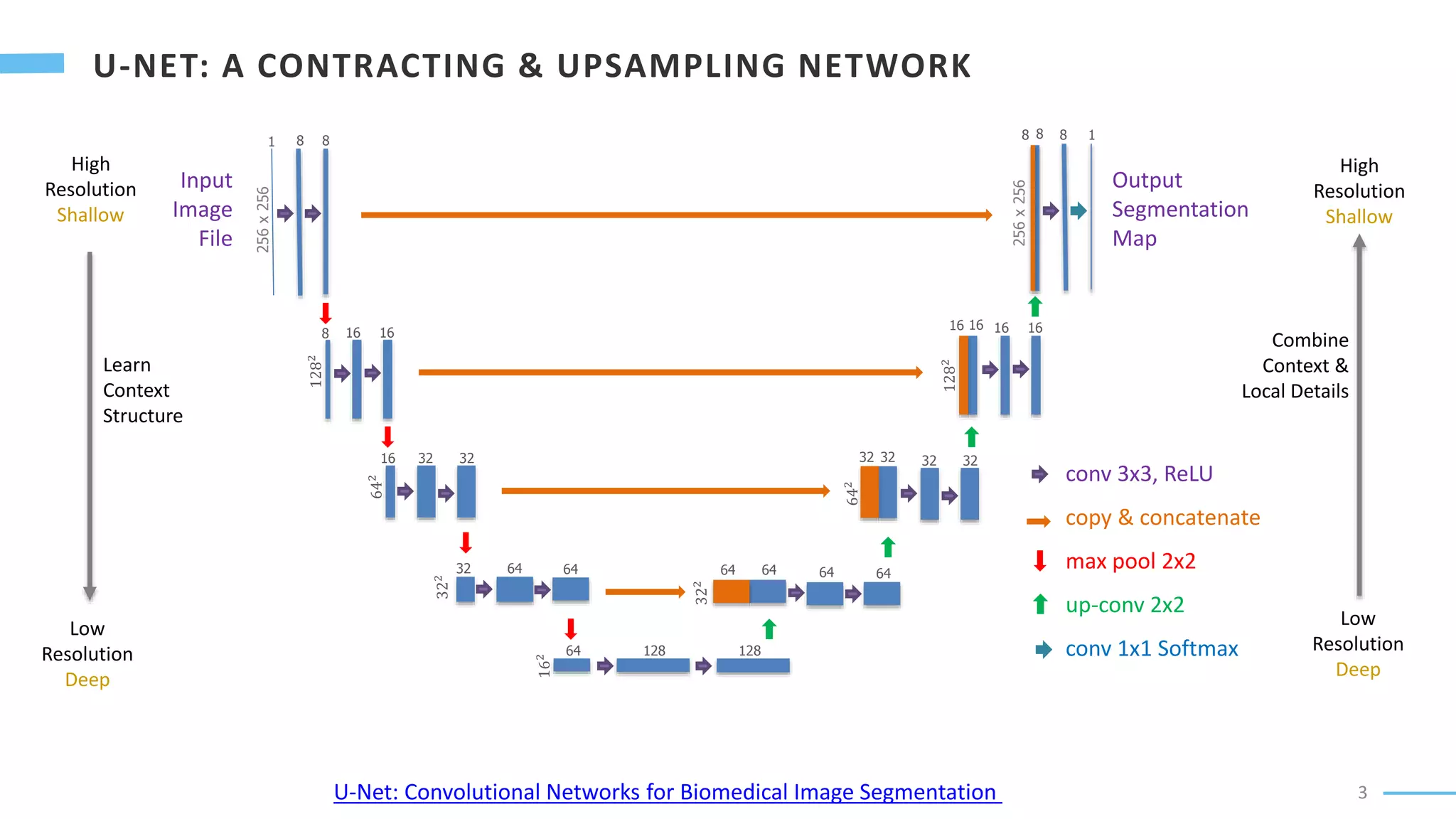
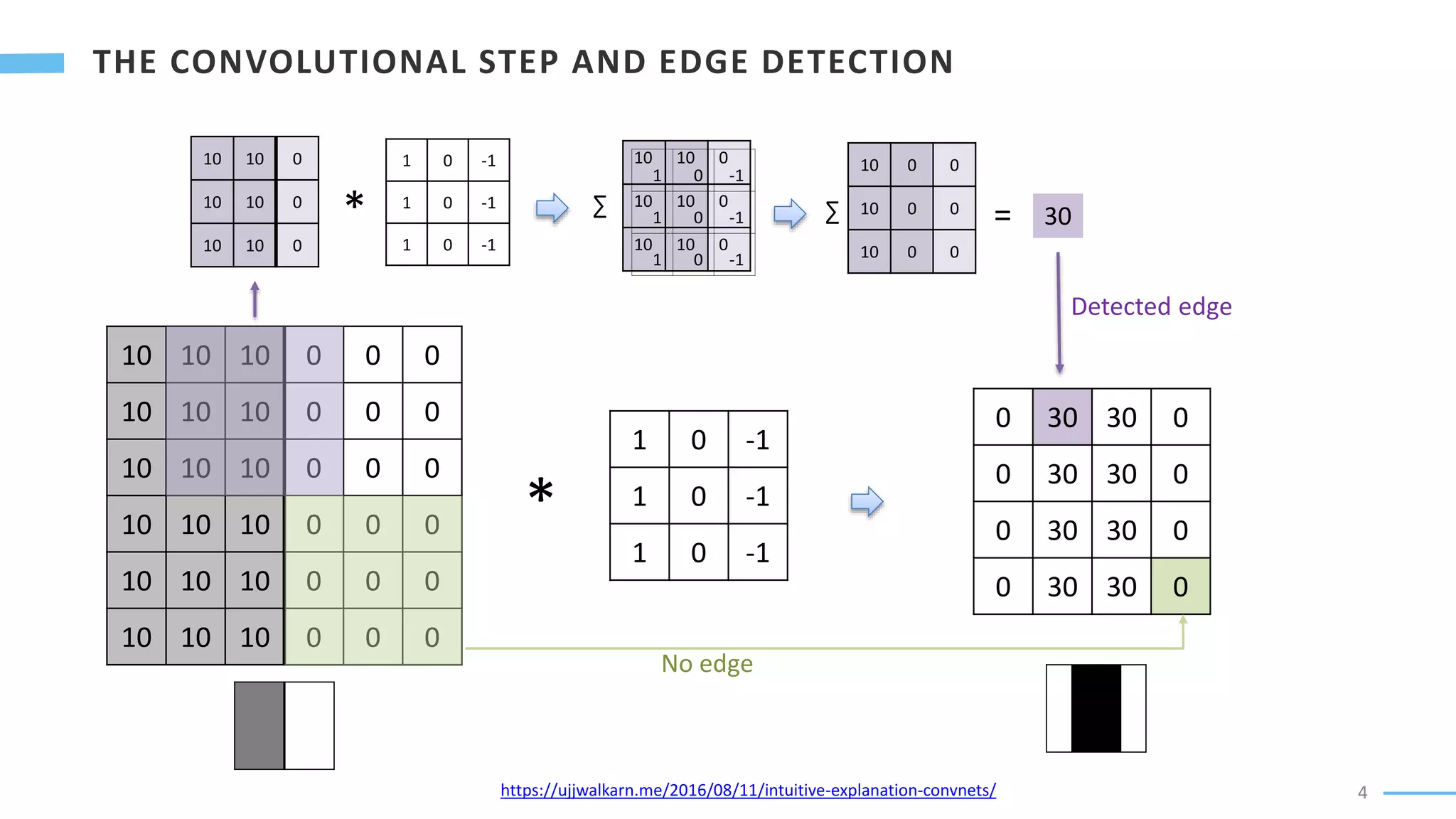
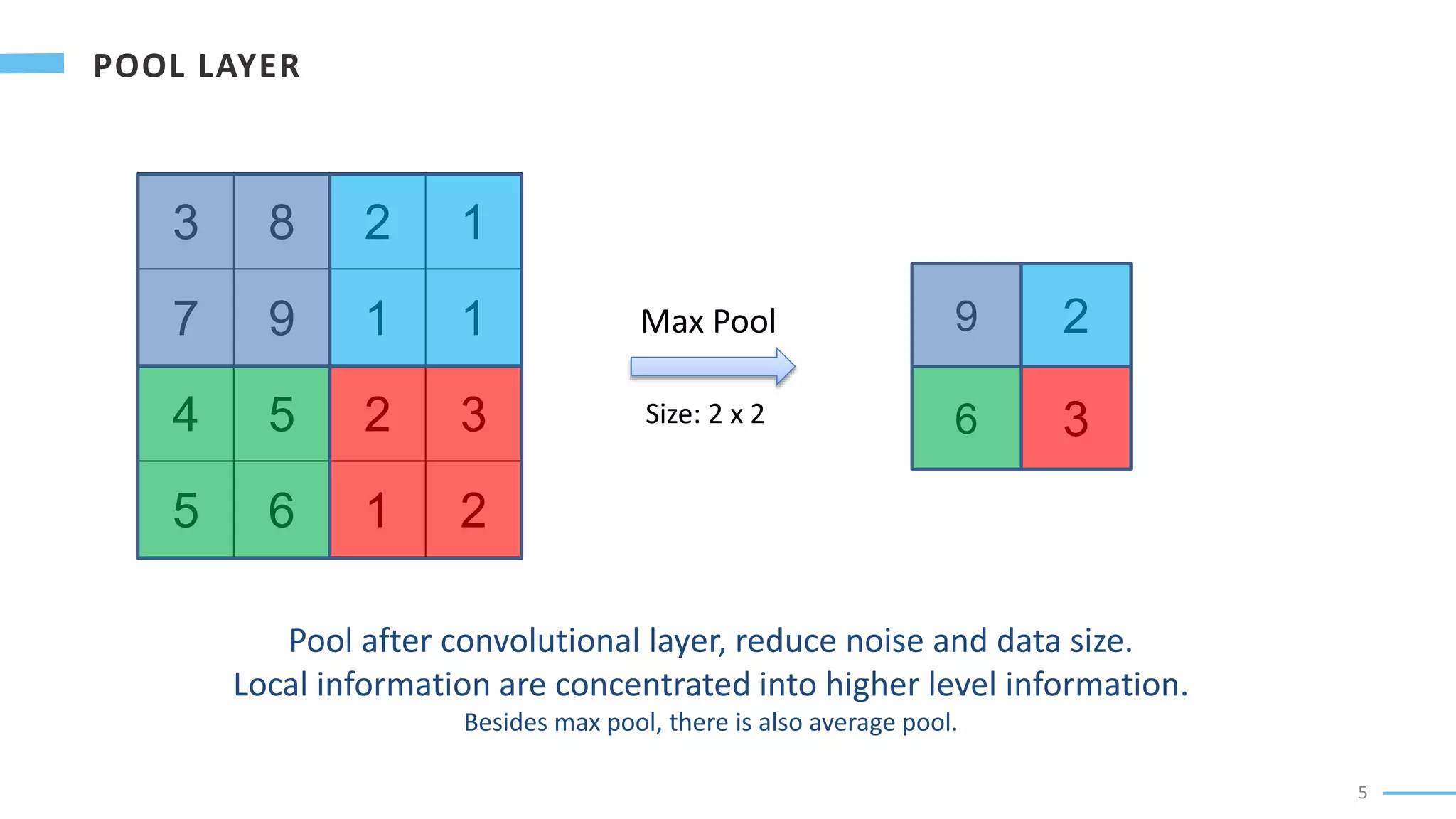
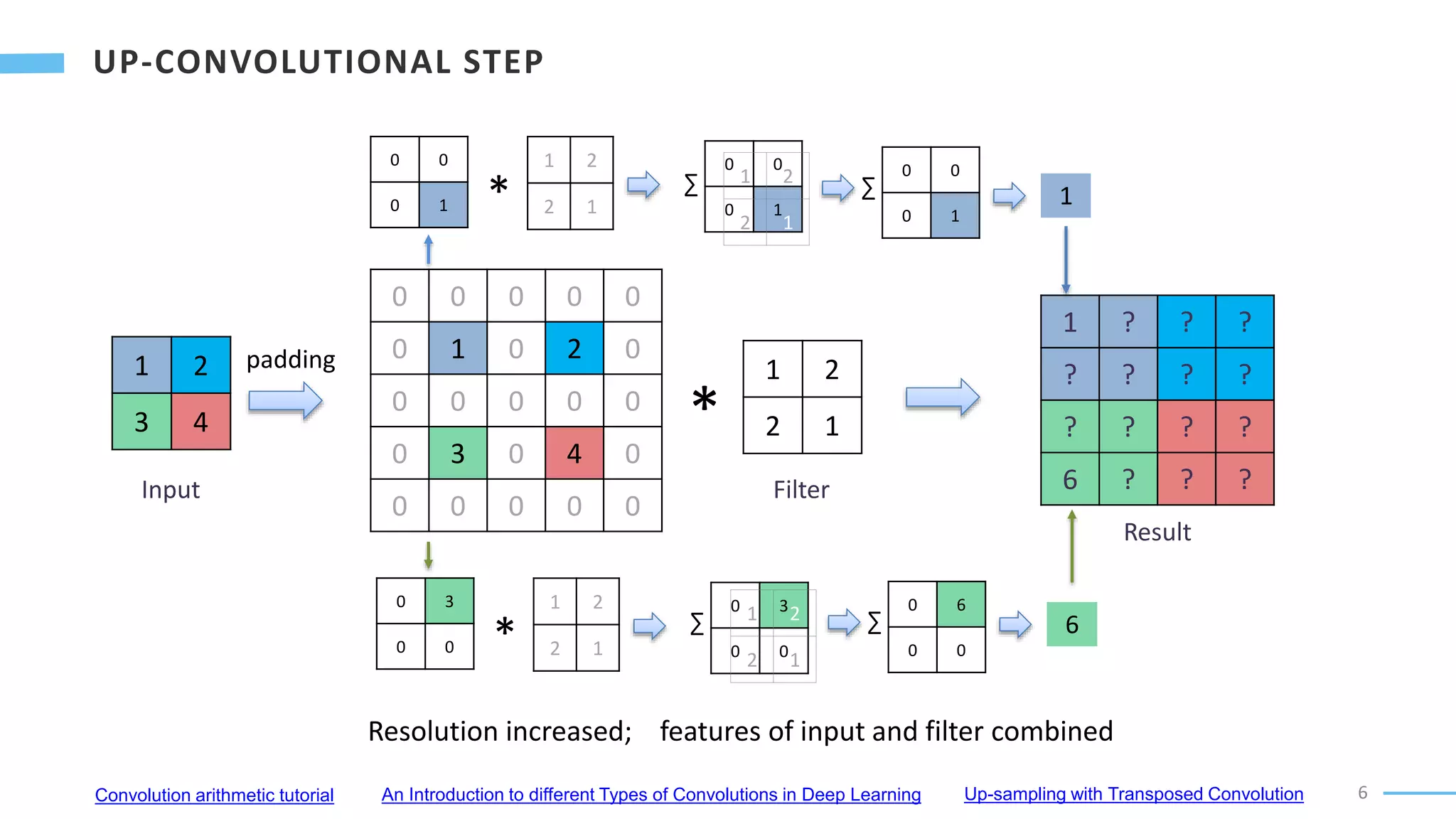
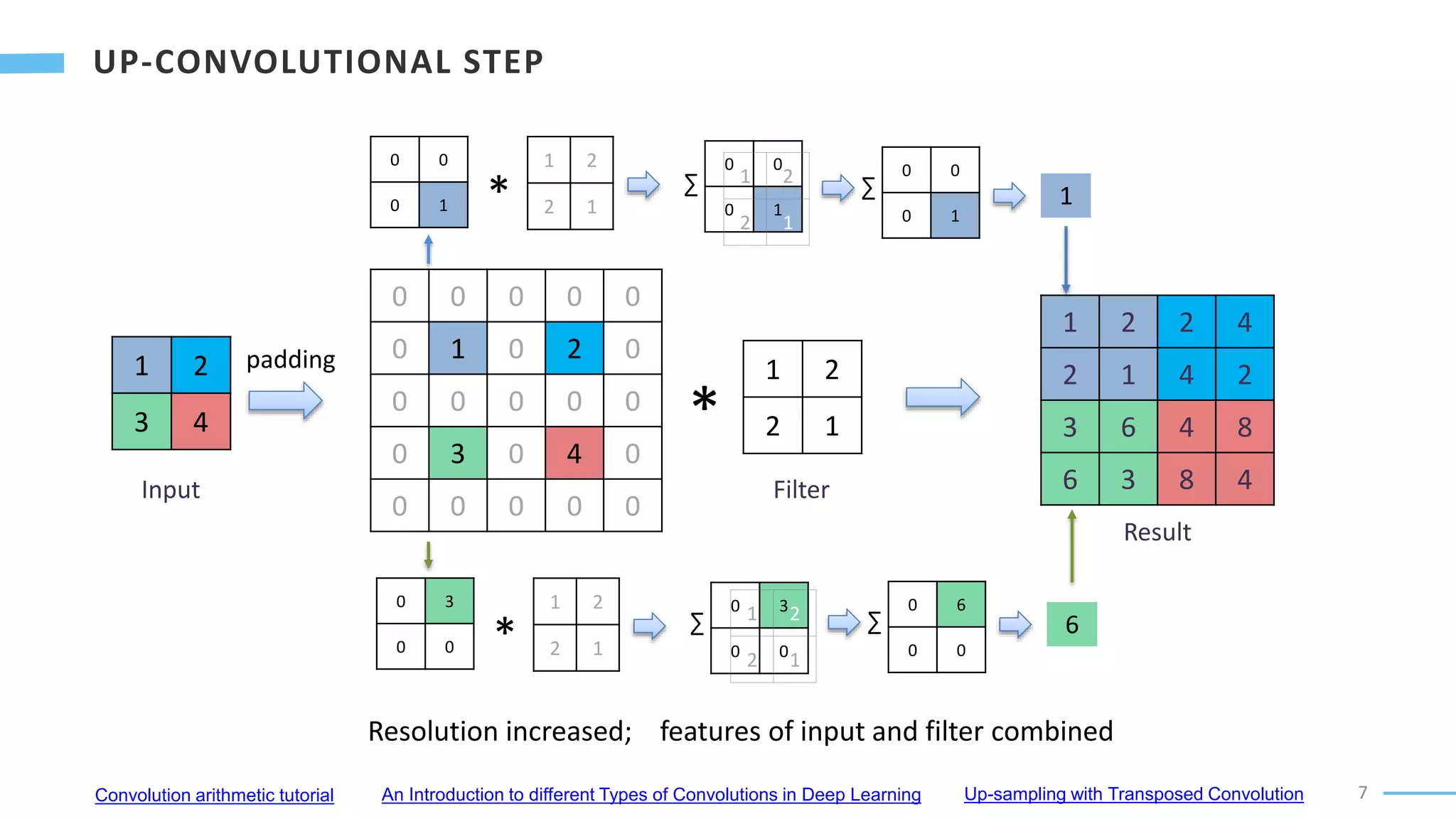
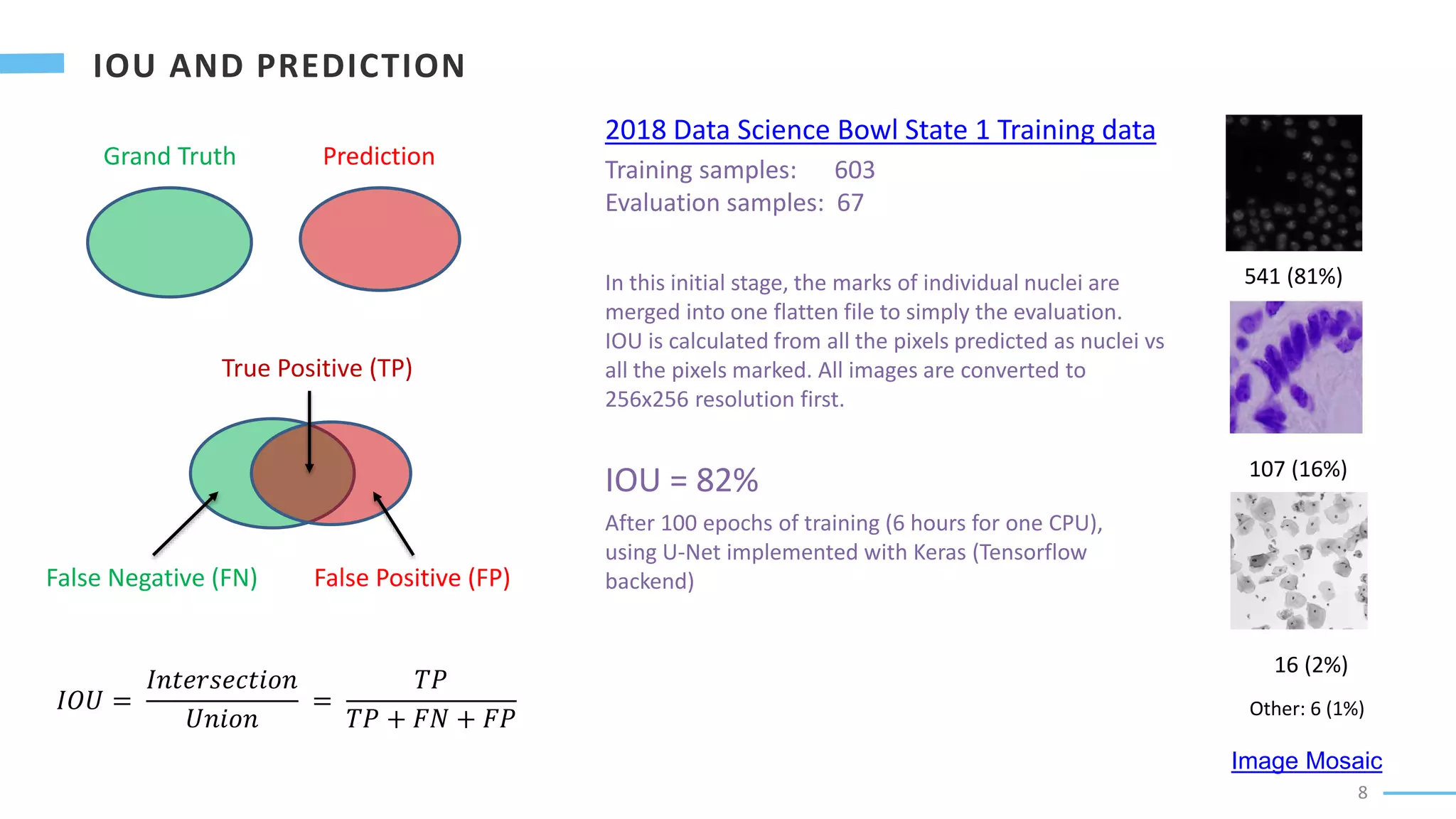
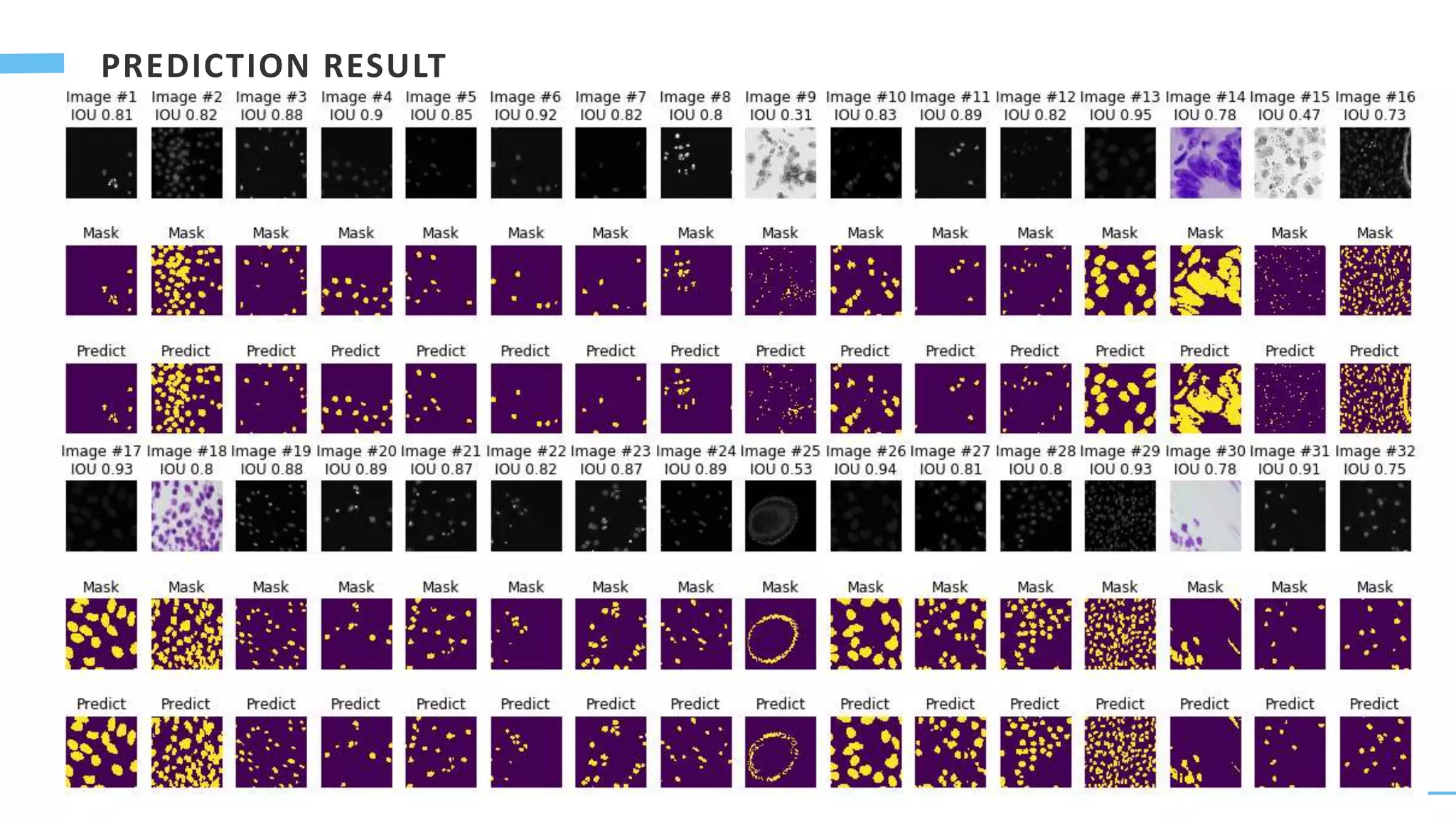
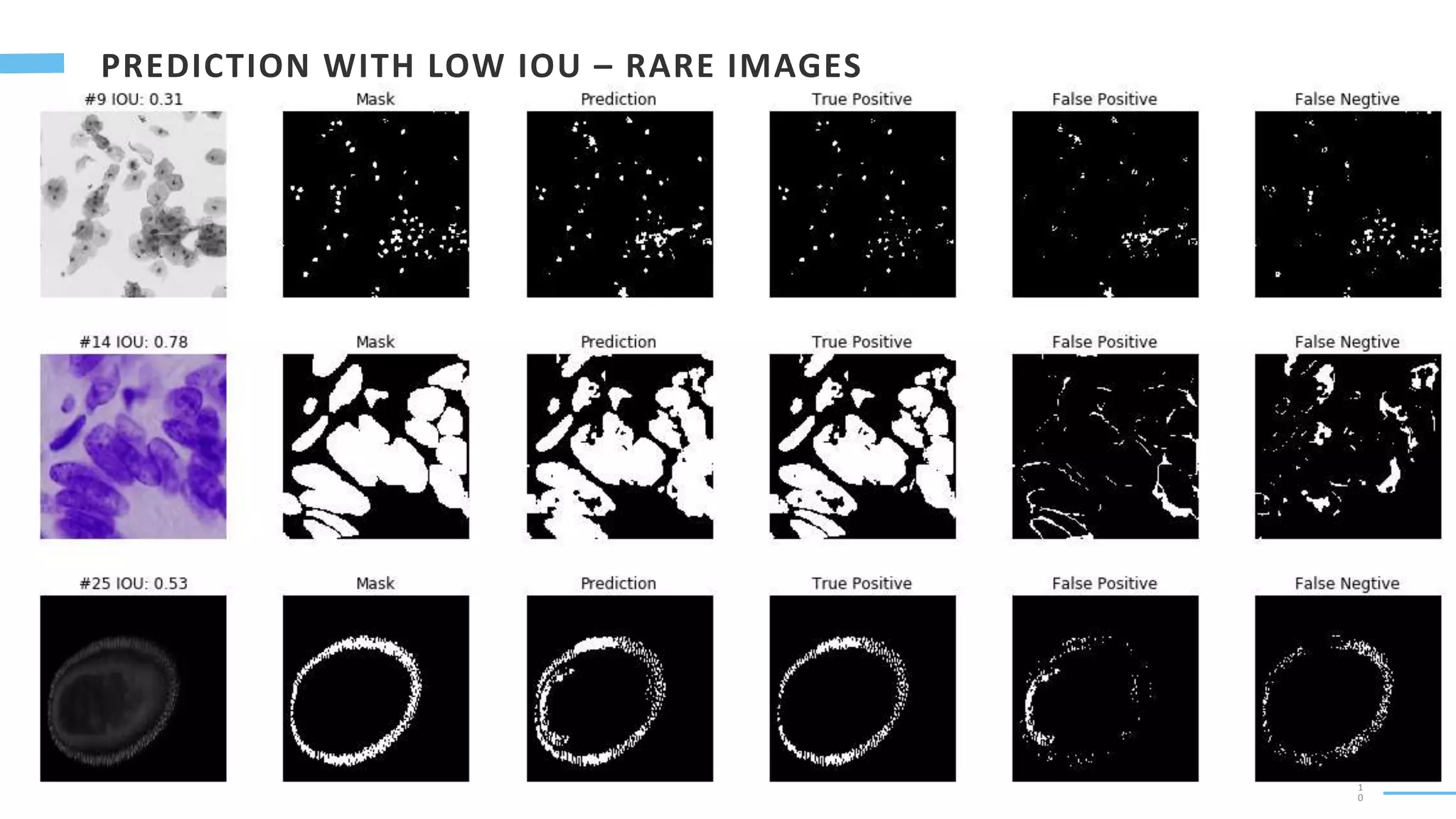
U-Net is a convolutional neural network used for biomedical image segmentation. It takes in an input image and outputs a segmentation map identifying nuclei pixels. The U-Net architecture consists of a contracting path to capture context and a symmetric expanding path that enables precise localization. The model was trained on microscopy images annotated with nuclei masks to achieve an intersection over union score of 85% after data augmentation was applied.