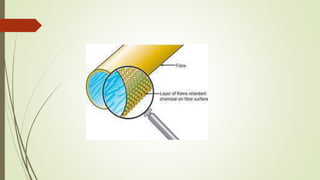
This document defines flame resistant fabrics and discusses their production and properties. It defines flame resistance as preventing or inhibiting combustion when exposed to an ignition source. Flame resistant fabrics use flame retardant chemicals in the fibers or finishes to react with heat and extinguish flames. They are produced using inherently flame resistant fibers, manufactured fibers with added chemicals, or finishes applied to materials like cotton. While providing safety benefits, flame resistant fabrics are typically less comfortable, more expensive, and require extra care than other fabrics.