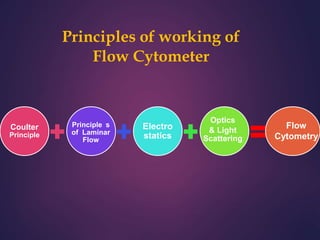
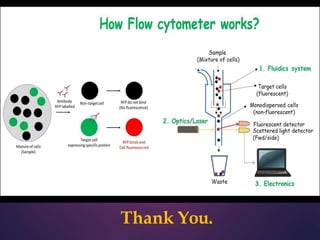
Flow cytometry is a technique that allows for the measurement and analysis of physical and chemical characteristics of cells and particles as they flow in a fluid stream through a beam of light. It works by using laser beams to interrogate cells as they flow through the instrument. Light scattering and fluorescent signals are detected and analyzed to provide information about properties like cell size, granularity, and expression of cell surface markers or intracellular proteins. Key applications of flow cytometry include immunophenotyping, cell sorting, cell cycle analysis, and detection of DNA content. It is a powerful tool widely used in research, clinical diagnostics, and other fields.