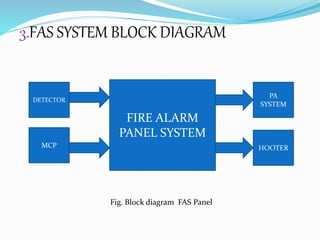
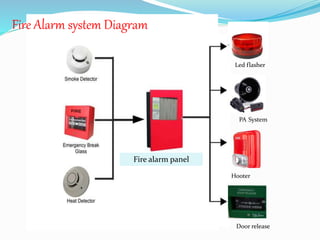
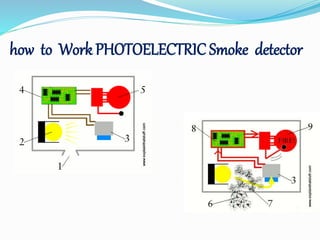
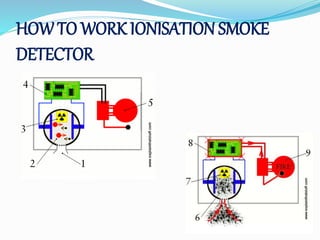
This document provides an overview of a fire alarm system. It discusses the components of a fire alarm system including detectors like smoke detectors, heat detectors, and manual call points. It also discusses the inputs to the fire alarm system from these detectors and the outputs from the fire alarm system including hooters, LED flashers, public address systems, and door releases. It provides details on the different types of detectors and the functions of the fire alarm indicator panel.