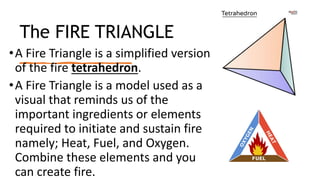
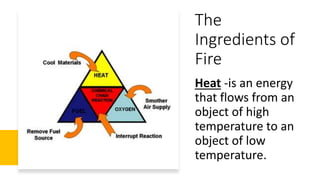
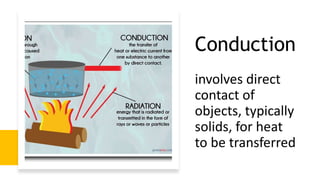
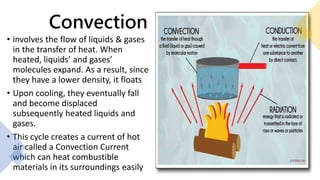
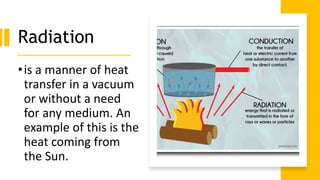
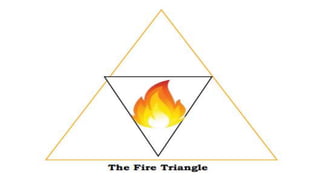
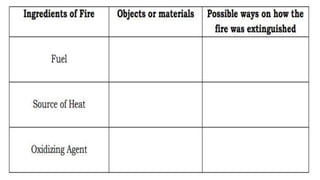
Here are the possible causes of fire identified in the passage and a brief explanation for each:
1. Electrical faults/wiring - Faulty electrical wiring or connections can cause sparks or overheating that ignites nearby combustible materials.
2. Gas appliances - Leaks from LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) tanks or lines used in stoves, heaters, etc. provide fuel that can ignite if a source of ignition is present.
3. Cooking accidents - Leaving cooking unattended on the stove can allow grease or other foods to overheat and ignite.
4. Cigarettes - Discarded cigarettes that are not fully extinguished can smolder and ignite combustibles like trash or mul