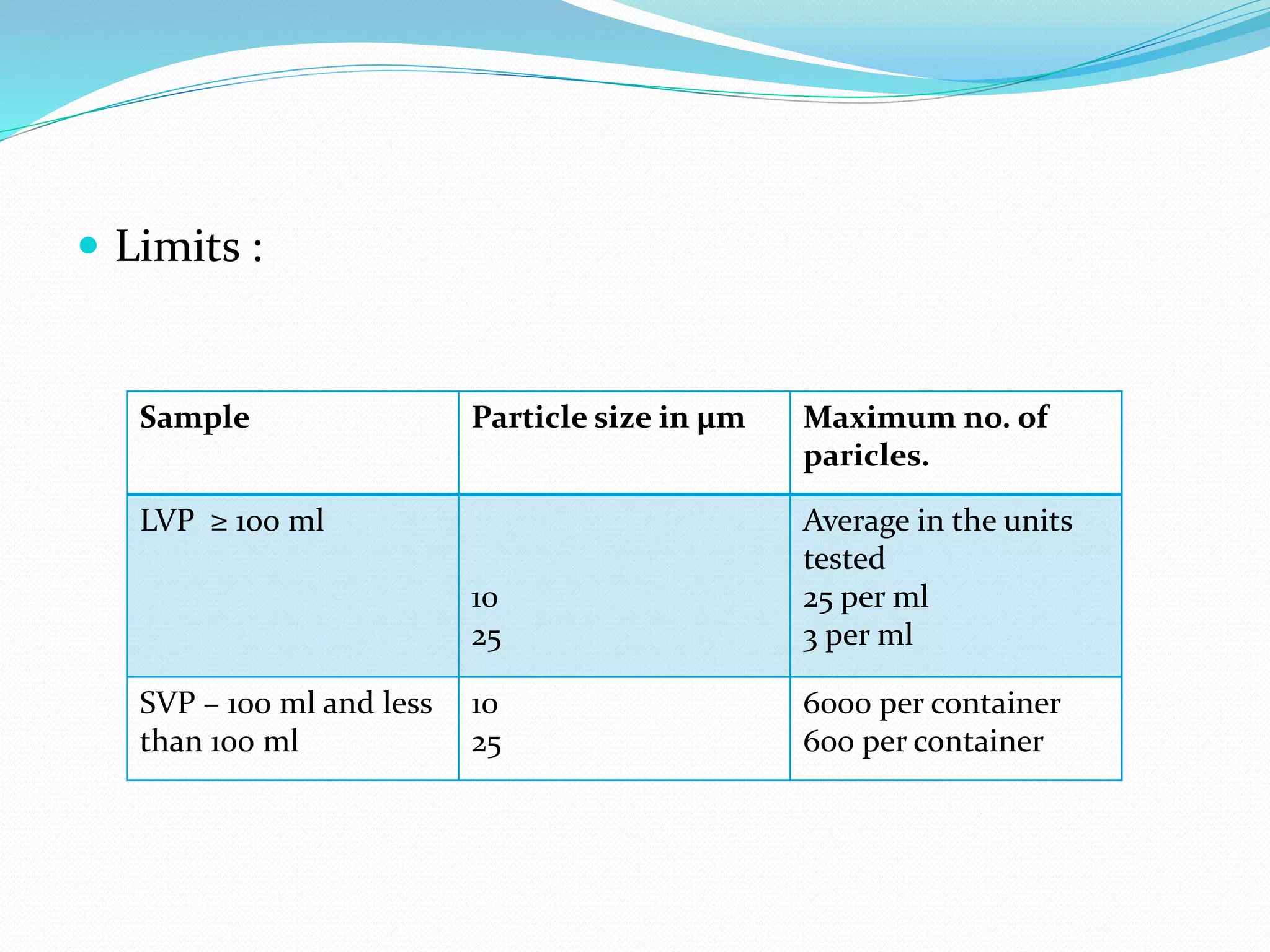
This document summarizes parenterals and their quality control testing. Parenterals are sterile dosage forms intended for administration other than orally that enter systemic circulation. Their advantages include quick onset, suitability for non-oral drugs, and use in emergencies. Disadvantages are the need for trained personnel and risks of pain, sensitivity, and expense. Quality control tests described include content uniformity, leakers, pyrogens, sterility, and particulates. Specific test methods and acceptance criteria are provided to ensure parenterals meet quality standards.