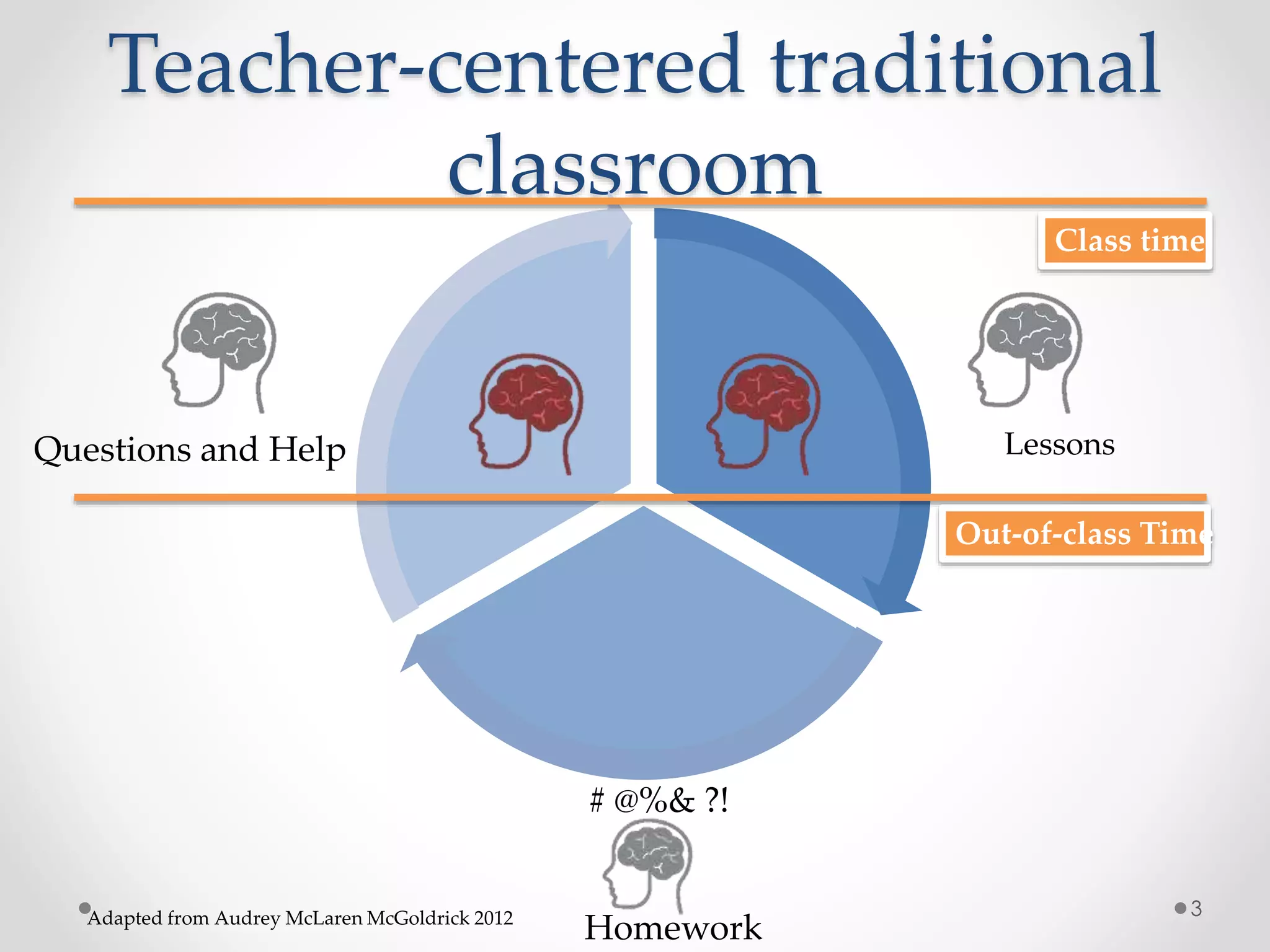
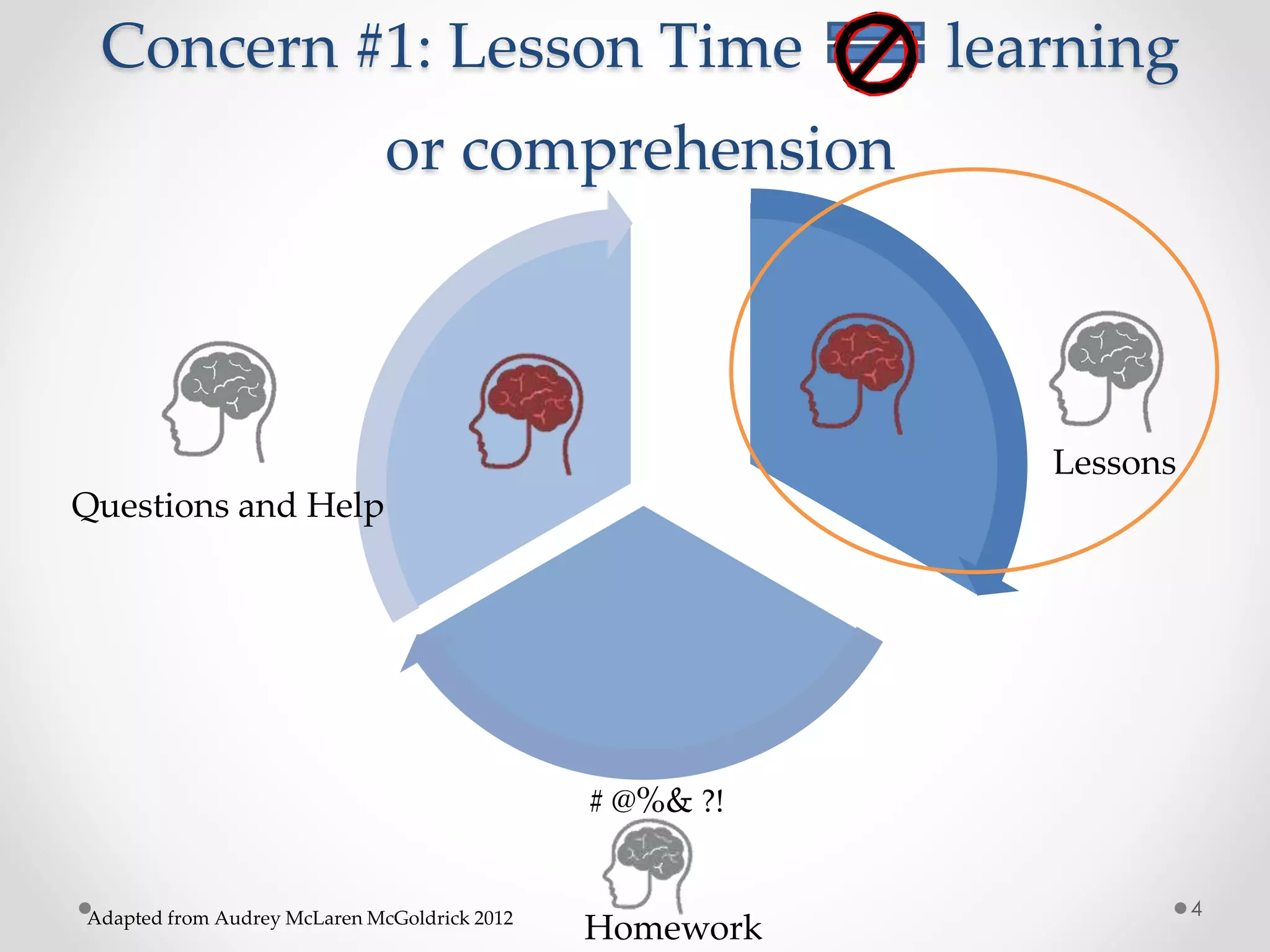
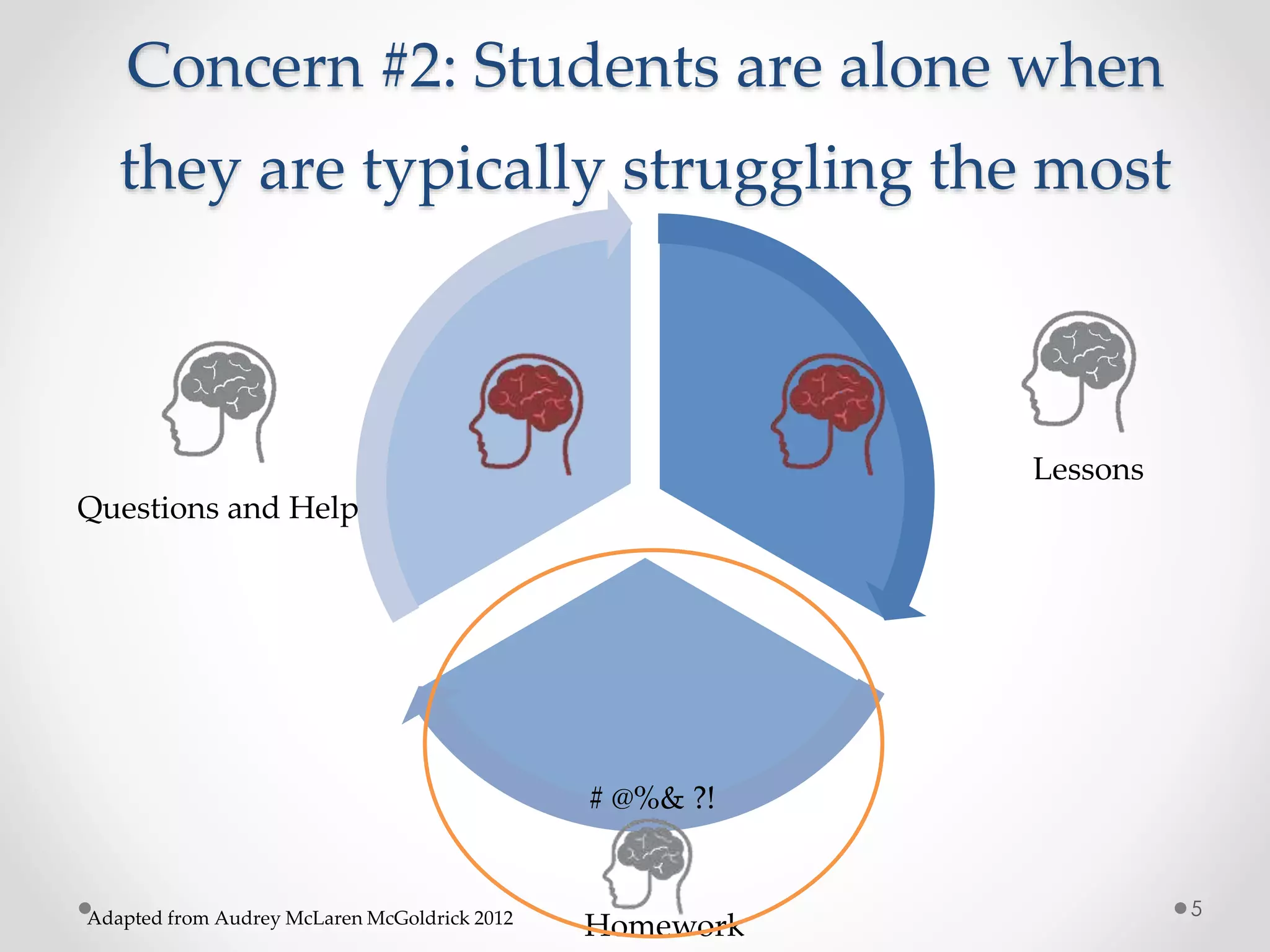
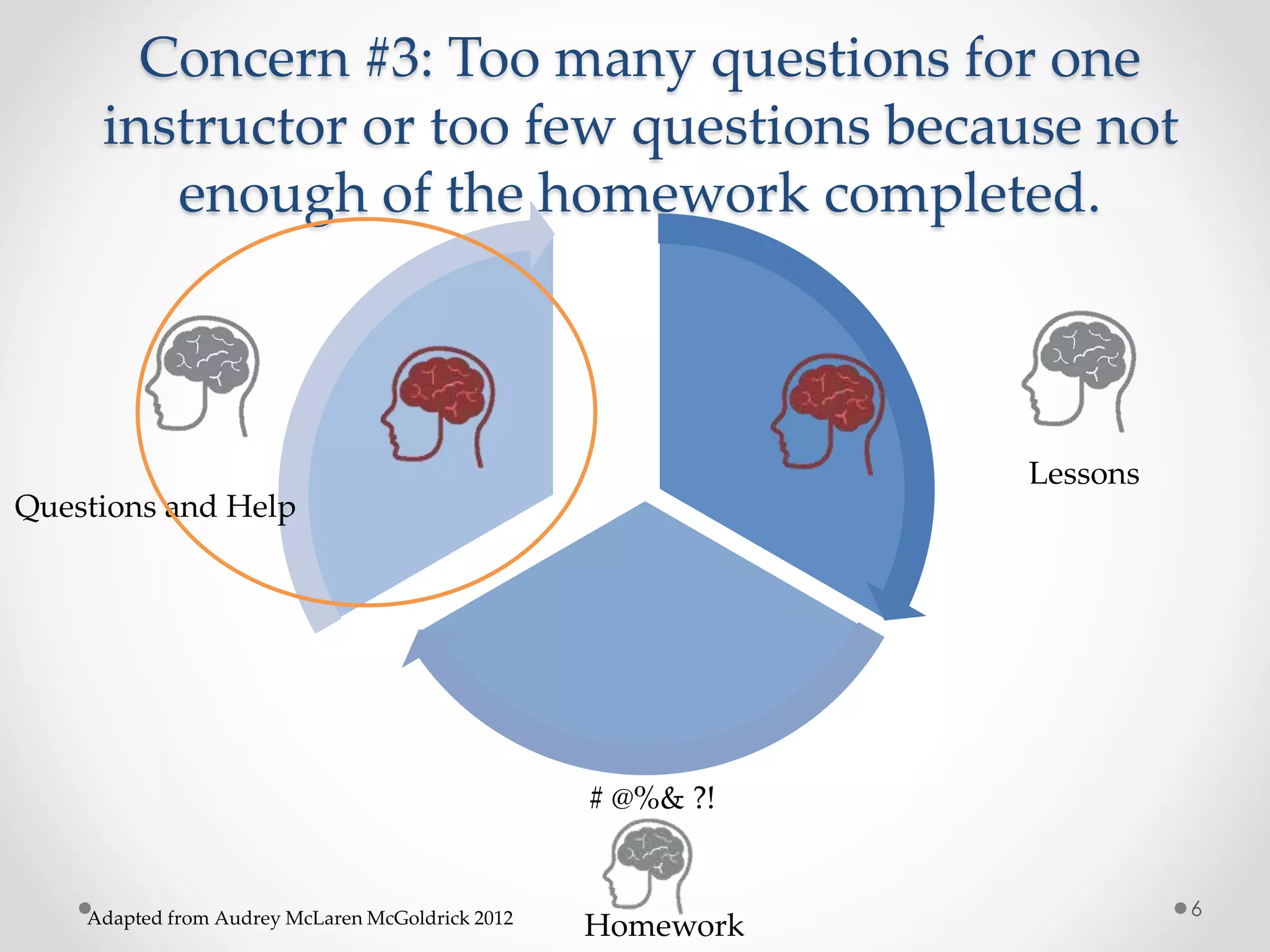
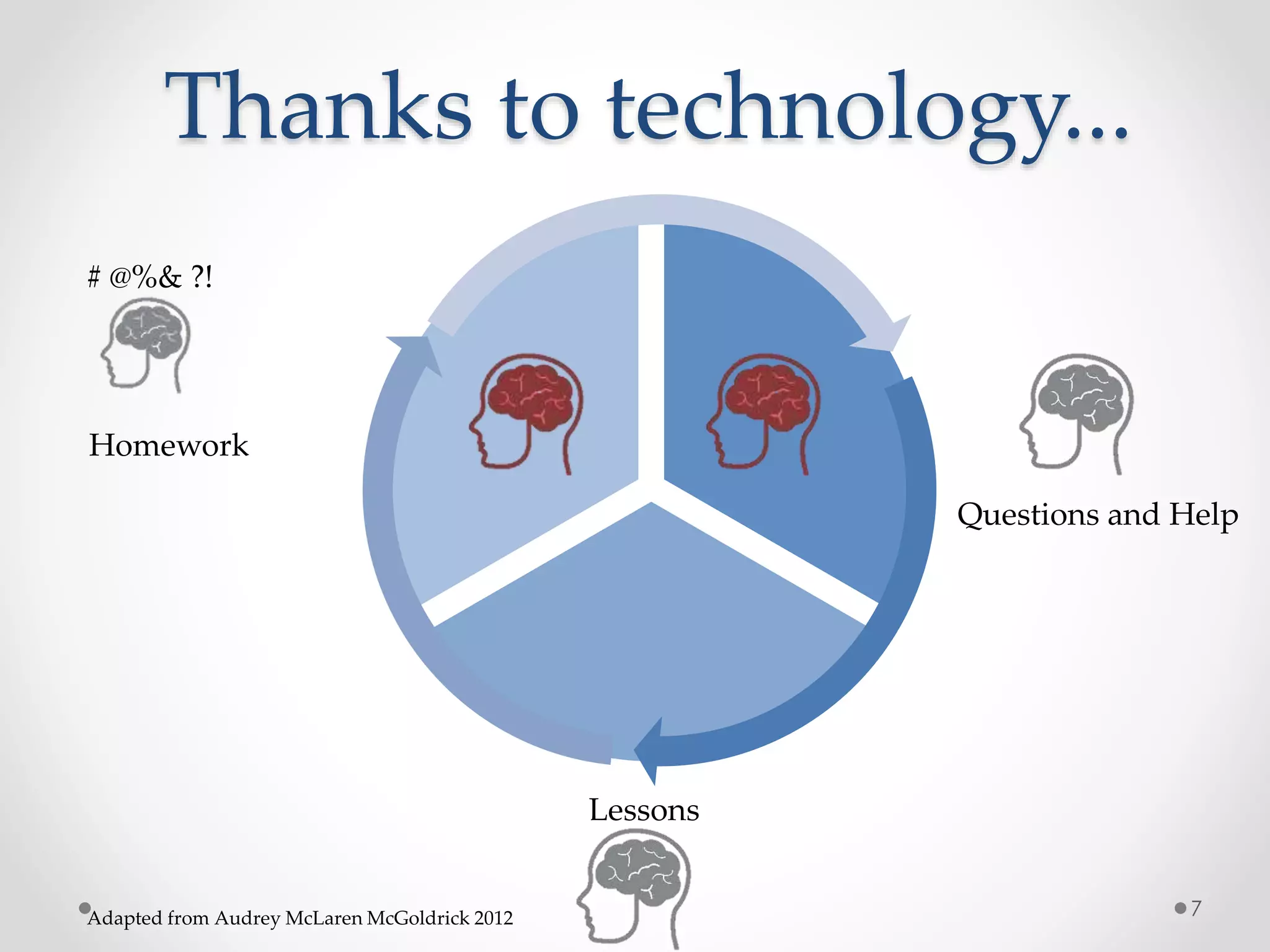
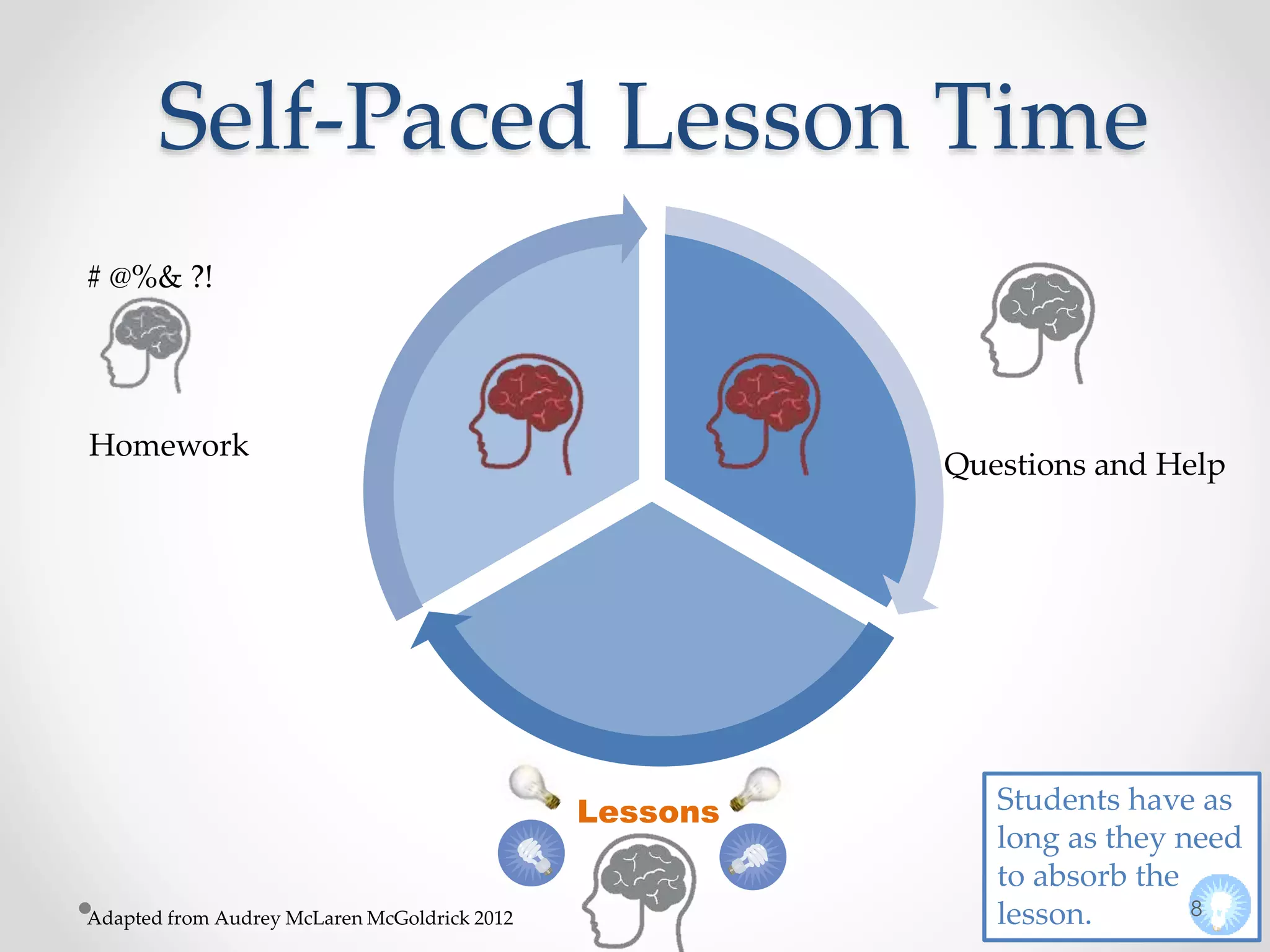
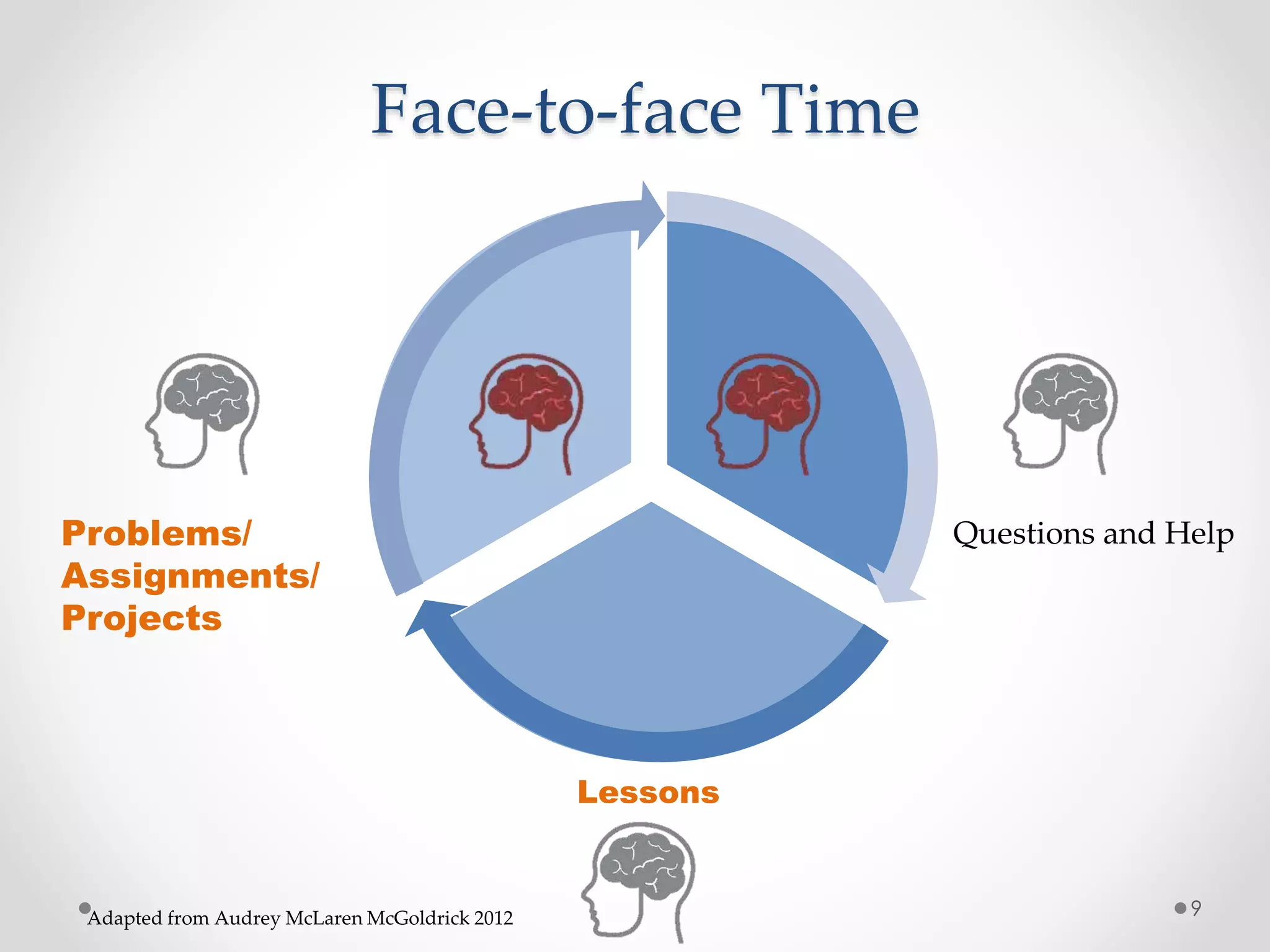
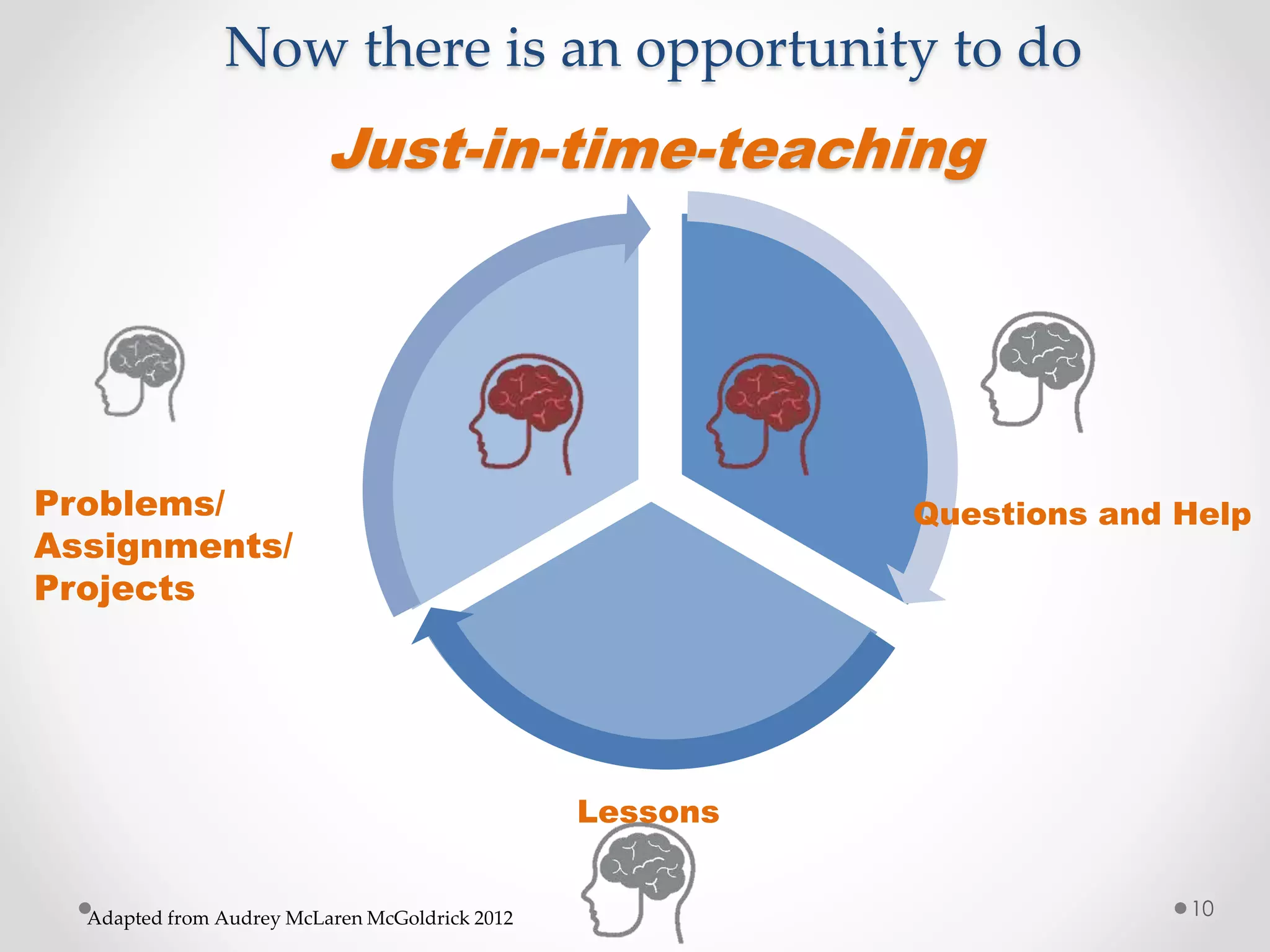
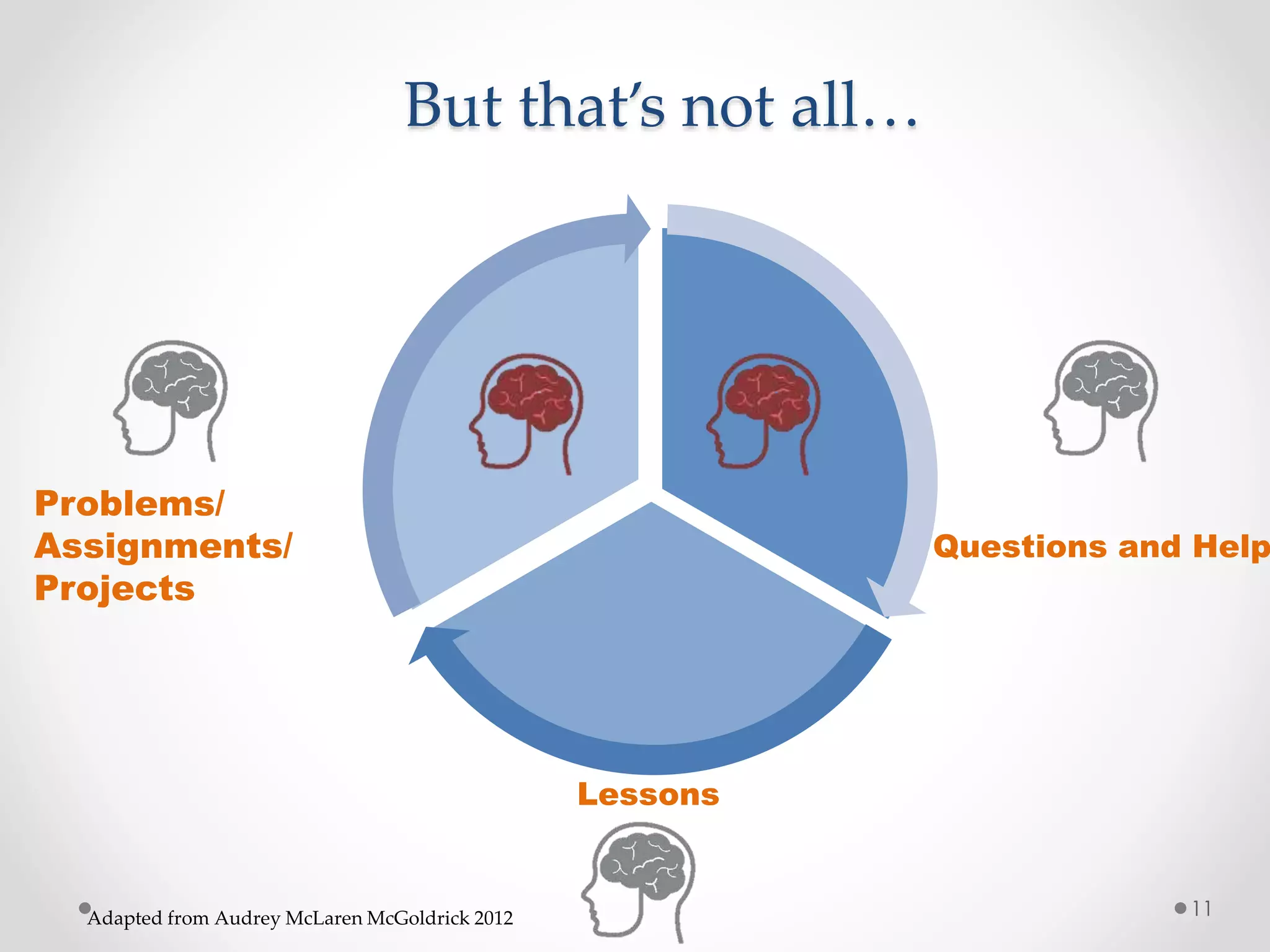
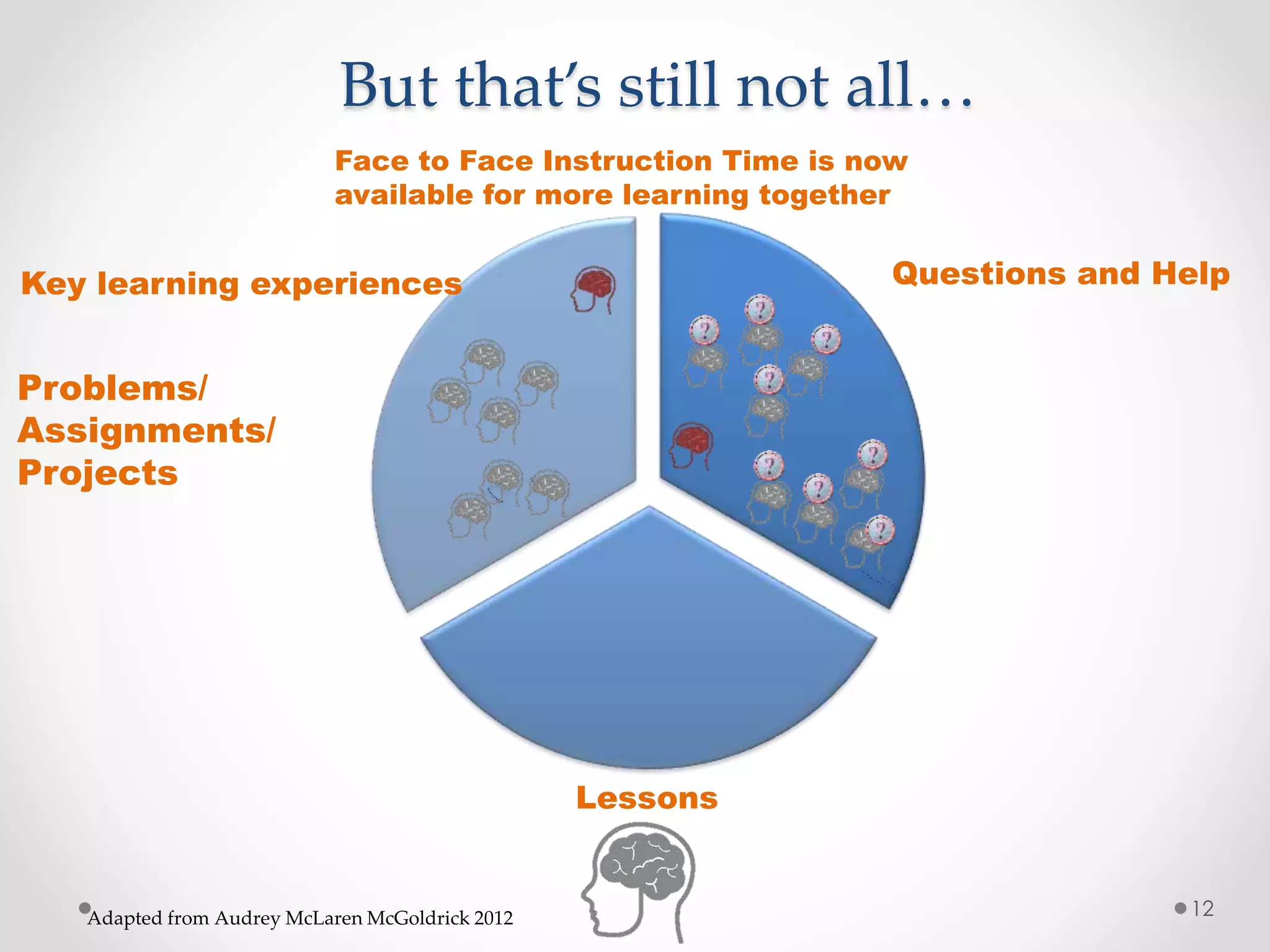
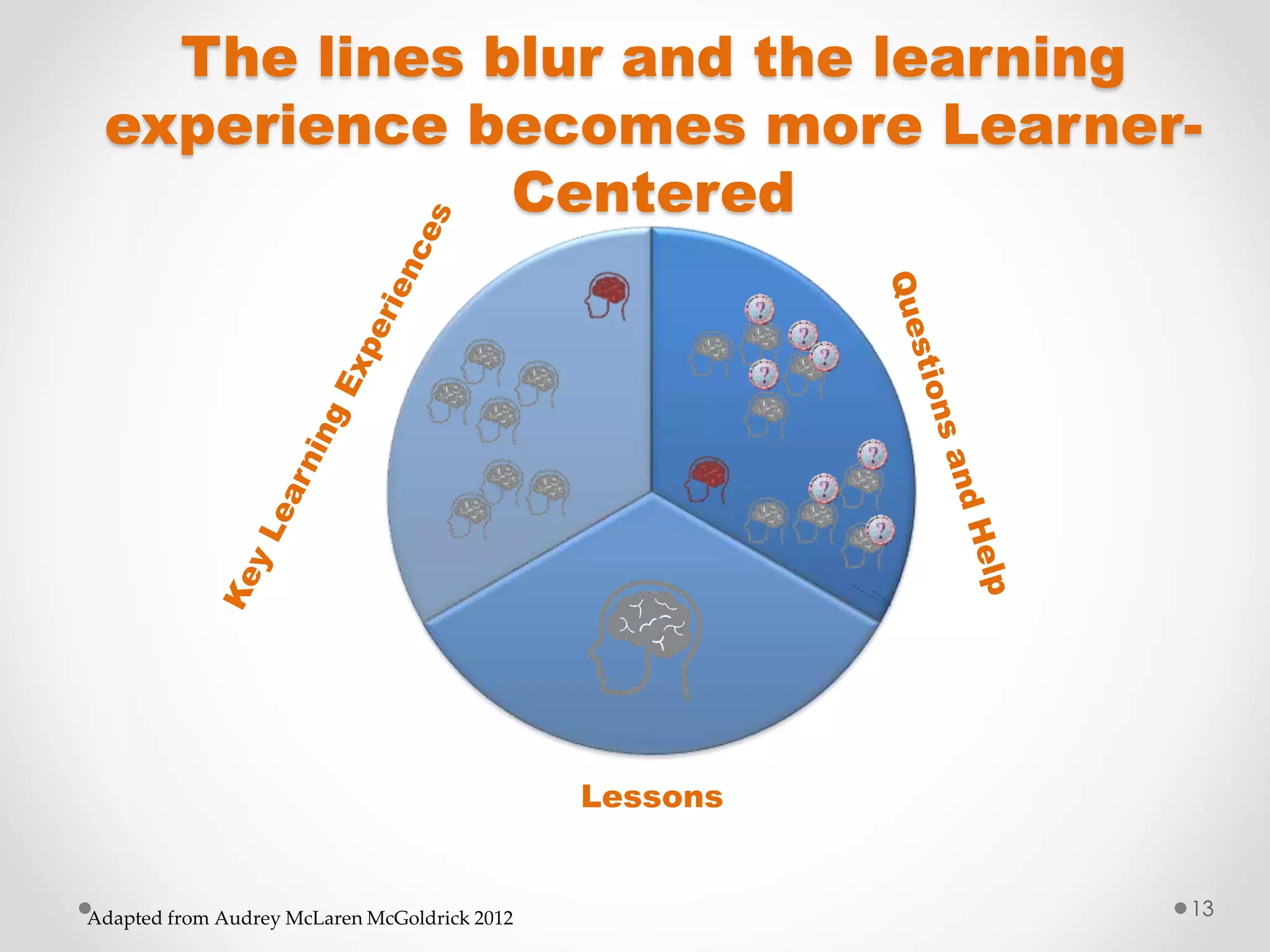
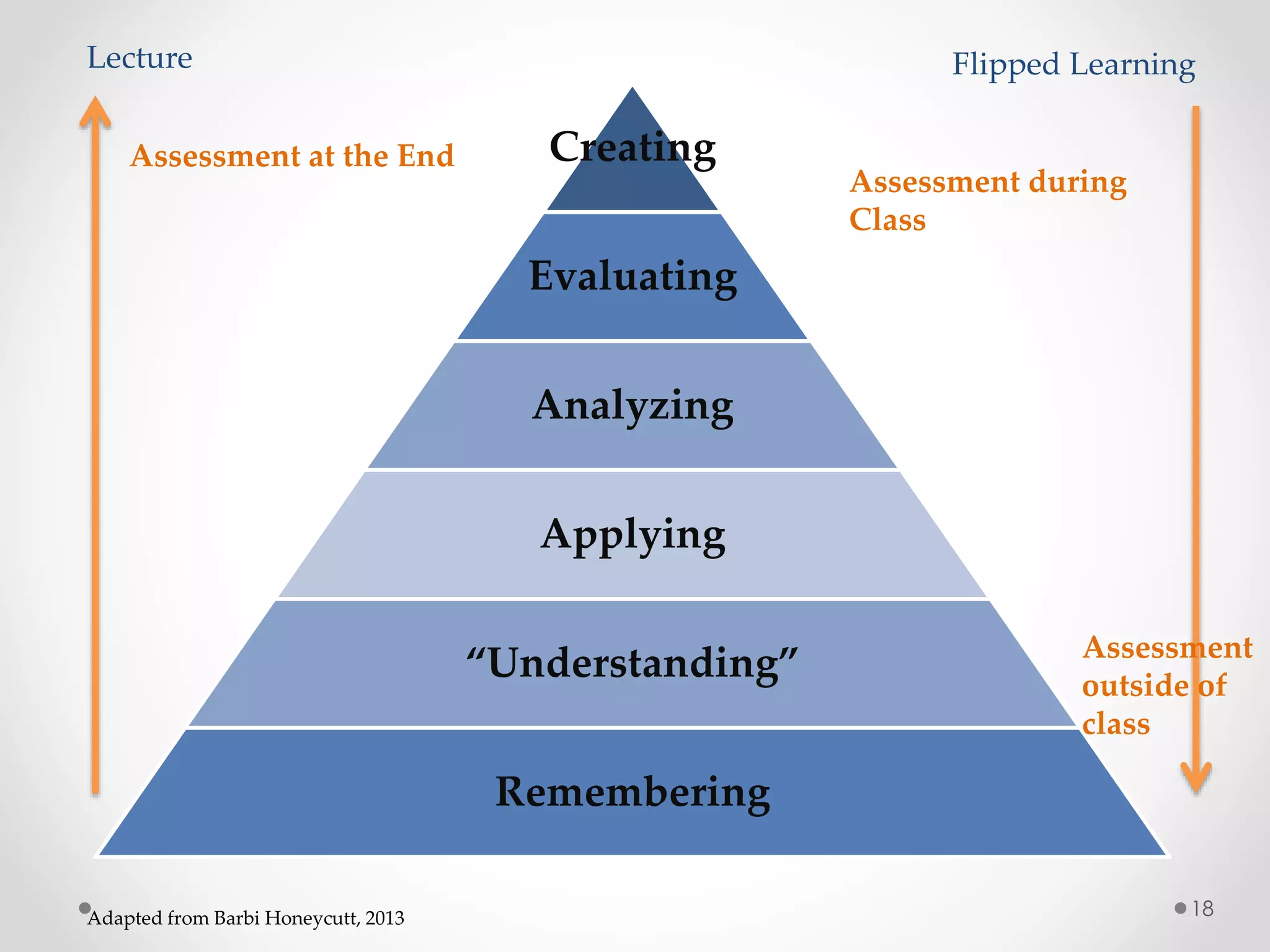
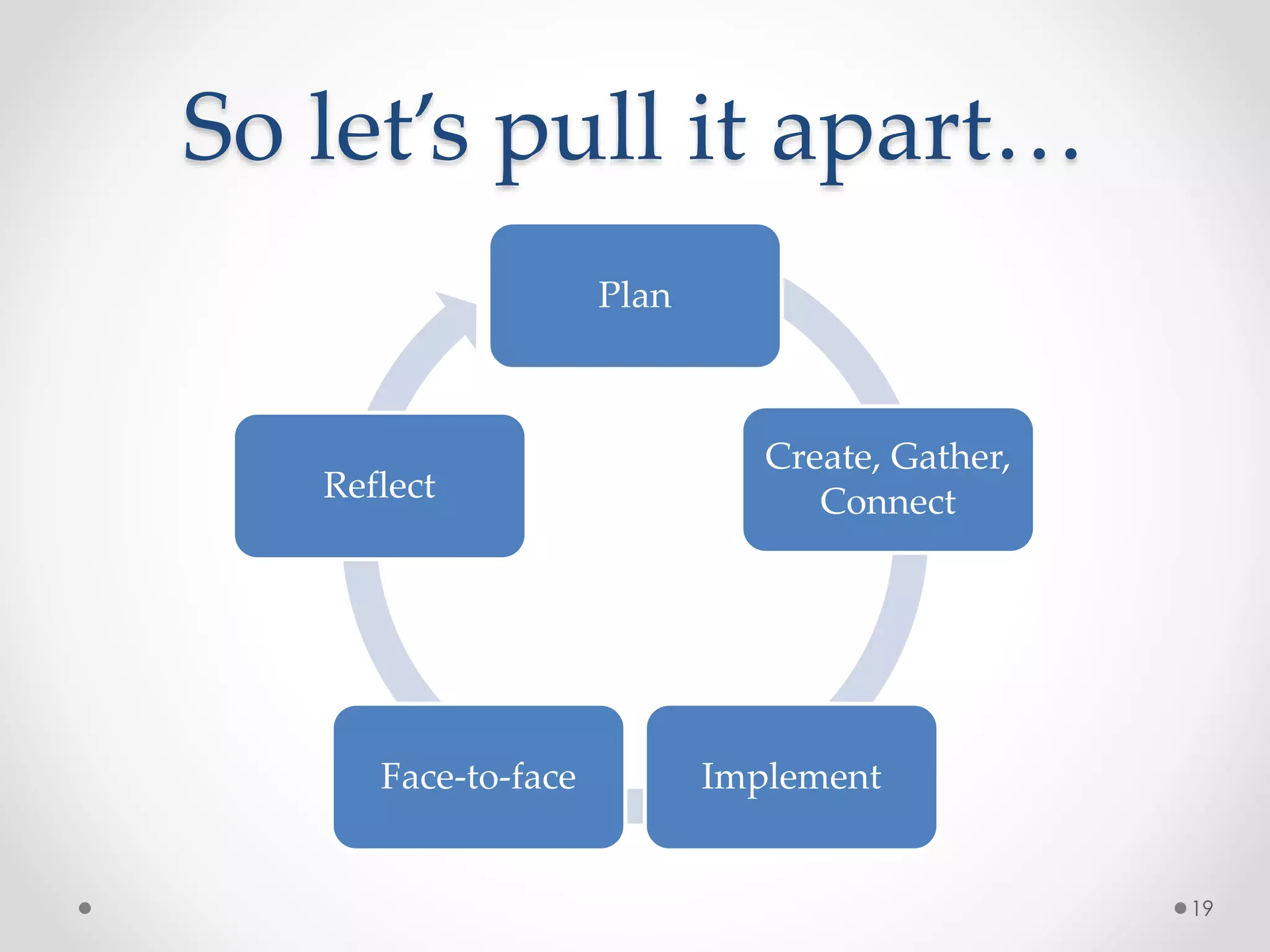
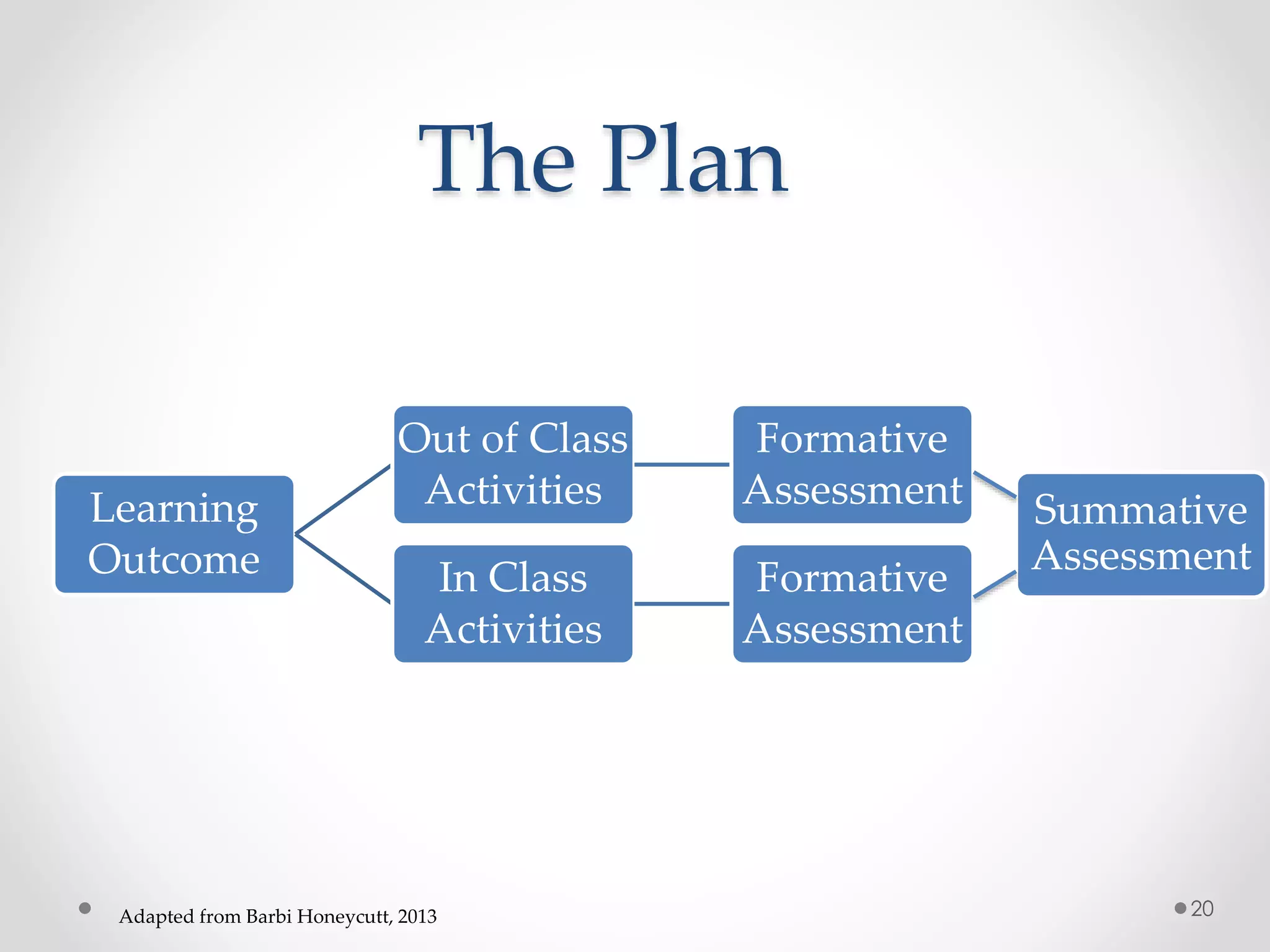
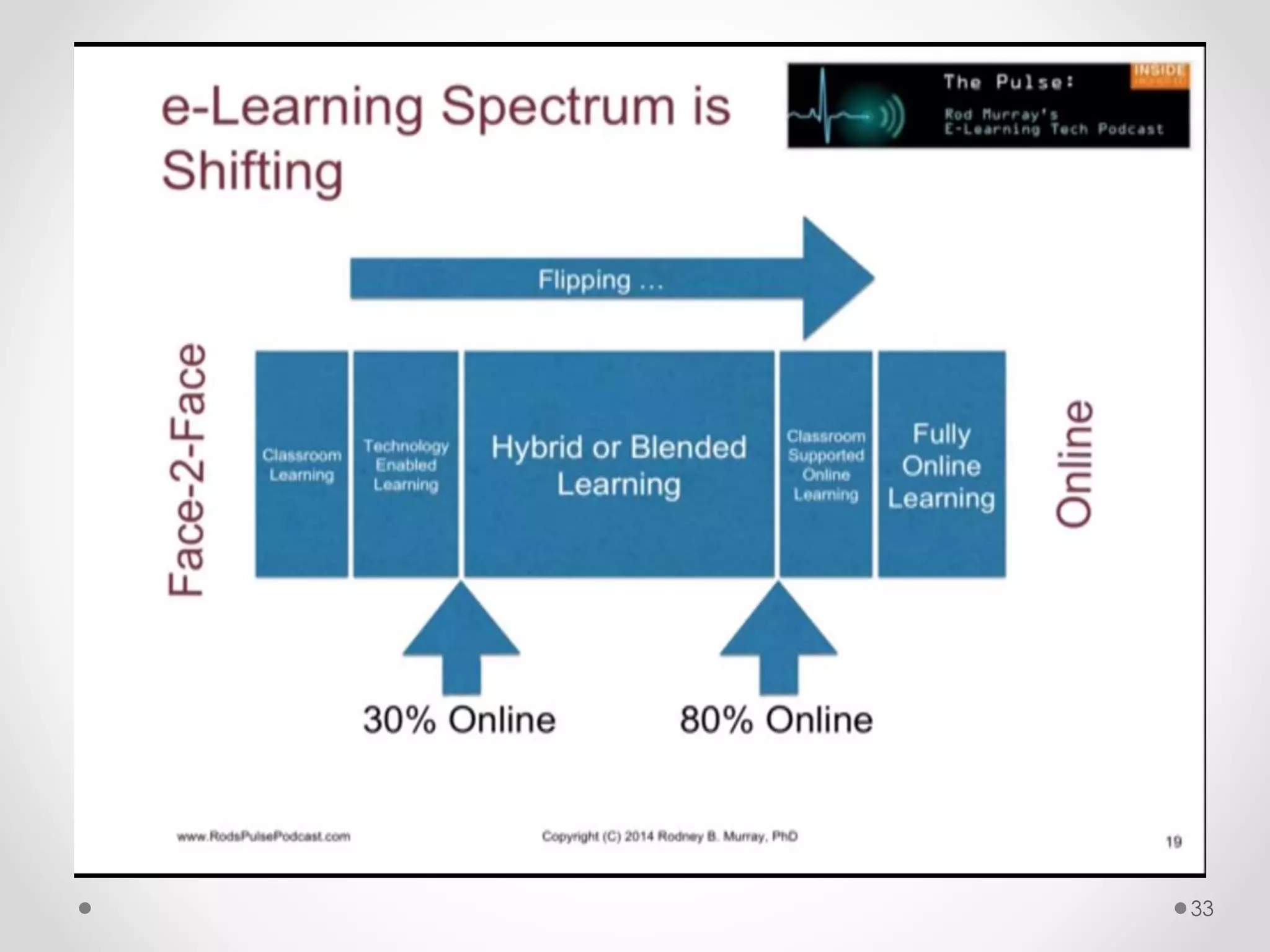
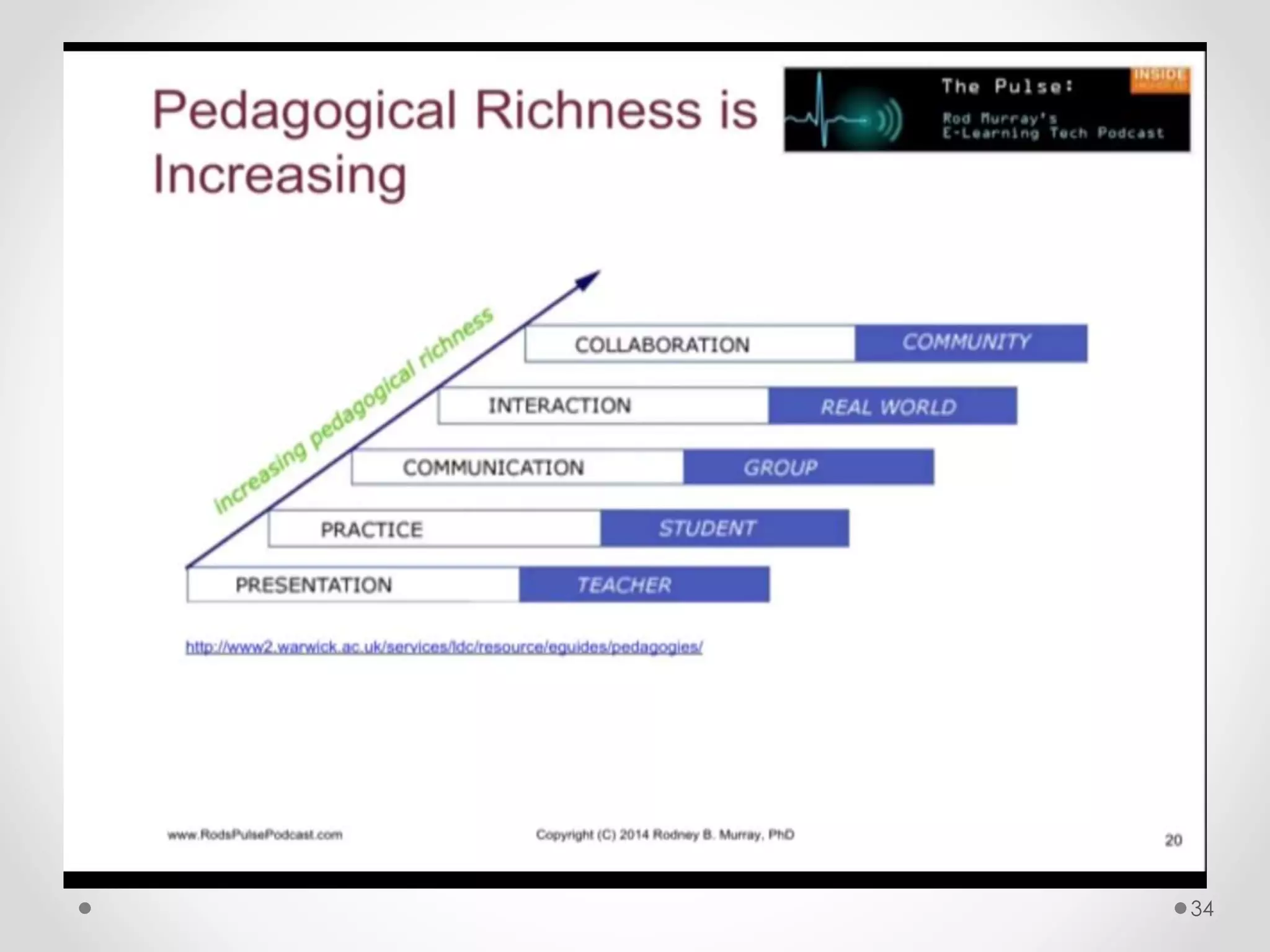
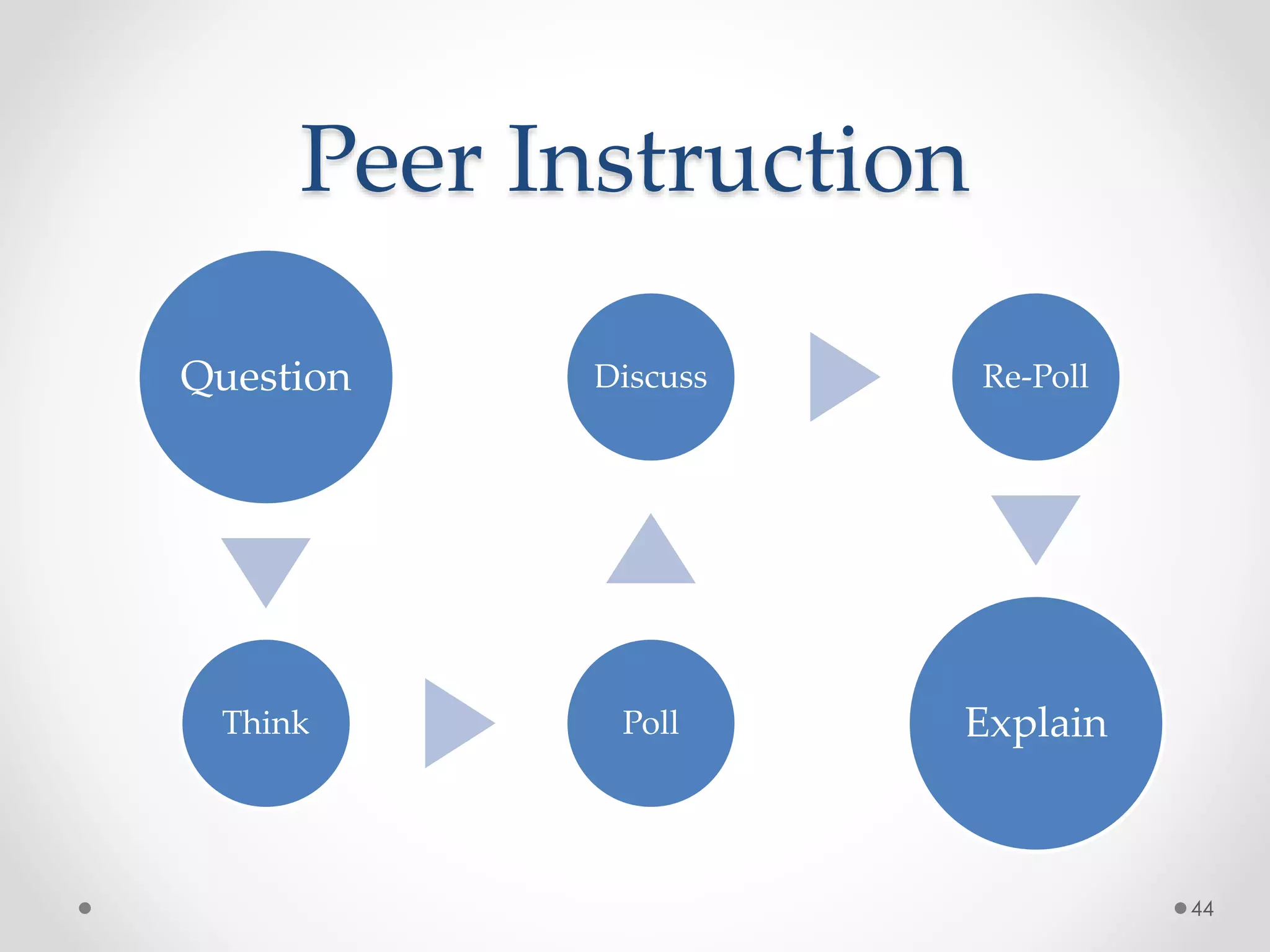
The document provides an introduction to flipped classroom learning. It defines flipped classroom as rearranging how time is spent in and out of class to shift ownership of learning from educators to students. Typically, lectures are viewed as homework outside of class through videos and in-class time is used for homework, projects, discussions and problem-solving. This allows educators to focus on higher-level application of concepts and address students' questions individually. The document outlines concerns with traditional models and benefits of flipped learning, including allowing self-paced learning and just-in-time teaching. It provides tips for implementation, including starting small, frequent assessment, and addressing student resistance to the change in responsibilities.