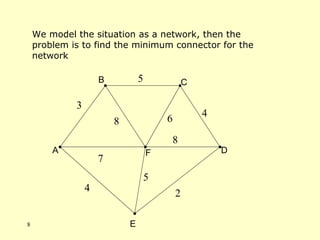
- A minimum spanning tree (MST) connects all nodes in a graph with the minimum total edge weight while avoiding cycles.
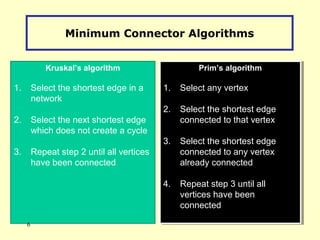
- There are different algorithms that can find an MST, such as Kruskal's algorithm and Prim's algorithm, which were introduced in the document.
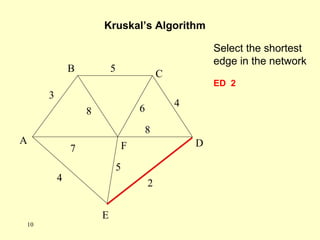
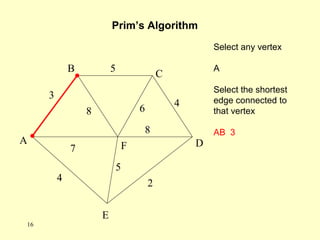
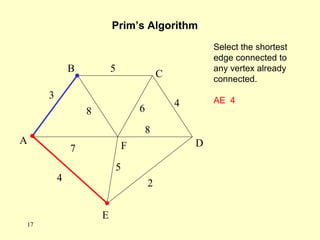
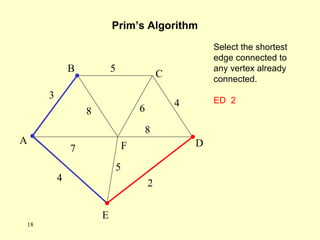
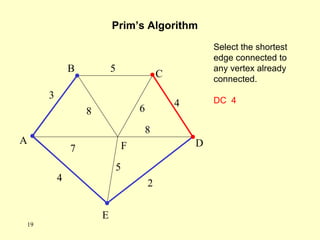
- Kruskal's algorithm works by sorting the edges by weight and building the MST by adding the shortest edges that do not create cycles. Prim's algorithm grows the MST from an initial node by always adding the shortest edge connected to the current MST.